NEET Biology Notes For Cell Cycle And Cell Division
Cell Division: The process of formation of a new cell from the pre-existing cell is called cell division.
Why Cell Divides:
- A cell divides due to a change in the nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio. This ratio is also known as the karyoplasmic ratio (KPR).
- A cell divides due to a change in surface area volume ratio (S/V ratio).
In small cells, the S/V ratio and KPR are high. As a cell increases in size, these two ratios decrease. In order to maintain these two ratios, a cell has to divide. Cells also divide due to the following points:
- \(\frac{R N A}{D N A}\) ratio determines the type of division.
- If \(\frac{R N A}{D N A}\) > 1 → Mitosis (reported by Hotta)
- If \(\frac{R N A}{D N A}\) < 1 → Meiosis (reported by Hotta)
Types of Cell Division: Cell division is further divided into direct and indirect cell divisions. These are explained below.
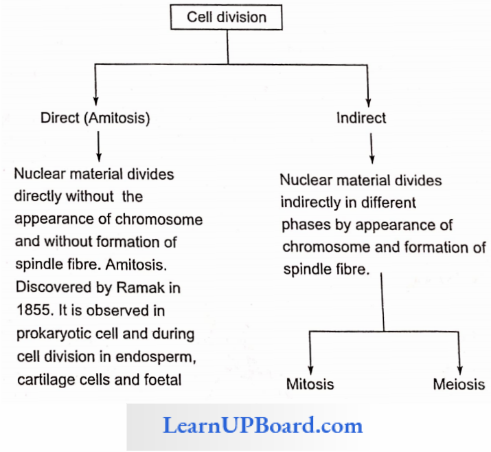
NEET Biology Notes For Cell Cycle And Cell Division Cell Cycle
Cell cycle was discovered by Howard in Vicia faba. Every dividing cell must pass through the cell cycle. The sequence of events through which a cell duplicates its content and divides into daughter cells is called the cell cycle.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
Stages Of Cell Cycle: The division of a cell includes the following sequence of stages
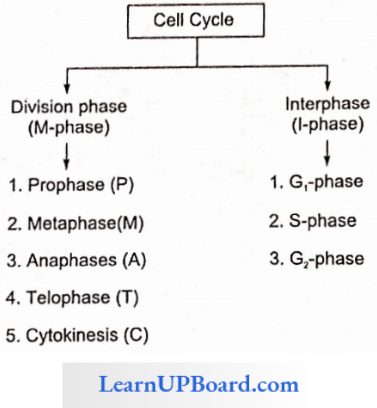
The cell cycle depicts the formation of daughter cells from one cell.
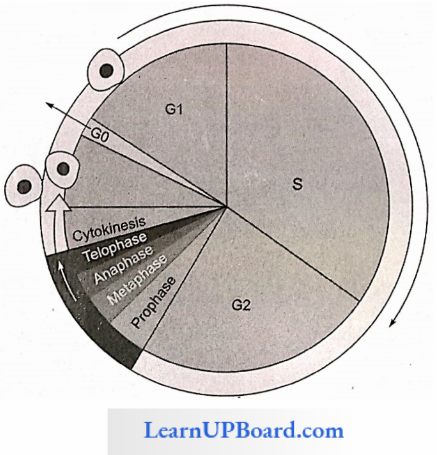
Interphase: Interphase is a longer phase of the cell cycle than the 1-phase. It is commonly called a resting phase because no visible changes in the nucleus take place. Interphase represents generation time. It is metabolically the most active phase, hence called the energy phase.
Synthesis of DNA, RNA, protein, ATP, enzyme, etc., takes place, hence the size of the nucleus increases. Chromosomes are present in the form of a chromatin network in this phase. This phase covers more than 95% time of the cell cycle.
Steps Of Interphase
G1-phase: G1-phase is also called post-mitotic, pre-synthetic, first gap, first growth phase.
- Longest phase of interphase.
- Synthesis of RNA and non-histone protein starts here and continues up to G2 phase.
- Cell increases in its size to the maximum (double).
