NEET Biology Notes PDF Free Download
NEET Biology Notes For Kingdom Protista
They are solitary, unicellular eukaryotic organisms. Few may be colonial.
- They are mostly aquatic organisms.
- A well-defined nucleus is present. Protists can be uni-nucleate, binucleate, or multinucleate.
- The cytoplasm contains, besides ribosomes, a variety of membrane-bound organelles. Many have centrioles also.
- Cell wall, if present, contains cellulose.
- Locomotion can occur through flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia. Ciliary mode is the fastest averaging to 2 mm/s.
- Flagella and cilia, when present, have 9 + 2 patterns of microtubular strands.
- The nutritive modes are variable: photosynthetic (holophytic), ingestive (holozoic, phagotrophic), and absorptive (saprobic, parasitic). The photosynthetic protists act as chief producers of food in the oceans and in freshwater.
- Some protistans are parasitic. Some live symbiotically as in the guts of other animals while a few act as decomposers.
- Reproduction is through asexual and sexual processes. Sexual reproduction involves meiosis and syngamy. Meiosis is zygotic in some and gametic in others.
- Reserve food can be starch, paramylum, chrysolaminarin, glycogen, and fat.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Notes For Photosynthetic Protists: Diatoms (Chrysophytes)
Salient Features Of Diatoms
- Basically unicellular and aflagellate except in the reproductive state.
- They possess beautiful colors and shapes.
- They may be marine, freshwater forms, or ones dwelling in moist terrestrial habitats.
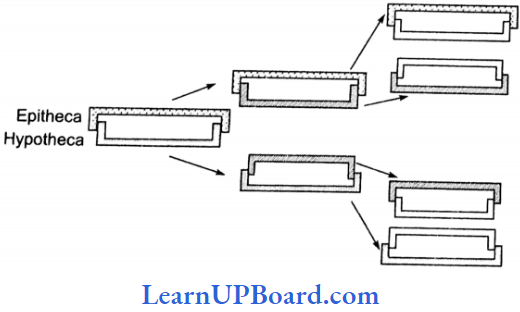
- A transparent, siliceous, bivalved frustule covers the body. It has two valves, the upper epitheca and the lower hypotheca. The frustule is variously sculptured. It may possess bilateral symmetry (centric as in Melosira) or radial symmetry (centric as in Melosira).
- Large central sap vacuole present. Primordial utricle condition exists.
- Nutrition: holophytic or photosynthetic. Plastids contain chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-c, carotene, and a variety of xanthophylls (diatoxanthin, etc.). The reserve food is oils and leucosin. Proteinaceous volutin granules are also present.
- Movement is brought about by mucilage propulsion.
- Diatoms synthesize about half the total organic matter synthesized in the biosphere. Oils extracted from fish are actually contributed by diatoms.
- Siliceous frustules of diatoms form diatomaceous earth diatomite or kieselguhr which is employed for a variety of purposes such as filtration, soundproofing, industrial catalysts, etc.
- They serve as sewage pollution indicators.
NEET Biology Notes For Reproduction In Diatoms
- Asexual Reproduction: By binary fission, each daughter cell receives the epitheca from the parent cell because of which the size goes on reducing in successive generations. Extrusion of protoplasm may serve to restore normal cell size. Resting spores called statospores may be formed by centric diatoms.
- Sexual Reproduction: It ranges from isogamy to oogamy. The zygote grows in size and forms a rejuvenescent cell called an auxospore.
- The life cycle is diploidic.
botany notes
NEET Biology Notes For Dinoflagellates – Salient Features Of Dinoflagellates
- These are basically unicellular (rarely palmelloid or filamentous), and biflagellate (rarely nonmotile) with heterokont conditions.
- They are mostly marine; some are freshwater species also.
- Cells are generally covered by a rigid coat (theca/lorica) of sculptured plates of cellulose and pectin Due to the presence of sculptured plates these are also called armored dinoflagellates.
- It is absent and replaced by pellicle/penpals in endosymbiotic dinoflagellates called zooxanthellae
- The longitudinal flagellum is narrow and smooth and lies in the longitudinal groove (sulcus).
The transverse flagellum is ribbon-like and lies in the transverse groove (cingulum/annulus/girdle):
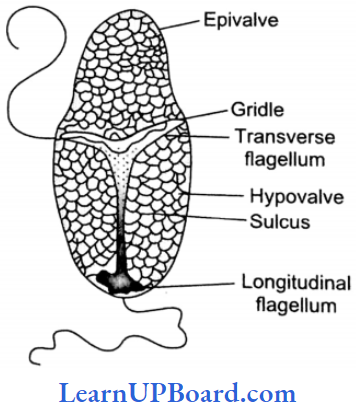
- Both flagella are oriented at right angles to each other and produce spinning movement.
- Therefore, these protists are also called “Whirling whips ”
- Holophytic or photosynthetic (rarely holozoic).
- Pigments are chlorophyll-a, c, carotene, and xanthophylls (such as peridinin).
- A non-contractile vacuole, called a pustule, is present.
- Reserve food: carbohydrates and oil.
- Gymnodinium and Gonyanlax cause red tides.
- Gonyaulax calendula produces saxitoxin (a neurotoxin) that accumulates in marine shellfish. When these shellfish are eaten by humans, it causes paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) that may be fatal.
- Bioluminescent dinoflagellates: Noctiluca, Pyrodinium, Pyrocystis.
- Some dinoflagellates possess trichocysts and cnidoblasts (nematocysts).
- The nucleus in dinoflagellates is called a mesokaryon (Dodge et. al). It is large and possesses permanently condensed chromosomes that lack association with histones.
- The life cycle is haplontic (for example, Ceratium) or diplontic (for example, Noctiluca)
NEET Biology Notes For Reproduction In Diatoms
- Diatoms Asexual Reproduction: Through cell division and encystment.
- Diatoms Sexual Reproduction: It is reported in some organisms such as Ceratium. It may be isogamotts or anisogamous.
