NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Introduction
The sum total of various processes by which an organism with-draws and utilizes the substances required for the development and sustaining life-related processes is called nutrition, and these substances are called nutrients.
- The absorption, distribution, and metabolism of various mineral elements by plants is called mineral nutrition. About 60 elements have been reported from plant ash (obtained after heating dry plant matter at 600°C). Out of these, 30 are present in all the plants.
- Inorganic nutrients are classified as essential and non-essential elements. Seventeen elements have been placed in essential elements. These are the elements without which the reproduction and life cycle of a plant cannot be completed. The essential elements are C, H, O, N, P. K. S, Mg, Ca, Fe, Mo, Mn, Ni, Zn, B, Cl, and Cu.
Amon and Stout proposed the following criteria of the essentiality of an element:
” mineral nutrition in plants”
- The element must be absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction.
- The requirement of the element must be specific and not replaceable by another element.
- The element must be directly involved in the nutrition of the plant.
- A deficiency of minerals causes diseases in plants. Magnesium. for example, is a constituent of the chlorophyll molecule and is essential for photosynthesis. It cannot be replaced by any other element for the same function. It is also required as a cofactor by many enzymes involved in cellular respiration and metabolic pathways. Similarly, iron is a constituent of cytochromes.
Depending Upon The Quantity In Which These Elements Are Present In Cell, They Are Classified As:
Macronutrients: They are the elements that are present in a quantity of 1—10 mg/g dry wt. of the cell. They are C, H, O, N, P, S, K, Mg, and Ca.
Micronutrients: They are the elements that are present in a quantity equal to or less than 0.1 mg/g dry wt. of the cell (often less than 1 ppm). They are Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Zn, B, Cl, and Cu.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Culture Medium
Soils normally contain sufficient quantities of essential minerals. However, three important elements need to be replenished in crop fields as they are depleted by repeated cultivation. These x fertilizer elements called critical elements are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK).
- The common sources of these elements used in India are nitrate of sodium, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, ammonium chloride, urea, etc. The NPK fertilizers comprising bags of fertilizers are labeled 17-18-19 or 15-15-15 or other combinations. These numbers refer to the percentage by weight of nitrogen, phosphorus, and water-soluble potassium
- To determine what elements are essential tor plant growth and deficiency symptoms of an essential element, a well-defined nutrient medium has to be used. Seeds are grown in highly washed pure sand in a glass, glazed porcelain, or plastic container and supplied with a carefully made-up nutrient solution.
Arnon And Hoagland’s Medium: Amon and Hoagland prescribed a medium containing micronutrients. Iron was earlier supplied as ferrous sulfate, but it often precipitated out. This problem has now been solved by dissolving ferrous sulfate along with a chelating agent Na-EDTA (disodium salt of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid).
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Culture
Solution culture is performed in glass jars or polythene bottles. The container is covered with black paper after pouring the solution into them. Black paper has two functions
- Prevention of the growth of algae.
- Prevention of reaction of roots with light.
Seeds are allowed to germinate over the cork. Cotyledons are removed after seedling formation. The plant is properly sup¬ported with the help of split cork. The solution is aerated at regular intervals and is changed after two to three days.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition– Hydroponics
The commercial technique of soil-less culture is called hydroponics, which was first developed by Goerick (1940). The culture is performed in large tanks of metal or RCC tanks. The tanks are covered with wire mesh. Tanks are provided with aerating and circulating techniques. Seeds are suspended in the solution from the wire mesh with the help of threads. As the plant grows, additional support is provided. it depicts the diagrammatic views of the hydroponic technique.