- No synthesis of DNA takes place, hence no change in DNA content.
- The cell divides under stress conditions, so the synthesis of ATP and amino acids takes place at the last stage of G1-phase, hence called antiphase (end of G1-phase).
- The decision of cell division takes place in this phase, hence it is called the restriction point or checkpoint.
- It is the most variable phase in different plant species. It takes different time period in different organisms. G0-phase (quiescent phase) is a temporary arrest of cell division and the cell undergoes differentiation, for example, heart cell, root tip.
cell cycle and cell division pdf notes
S-Phase (Synthetic Phase): The replication of DNA takes place, hence replication of chromosomes takes place. The DNA content becomes doubled, but no change in the number of chromosomes so the ploidy level remains the same in the cell.
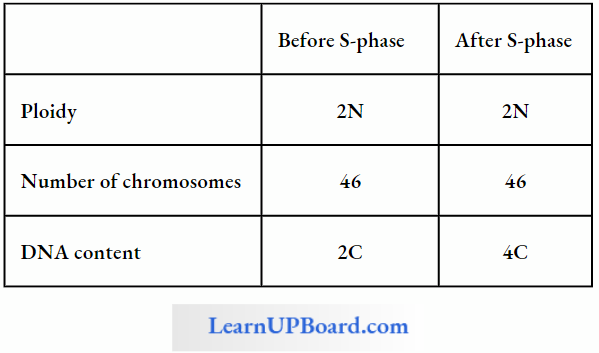
The duplication of centriole and synthesis of histone protein takes place in animal cells in S-phase. It is called the invisible phase because replicated chromosomes are not visible.
G2-phase: This phase is also known as the post-synthetic or premitotic phase second gap or second growth phase.
- G2 is called the period of cytoplasmic growth.
- Duplication of cell organelles takes place except cen-triole.
- Synthesis of RNA and non-histone protein is continued up to this stage.
- Synthesis of tubulin protein required for spindle formation takes place.
- Repairing of damaged DNA takes place.
- Synthesis of cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDC- kinase) takes place, which controls the cell cycle.
- Kinase enzyme causes the phosphorylation of the nuclear membrane, hence it disappears in late prophase.
- G1 to S-transition (major checkpoint) requires G2-cyclin + CDC-2 kinase.
- G2– to M-transition (minor checkpoint) requires mitotic cyclin + CDC-2 kinase. It is called the maturation-promoting factor (MPF).
NEET Biology Notes For Cell Cycle And Cell Division Mitosis (Equational Division)
The term mitosis was coined by W. Flemming. Mitosis was discovered by Strassburger in plant cell and by W. Flemming in an animal cell. Mitosis is a type of indirect cell division in which one mother cell divides into two daughter cells in which the number of chromosomes is similar to the number of mother cells and both daughter cells are also similar to each other.
Generally, mitosis takes place is somatic cells, but also takes place in reproductive cells to increase the number. In animals, mitosis only takes place in diploid somatic cells, while in plants, it takes place in both haploid and diploid cells. A brief outline of the mechanism of mitosis is given below.
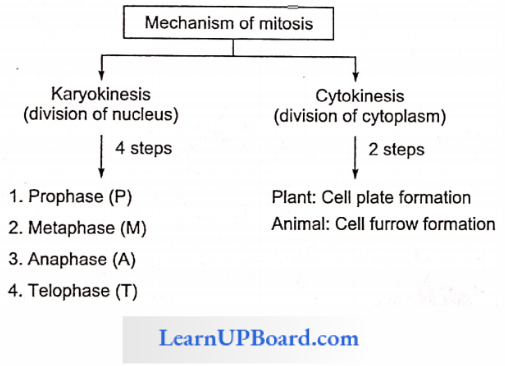
Karyokinesis: Karyokinesis takes place in the following phases
1. Prophase
- The longest phase of M-phase.
- Condensation and dehydration of the chromatin network take place resulting in the formation of chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are much elongated and ends are not distinct. Hence, early prophase is also called the ball of wool or spireme stage.
- Chromosomes appear in the form of double strands.
