NEET Biology Notes PDF Free Download
NEET Biology Notes For Virus
General Structure Of Virus A Virus Has Following Parts:
- Envelope: It has smaller subunits, known as telomeres. For example, herpes virus, HIV, etc.
- Capsid: Protein coat made up of subunits called capsomeres.
- Nucleoid: Viruses contain either DNA or RNA.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
On the basis of the type of genetic material, viruses are classified as:
- Deoxy Viruses:
- Contain double-stranded DNA (ds DNA), for example, pox virus, and cauliflower mosaic virus.
- Contain single-stranded DNA (ss DNA), for example, x 174.
- Riboviruses:
- Contain ds RNA, for example, reovirus, wound tumor virus.
- Contain ss RNA, for example, TMV, HIV, and influenza vims.
NEET Biology Notes For Structure Of Some Viruses
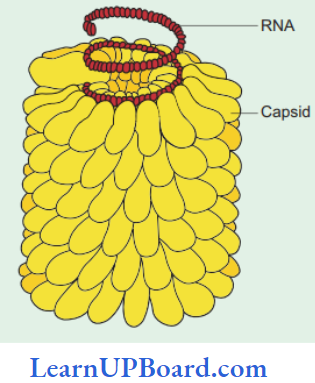
- Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is elongated rod-like, 300 (one, ISO in diameter with a molecular weight, of 39.4 x 106. 2130 capsomercs are arranged helically to form the capsid. 40 capsid tires present in three turns and 130 turns in complete virus capsid. UNA strand is helical ssRNA and consists of 6400 nucleotides. Thus, the ratio of nucleotides and capsomeres =3:1.
- Pox virus/variola is the causal agent of smallpox. These are among the largest of animal viruses and are rectangular (brick-shaped), 300 x 230 nm in size. The genome is dumbbell-shaped with a central core of dsDNA. The core has two enzymes: RNA polymerase and ATP phosphohydrolase.
- AIDS virus consists of ssRNA. It has two copies of ssRNA. The outer cover has five-layer, the outermost glycoprotein, followed by a double lipid layer, and the innermost has two protein layers
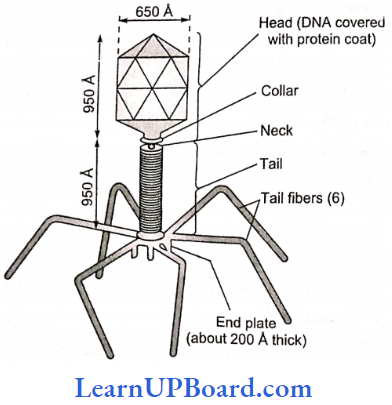
- T4 bacteriophage has a tadpole-like structure with a polyhedral head connected to a helical tail. J lic head consists of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat or capsid. Nucleic acid is double-stranded f)NA. The tail is proteinaceous tube-like, core surrounded by a sheath. At one end, lube is jointed to the head by a thin collar. At the other end, it has a hexagonal base plate with six small tail pins and six tail fibers which help in the attachment of the phage to the host cell.
Reproduction In Virus: Reproduction is of two main types: phagic and pinocytic.
- Phagic Reproduction: It is further of two types:
- Lytic Cycle: Occurs in virulent phages, for example, T4 bacteriophages.
- Lysogenic Cycle: Occurs in temperate viruses such as phage.
- Pinocytic Reproduction: An example, occurs in TMV.
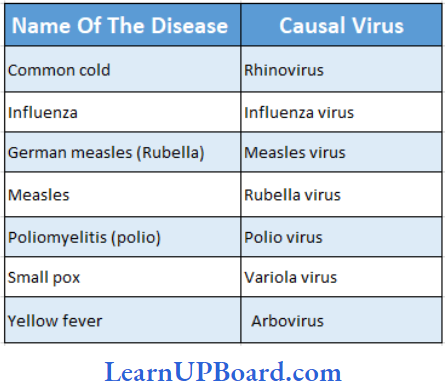
Diseases Caused by Virus in Man
1. Cryptogram of Virus
The International Committee of Virus Nomenclature has developed a system for naming viruses. The system consists of two parts: the common name and the coded information about the virus. This is called a cryptogram.
- Cryptogram Of TMV: R/1: 2/5: E/E: S/A
- Cryptogram Of Pox Virus: D/2, 160/5-7.5,X/*,V/0
- Cryptogram Of Poliovirus: R/1, 2.5/30, S/S, V/O
- Cryptogram Of T4 Bacteriophage: D/2, 130/40, X/X, B/O
In a cryptogram,
- The first pair represents the type of nucleic acid/number of strands in nucleic acid.
- The second pair represents the molecular weight of nucleic acid/amount of nucleic acid expressed as a percentage.
- The third pair denotes the shape of the virus/shape of nucleoprotein.
- The fourth pair denotes the type of host/carrier used in the transmission of the virus.
2. Viroids And Prions:
Viroids were discovered by T.O. Diener. It has RNA without a protein coat. Viroids cause potato spindle tuber disease (PSTD), Chrysanthemum stunt, citrus exocortis, cucumber pale fruit, etc.
Prions are proteinaceous infectious particles. It causes:
- Kuru (laughing death) disease
- Mad cow disease (C-Jakob)
- Alzheimer’s disease in human beings
- Scrapie disease in sheep