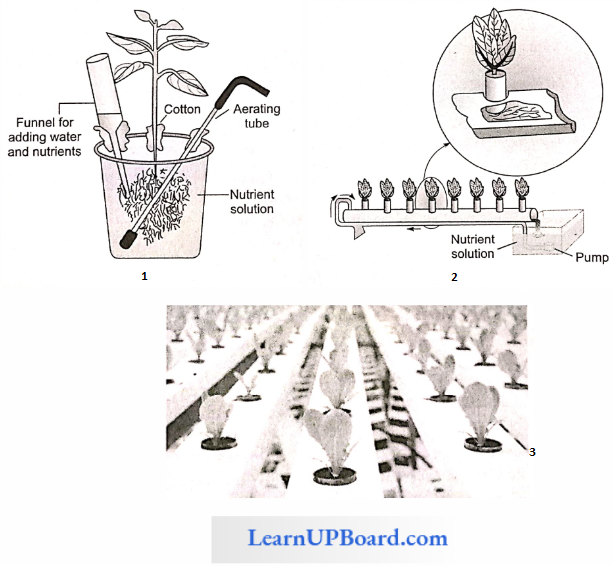
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Liebig’s Law Of The Minimum
As per this law, “the yield of a crop plant is determined by the amount of the necessary element which is present in minimum quantity in proportion to the demand of the plant.”
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition General Functions Of Mineral Elements
Frame Work Elements: They form carbohydrates that form cell walls, for example, C, H, and O.
Protoplasmic Elements: They form protoplasm, for example, C, H, O, N, S, P.
Catalytic Elements: Fe, Cu, Zn, Mo, Mg, Mn, K (activator of over 40 enzymes)
Balancing Elements: Ca, Mg, and K counteract the toxic effect of other minerals.
Storage Elements: C, N, S, P.
Critical Elements: N, P, K.
Elements Affecting Cell Permeability: Monovalent cations (Na+, K+) increase the permeability of membranes while divalent and trivalent cations decrease it.
Toxic Elements: Al, As, Hg, Pb, Ag.
Non-mineral Elements: C, H, O, N. Nitrogen is a mineral as well as a non-mineral element.
Functional Elements: They are non-essential in most plants but have a definite activity in some species, for example, silicon in grasses.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Nitrogen Fixation
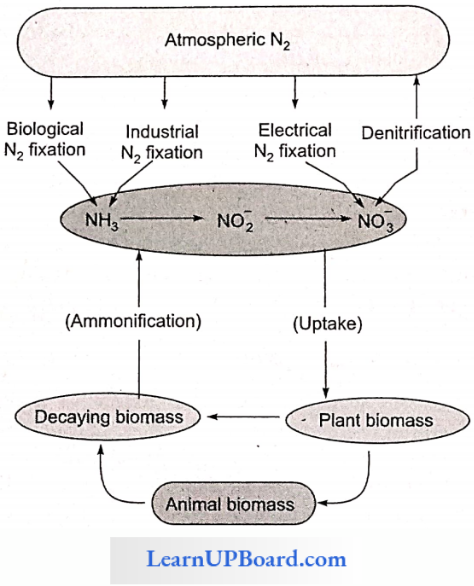
Atmosphere is the ultimate source of nitrogen. Nitrogen is a highly inert gas. It cannot be used directly but has to be combined with C, H, N, and O to form compounds before being used. Higher plants utilize nitrogen in the oxidized forms such as nitrate (NO3–) and nitrite (NO2–) or in the reduced form (NH4) made available to plants by the nitrogen fixers.
The best-known nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium is Rhizobium. This bacterium lives in the soil to form root nodules in plants belonging to the family Leguminosae such as beans, gram, groundnut, and soya bean. Root nodules are little outgrowths on roots.
- When a section of the root nodule is examined, it appears pinkish due to the presence of a pigment called leghemoglobin. Like hemoglobin, leghemoglobin is an oxygen scavenger. The enzyme that catalyses the fixation of nitrogen is nitrogenase which functions under anaerobic conditions. Leghemoglobin combines with oxygen and protects nitrogenase.
- Free-living microorganisms such as the cyanobacteria can also fix nitrogen. Some cyanobacteria also have symbiotic as¬sociation with plants. They are found in lichens. Anthoccros. Azollcu and coralloid roots of Cycas.
- In the process of biological nitrogen fixation, the dinitrogen molecule is progressively reduced by the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms so that the three bonds between the two nitrogen atoms are cleaved and ammonia is formed.
These reactions occur only in the presence of a single enzyme nitrogenase. The process of nitrogen fixation is energy-intensive.