- It is composed of two chromatids, and both chromatids are attached to centromere.
- All chromosomes become arranged at the periphery of the nucleus.
- During the late prophase, the nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
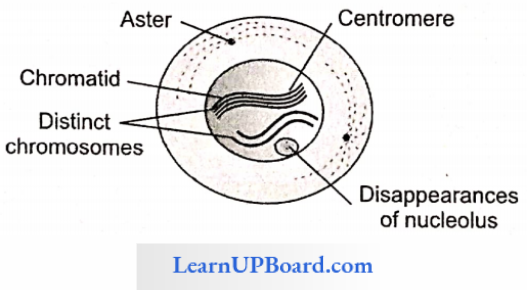
- During prophase, the viscosity and refractive index of cytoplasm increases.
- In animal cells, the already-divided centriole reaches to poles from which astral ray develops. Hence, animal mitosis is called amphiastral.
- In plant cells, mitosis is called anastral due to the absence of an astral ray.
- At the end of this phase, the cell does not show a Golgi body, ER, nucleolus, or nuclear envelope.
2. Metaphase
- During metaphase, maximum dehydration of chromosome takes place. Hence, the chromosome becomes much shorter and thicker.
- Hence, the size of the chromosome is measured in this stage. The morphology of chromosomes can be most easily studied in this phase.
- All chromosomes are arranged at the central part of the cell to form an equatorial or metaphase plate.
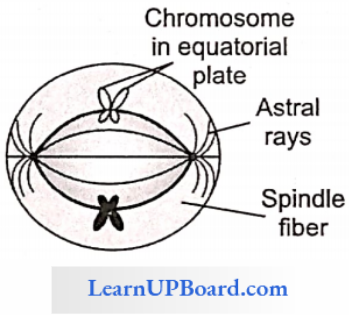
- The formation of a single metaphase plate takes place in mitosis.
- Appearance of spindle fiber takes place.
- Spindle fiber is composed of tubulin protein (97%) and RNA (3%).
- The two types of spindle fiber are (1) continuous fiber (these attach to both poles of the cell) and (2) chromosomal fiber (one end attaches to the pole and the other end attaches to the kinetochore of the chromosome).
The arrangement of chromosomes in metaphase is called congression. Centromeres of chromosomes are aligned toward the equatorial plate and arms are toward the pole.
3. Anaphase
- It is the shortest phase of the M-phase.
- During early anaphase, the division of the centromere takes place. Hence, both chromatids of a chromo¬some separate from each other, and the separated chromatids are called daughter chromosomes.
- During late anaphase, daughter chromosomes move to their respective pole due to
- Contraction of spindle fiber
- Relaxation of interzonal fiber which forms between two daughter chromosomes.
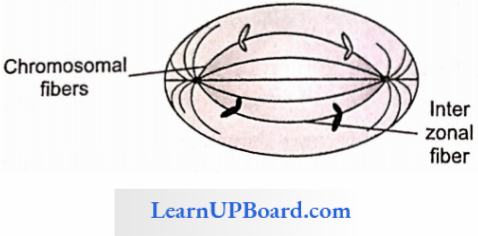
- The shape of the chromosome is observed in anaphase.
- The movement of chromosomes toward the pole requires 30 ATPs.
- Cytokinesis also starts during anaphase.
4. Telophase
- In telophase, all events are reverse of prophase.
- Chromosomes reach to their poles.
- Spindle fibers disappear. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear at both poles.
- Hydration and de-condensation of chromosomes take place.
- It results in the formation of two daughter nuclei.
- At in this stage, the chromosomes lose their individuality.
- The nucleolus, Golgi body, and ER are reformed.
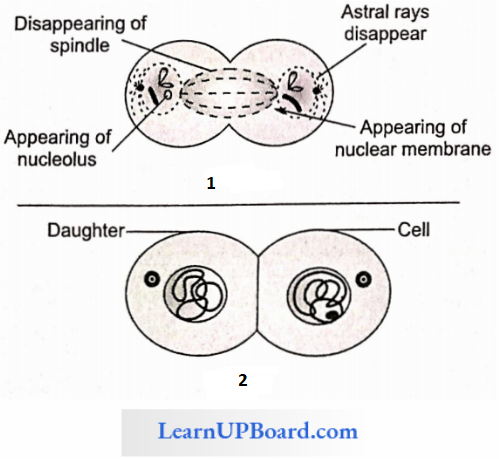
Cytokinesis: The division of cytoplasm is known as cytokinesis.
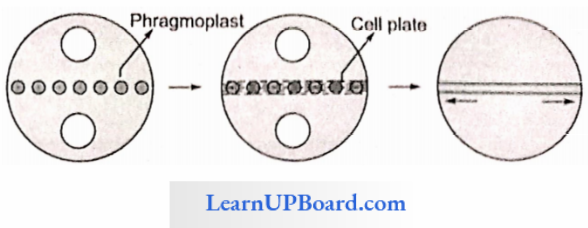
1. In Plants: Cytokinesis takes place by cell plate formation. Phragmoplast develops between two daughter nuclei by the deposition of spindle fiber and vesicles of GB. The growth of phragmoplast takes place centrifugally. These phragmoplasts form a cell plate.
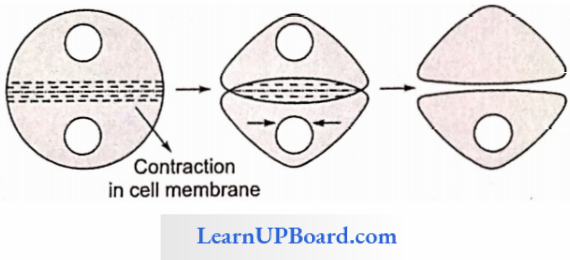
2. In Animals: Cytokinesis takes place by cell furrow method. Contraction in the cell membrane takes place between two daughter nuclei which move centripctally forming two daughter cells.
Significance Of Mitosis
- In unicellular organisms, it increases the number of individuals.
- In multicellular organisms, it is responsible for the growth of the body and the repairing of body parts.
- It maintains the number of chromosomes in all cells of organisms.
- It also maintains S/V ratio and KPR.
NEET Biology Notes For Cell Cycle And Cell Division Mitosis Points To Remember
Number of mitosis required for n number of cells is (n – 1), where n is the required number of cells, A number of cells formed in n generation is 2″, where n is the number of generations.
- Chemicals that induce mitosis are auxin, gibberellins, cytokinin, insulin, and lymphokines.
- Mitotic poison includes those chemicals that inhibit mitosis, for example, chalones, mustard gas (agglutinates the chromosomes), ribonuclease, colchicine, cyanide (inhibits prophase), azides (inhibits prophase), and X-ray.
- Eumitosis: It is extranuclear mitosis, i.e., nuclear membrane degenerates.
- Pre-mitosis: It is intranuclear mitosis, i.e., the nuclear membrane does not degenerate but intranuclear spindle formation takes place, for example, fungi, protozoa, some algae, etc.
- Free Nuclear Division: Karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis and multinucleate cell forms, for example, Rhizopus, Vaucheria, Mucor, slime mold, etc.
- Denomitosis: In this type of mitosis, the nuclear membrane does not disappear and it is only found in dinoflagellates.
- Endomitosis was discovered by Meyer. The division of chromosomes takes place, but no division of the nucleus. Hence, all divided chromosomes remain present in the same nucleus. That is why the number of chromosomes has doubled.
- Endomitosis produces polyploidy, for example, tapetum cells. Endomitosis can be artificially induced by colchicines. Such mitosis is called C-mitosis (colchicines- induced mitosis).
- Colchicines dissolve microtubules and hence split or stop spindle fiber formation.
- Colchicines are produced from Colichicum autums of Liliaceae.
NEET Biology Notes For Cell Cycle And Cell Division Meiosis
Meiosis takes place in diploid cells called as meiocytes. This division occurs only in reproductive cells. The term meiosis was coined by Fanner and Moore. It was discovered by von Benden and Winiwarter.
- It is a type of indirect cell division in which one diploid reproductive mother cell divides into four haploid daughter cells.