Requirements Of N2 Fixation
- Nitrogenase enzyme complex (synthesized by nif genes of bacteria) is the seat of nitrogen reduction and contains Mo, Fe, and S.
- It is a strong reducing agent, for example, NADPH2, FMNH2, ferredoxin, etc.
- It takes place under anaerobic conditions.
- The energy source is ATP.
- Cofactors included are TPP, CoA, Mg+2.
- Electron and H+ donor (generally glucose-6-phosphate)
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Process Of Nodule Formation
Nodules are little out growths on the roots. When a root hair of a legume comes in contact with Rhizobium, there occurs an ex-change of plant and bacterial signals. Bacteria secrete nod fac-tors which result in the curling of root hair tips.
The plant responds by forming an infection thread that grows inward and carries the bacteria to the cortical cells of the root. Some of bacteria enlarge to become membrane-bound structures called bacteroids which are the seat of N2 fixation. Plant flavones act as the inducers of nod genes which specify early events of modulation.
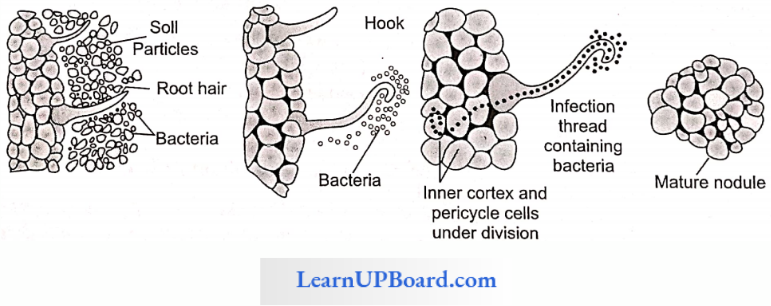
” mineral nutrients in plants”
Cortical cells are stimulated to divide rapidly. It is due to auxin secreted by plants and cytokinin contributed by bacteria. Nodules are pink in color due to leghemoglobin which is an oxygen scavenger and protects nitrogenase. Its heme comes from bacteria and globin from legumes.
Process Of N2 Fixation Can Be Summarized As: N2 + 8e– + 8H+ + 16 ATP → 2NH3 + H2 + 16ADP + 16Pi
Ammonium ions can be taken up by higher plants but plants are more adapted to absorb nitrate (NO3–) than ammonium ions (NH4+) from the soil. Soil bacteria such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrococcus convert ammonia to nitrite (NO2–) ions. Nitrobacter oxidizes nitrite to nitrate. This process of converting ammonia into nitrate, a form of nitrogen more available to plants, is called nitrification.
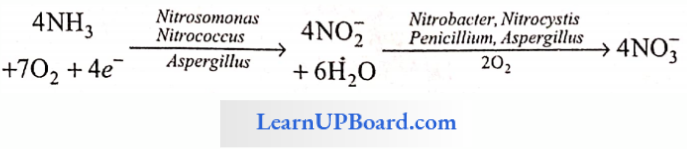
This process is an oxidation process and releases energy which is used by nitrifying microbes.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Nitrate Assimilation
The process of nitrate reduction to ammonia is called nitrate assimilation and is accomplished in two steps mediated by two specific enzymes. First, the nitrate is reduced to nitrite by an enzyme called nitrate reductase. This enzyme is a flavoprotein and contains molybdenum.
The nitrite ions are then reduced to ammonia by an enzyme called nitrite reductase. Ferredoxin is the most detect source of electrons for nitrite reduction and hence it occurs specifically in leaves. Therefore, nitrite ions formed in other parts of the plant are transported to leaves arid and further reduced to ammonia. Nitrite reductase does not require molybdenum but contains copper and iron.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Synthesis Of Amino Acids
There are two main processes for amino acid synthesis.
1. Reductive Animation: From glutamic acid all other amino acids can be synthesized by the process of transamination.
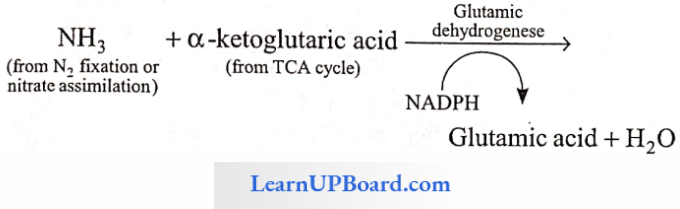
2. Transamination: It involves the transfer of amino groups from one amino acid to the keto group of the keto acid. The reactions are catalyzed by the enzyme transaminase.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Mineral Absorption
Mineral Absorption Occurs By Two Ways:
- Passive and
- Active.
- Passive Mineral Absorption: The main theories of passive mineral absorption. In most cases, the movement of mineral ions into the root occurs by diffusion. Molecules or ions diffuse from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration. The movement of mineral ions into root cells as a result of diffusion is called passive absorption.
- Donnan Equilibrium Theory: This theory was proposed by Donnan (1911). The entry of ions into the cell across the plasma membrane to maintain electrical equilibrium is called Donnan equilibrium. Some anions/cations get firmly attached to the inner surface of the plasma membrane (fixed and non-diffusible ions). To neutralize these, ions of opposite charges gain entrance in the cell passively against the concentration gradient without energy expenditure.
- Ion Exchange Theory: It was proposed by Jenny and Overstreet (1938). The exchange of anions and cations absorbed on a colloidal fraction of the soil (clay and humus) with the ions adsorbed on the root surface is referred to as ion exchange. The small space in which the cations and anions attached to the surface of roots and particles oscillate is called oscillation volume. It is of two types
- Contact Exchange: This includes the exchange of cation and anions from the root with similarly charged ions of soil solution.
- Carbonic Acid Exchange: This includes the exchange of H+ and CHO3– ions from the root with similarly charged ions of the soil solution.
- Bulk Flow/Mass Flow Theory: It was proposed by Hylmo (and supported by Kramer). According to it, the movement of ions occurs through roots along with the stream of water under the influence of transpiration.
- Active Mineral Absorption: The uptake of mineral ions against a concentration gradient is called active absorption. Such movement of minerals requires the expenditure of energy by the absorbing cell. This energy is derived from respiration and is supplied through ATP. Hence, when the roots are deprived of oxygen, they show a sudden drop in the active absorption of minerals. Mostly minerals are absorbed by active mechanisms. Various theories are given for the active uptake of minerals.
- Carrier Concept (By Van den Honert): Carriers are specific proteins in membranes that form complexes with ions. This complex is capable of moving across the membrane and releasing ions on the inner side. There are separate carriers for cations and anions.
- Cytochrome Pump (By Lundegardh And Burstrom): Cytochromes are iron-containing proteins in the membrane. They transport electrons from the inner surface to the outer surface of the membrane and also transport anions from the outer surface to the inner surface. Anions are transported actively while cation transport is passive. Anion uptake increases the rate of respiration called salt respiration.
- Protein Lecithin Carrier (by Bennet and Clark): Carrier is a protein associated with a phosphatide called lecithin. It is an amphoteric earner and transports both cations and anions.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Mobility
The elements that cannot move freely in the plants (for example, Ca, B, S, Fe, etc.) are called immobile elements. Deficiency symptoms of such elements first appear in young leaves. Those elements that can move from old leaves to young leaves and growing tips (N, P, K, Cl, Mg) are called mobile elements. Their deficiency affects old leaves.
” where are the mineral nutrients mostly used in plants”
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Points To Remember
Sodium (Na) is required by a desert shrub Atriplex and not by most of the other species.
- Efforts are being made to develop varieties of plants that can mine metals from the soil so that that soil can be reclaimed for agriculture practice, called phytore¬mediation.
- Foliar application of Fe, Mn, and Cu is more efficient than application through the soil.
- Aeroponics (by Soifer Hillel and David Durger) is a system where roots are suspended into some plastic vessel and misted with oxygenated, nutrient-en-riched water.
- Winogradsky (1891) discovered biological nitrogen fixation.
- Cobalt is found mostly in hydathodes and is required in N2 fixation.