- Daughter cells are quite different from each other. The number of chromosomes in a daughter cell reduces to half of the mother cell.
- Two divisions of the nucleus and only one division of the chromosome take place in meiosis.
- The structural division of chromosomes takes place in meiosis II and the numerical division of chromosomes takes place in meiosis I.
- In angiosperms, in the bud stage, the anther and ovule show meiosis.
- Anther and ovule is the most suitable structures for meiosis study.
- In algae, the zygote undergoes meiosis.
- In bryophyta, pteridophyta, and gymnosperms, SMC (spore mother cell) undergoes meiosis.
In Fungi:
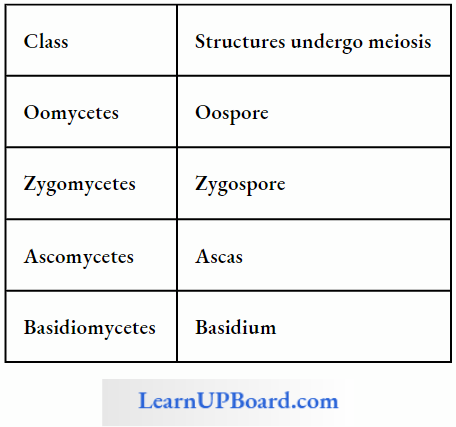
- Brachymeiosis was discovered by Gynenvaughan in fungi. Double reduction takes place in chromosome number in a tetraploid cell to produce a haploid cell.
- The S-phase of meiosis is much longer than mitosis. Replication of DNA takes place here.
- G2-phase is either very short or absent in meiosis.
- Interkinesis is the period in between meiosis-1 and meiosis-2. It may or may not be present. It is generally present in animal cells. There is no S-phase and no DNA synthesis. Hence, called interkinesis.
- Only duplication of centrioles takes place during interkinesis.
Types Of Meiosis
- Zygotic Or Initial Meiosis: Thallophyta (algae, fungi).
- Sporic Or Intermediate Meiosis: Bryophta to angiosperm.
- Gametic Or Terminal Meiosis: Animal and some brown algae.
Mechanism Of Meiosis: Meiosis includes the following phases
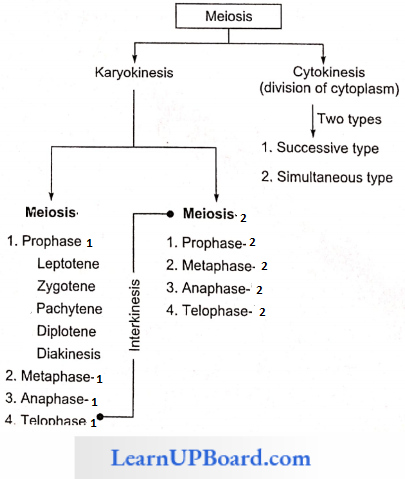
Meiosis 1
1. Prophase 1: It is the longest phase of meiosis, hence divided into five phases.
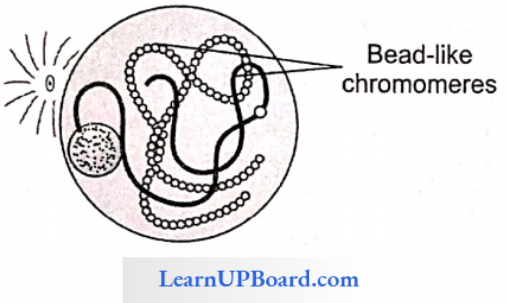
Leptotene: In this phase, condensation and dehydration of the chromatin network initiate.
- Chromosomes appear as elongated, single-stranded, as shown. Beaded structures represent the chromomere.
- Chromosomes always appear in homologous pairs; hence, they are diploid.
- Each chromosome is composed of two chroma¬tids but these chromatids are not visible.
- Both ends of the chromosome become attached to the nuclear lamina of the nuclear membrane and form a loop-like structure. Hence, this is also called the bouquet stage.