- Selenium is found in Astragalus.
- Excess of manganese may, in fact, induce the deficiency symptom of iron, magnesium, and calcium (toxicity of micronutrients).
- Gallium accumulates in Lcinnci and Aspergillus.
- Phytotron: When a plant is grown in controlled conditions of temperature, and light. pH, etc.
- Asparagine and glutamine are two amides formed from aspartic acid and glutamic acid, respectively, in a plant. Amides are the storage form of nitrogen.
- Stem nodules are found in Sesbania.
- Leaf nodules are found in Pavetta. Dioscorea.
- Associative symbiosis (loose symbiosis) is found in tropical grass (with Azotobacter) and maize and sorghum (with Azospirillum).
- True humus plant is Wullschleigelia aphylla.
- Single ion channels (discovered by Neher and Sakmann) are transmembrane proteins meant for the entry of specific ions.
- Aquaporins are water-filled pores in membranes.
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Which is not a criterion for the essentiality of a mineral?
- Direct role in metabolism
- Requirement is specific
- Deficiency causes hunger signs
- Dispensable for growth
Answer: 4. Dispensable for growth
Question 2. Essential elements are
- Only macronutrients
- Only micronutrients
- Both macro and micronutrients
- C, H, O, and N only
Answer: 3. Both macro and micronutrients
Question 3. Which is not a trace element?
- Mn
- Cu
- Mo
- K
Answer: 4. K
Question 4. Which is not a true statement regarding macronutrients?
- Macronutrients form plant structure.
- Macronutrients become toxic when present in excess.
- Macronutrients have no role in electron transfer.
- Macronutrients develop osmotic potential.
Answer: 2. Macronutrients become toxic when present in excess.
Question 5. Choose the false statement regarding micronutrients.
- Micronutrients become toxic in excess.
- Micronutrients do not cause osmotic potential.
- Micronutrients have little role in protoplasmic structure.
- Micronutrients play a secondary role in enzyme activation.
Answer: 4. Micronutrients play a secondary role in enzyme activation.
Question 6. Deficiency in plant growth and disorders caused by the reduced availability of a critical element is called
- Critical deficiency
- Secondary deficiency
- Primary deficiency
- Complete deficiency
Answer: 3. Primary deficiency
Question 7. Who prescribed a medium containing microelements for the first time?
- Gericke
- Arnon Ploagland
- Knop
- Stout
Answer: 2. Arnon Ploagland
Question 8. Excess of manganese may induce the deficiencies of
- Iron
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 9. A partial mineral element is
- N
- P
- K
- S
Answer: 1. N
Question 10.The deficiency of which element causes the deficiency of nitrogen?
- Mo
- K
- Mn
- S
Answer: 1. Mo
Question 11. Minerals associated with redox reactions are
- N, Cu
- Fe, Cu
- Fe, K
- Mn, Mo
Answer: 2. Fe, Cu
Question 12. Minerals that maintain cation-anion balance in cells are
- Cl, K
- Fe, Cu
- K, P
- Ca, Fe
Answer: 1. Cl, K
“mineral nutrients “
Question 13. Interveinal chlorosis is due to the deficiency of
- Fe
- Mn
- N
- B
Answer: 1. Fe
Question 14. Match columns A and B correctly.
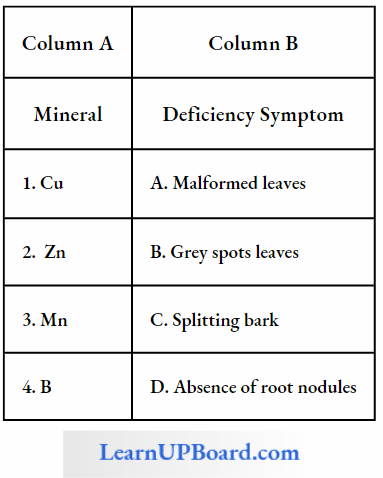
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (D), (4) → (B)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
- (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3)→(D), (4)→ (A)
- (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C), (4) → (D)
Answer: 2. (1) → (C), (2) → (A), (3) → (B), (4) → (D)
Question 15. Which of the following groups of elements are mobile?