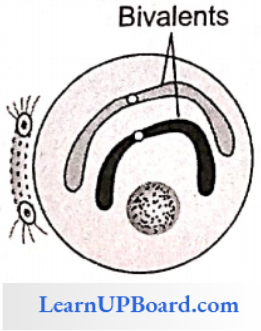
Zygotene: Dehydration of chromosomes continues. Hence, it becomes shorter and thicker.
- Both chromatids of a chromosome are called diad.
- The formation of recombination nodules takes place at several points in divalent chromosomes.
- Exchange of part of nonsister chromatid takes place. This process is called as crossing over.
- Formation of the synaptonemal complex takes place between bivalent chromosomes composed of ribonucleic protein (RNA 5% + Protein 95%) reported by Montrose
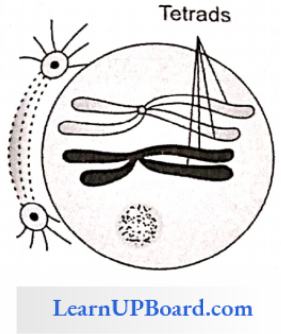
Pachytene: Both chromatids of chromosomes become visible, hence each bivalent is composed of chromatids called tetrad.
- The formation of recombination nodules takes place at several points in divalent chromosomes.
- Exchange of part of non-sister chromatid takes place. This process is called as crossing over.
Diplotene: Crossing over is an enzyme-mediated process and the enzyme involved is called recombinase.
- In the oocyte of the same vertebrate, the diplotene stage can last for months or years.
- The breaking of the synaptonemal complex starts. Hence, both chromosomes of bivalent tend to separate from each other called terminalization.
- Both chromosomes are not separated completely due to the formation of an X-like structure at the point of crossing over called chiasmata.
- Charismata is the result of crossing over.
- Terminalization starts here but does not complete here.
- The process of degeneration of the synaptonemal complex is called desynapsis.
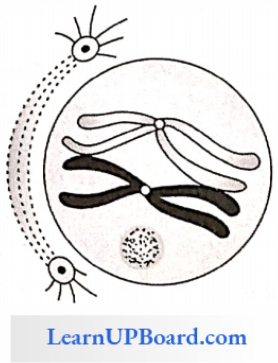
Diakinesis: Both chromosomes of bivalent become separate, i.e., the process of terminalization is complete here. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
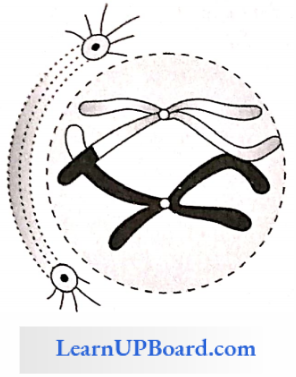
2. Metaphase 1: The formation of a double metaphase plate takes place at the equator. Spindle fibers appear which attach to the centromeres and pull the chromosomes.
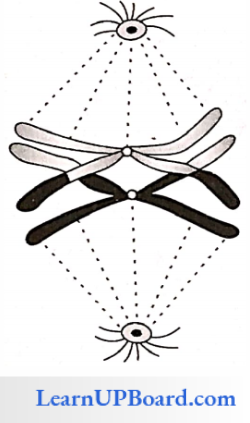
3. Anaphase 1: Both chromosomes of a bivalent move to opposite poles due to contraction of the spindle fiber. This is called disjunction. There is no division of centromere.
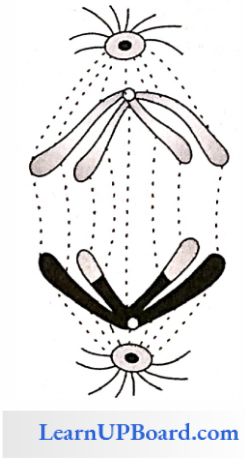
4. Telophase 1: Chromosomes continuously move and reach to their respective poles. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear. It results in the formation of two daughter cells containing a haploid number of chromosomes and each chromosome is composed of two chromatids.
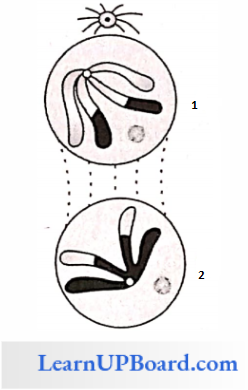
Meiosis 2: Both daughter nuclei divide by mitosis to form four haploid daughter nuclei. Each daughter nucleus is haploid but the chromosome is composed of a single chromatid due to the division of centromere in anaphase 2.
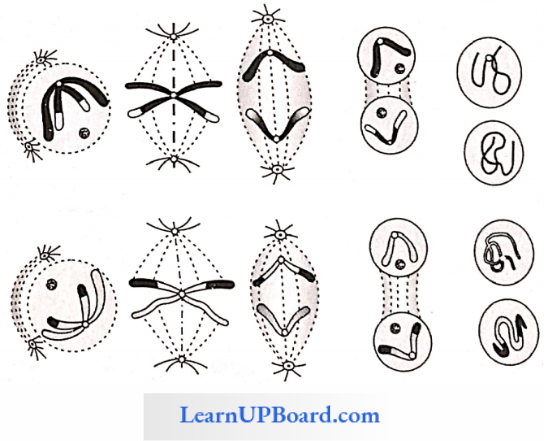
Different stages of meiosis are collectively shown.
cell cycle and cell division pdf notes
Cytokinesis: Cytokinesis is mainly of two types
- Successive Type: Cytokinesis takes place after meiosis 1 and 2 resulting in the formation of the isobilateral tetrad, for example, a monocot. It is of advanced type. In successive types, three cytokines are involved, first after meiosis 1 and two after meiosis 2.
- Simultaneous Type: Cytokinesis only takes place after meiosis 2 resulting in the formation of tetrahedral tetrad, for example, dicot.
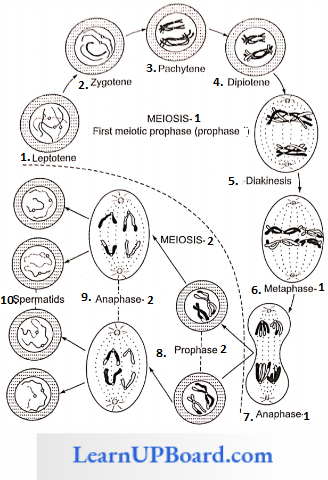
Significance Of Meiosts
- Mciosis maintains the number of chromosomes in each generation of organisms during sexual reproduction.
- Crossing over lakes places in meiosis which produces variation, which plays an important role in evolution.
- It is also required to complete the sexual life cycle of organisms.
- Number of meiosis required for:
- Formation of n number of pollen grams = \(\frac{n}{4}\)
- Formation of n number of eggs = n
- Formation of n number of seeds = n + \(\frac{n}{4}\)
- The formation of n number of seeds in Cypraceae is n + n, i.e., 2n.
NEET Biology Notes For Cell Cycle And Cell Division Assertion Reasoning Type Questions And Answers
In the following questions, an Assertion (A) is followed by a corresponding Reason (R). Mark the correct answer.
- If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- If both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- If Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
- If both Assertion and Reason are false.
cell cycle notes pdf
Question 1. Assertion: Endomitosis does not cause karyokinesis or cytokinesis.
Reason: In endomitosis, mitosis occurs within the nucleus.
Answer: 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Question 2. Assertion: Synaptonemal complex develops between two synapsed homologous chromosomes.
Reason: Mitosis cannot be completed without the synaptonemal complex.
Answer: 3. If Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
Question 3. Assertion: During anaphase 2, the chromatids of a chromosome separate.
Reason: The Centromere of a mitotic chromosome divides during anaphase.
Answer: 2. If both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion
Question 4. Assertion: Dictyotene stage occurs in females only.
Reason: Gametogenesis rests for a long period at the diplotene stage in females.
Answer: 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Question 5. Assertion: Each chromosome of bivalent attaches with two spindles in metaphase.
Reason: In metaphase, bivalents migrate toward metaphase plate.
Answer: 4. If both Assertion and Reason are false.