- Fe, Ca, B
- N, P, K
- B, K, Ca
- Ca, Mg, K
Answer: 2. Fe, Ca, B
Question 16. Which of the following elements are required for chlorophyll synthesis?
- Fe and Mg
- Mo and Ca
- Cu and Ca
- Ca and K
Answer: 1. Fe and Mg
Question 17. If chloroplast is burnt, then which of the following is left?
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Iron
- Sulfur
Answer: 1. Magnesium
Question 18. Which one of the following is a sulfur-containing amino acid?
- Valine
- Methionine
- Tryptophan
- Phenylalanine
Answer: 2. Methionine
Question 19. Copper deficiency leads to
- Exanthema
- Whiptail of cauliflower
- Little leaf condition
- Interveinal chlorosis
Answer: 1. Exanthema
Question 20. Phosphorus is found maximum in
- Roots
- Fruits
- Flowers
- None of these
Answer: 2. Fruits
Question 21. Which of the following is required for auxin synthesis?
- Calcium
- Zinc
- Sugars
- Proteins
Answer: 2. Zinc
Question 22. Reversible binding of cations, a property possessed by clay particles, is known as
- Retentive capacity
- Cation exchange
- Adsorption
- Chelation
Answer: 2. Cation exchange
Question 23. A characteristic of ion channels is/are
- They are transmembrane proteins functioning a selective pores
- They were discovered by Neher and Sakman
- They are gated canners
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 24. The theory of Donnan equilibrium explains the process of some
- Fixed diffusible cations on the inner side
- Fixed non-diffusible anions on the inner side
- Non-fixed diffusible anions on the inner side
- Non-fixed diffusible cations on the inner side
Answer: 2. Fixed non-diffusible anions on the inner side
Question 25. Mineral salts which are absorbed by the roots from the soil, are in the from of
- Very dilute solution
- Dilute solution
- Concentrated solution
- Very concentrated solution
Answer: 1. Very dilute solution
Question 26. The movement of electrolytes through the roots is a general
- Against the electrochemical gradient and requires energy
- Along the electrochemical gradient and does not require energy
- A passive process
- Dependent on aquaporins
Answer: 1. Against the electrochemical gradient and requires energy
Question 27. Ionic uptake against electrochemical gradient without the expenditure of metabolic energy can be explained by
- Ion exchange
- Donnan equilibrium
- Carrier proteins
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 28. Transpiration pull or water tension in leaf is responsible for which one of the following methods of absorption of minerals by the plants from soil?
- Active absorption of minerals
- Mass flow
- Donnan equilibrium
- Ionic exchange
Answer: 2. Mass flow
Question 29. If nitrogen is bubbled in the rooting medium, active absorption of minerals will
- Increase
- Decrease
- Remain same
- Stop immediately
Answer: 2. Decrease
Question 30. During ionic flux, the uptake of ions into inner space is
- Active
- Passive
- Energy-dependent
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (3)
Question 31. Carrier proteins for active salt uptake
- Have pores
- Form complex with ions
- Function under transpiration pull
- All of these
Answer: 2. Form complex with ions
Question 32. The translocation of solute is
- Equal to the rate of translocation of water
- Dependent on transpiration pull
- Through xylem vessel
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 33. Find the odd one (with respect to the critical element).
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
- Nickel
- Phosphorus
Answer: 3. Nickel
Question 34. The process of conversion of NH4 → NO2 → NO3 is called
- Ammonification
- Nitrification
- N2 fixation
- Denitrification
Answer: 2. Nitrification
Question 35. Which of the following is/are diazotrophs?
- Rhizobitnn and Azotobacter
- Frankia and Klebsiella
- Anabaena and Nos toe
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 36. Which is not true for nitrogenase enzyme in root nodules in legumes?
- Synthesized by nit genes of Rhizobium
- Site of reduction of N2 into NH3
- It is a Mo-Fe protein
- Resistant to O2 concentration
Answer: 4. Resistant to O2 concentration
Question 37. Cell division in root nodules is promoted by se creted by plants and secreted by bacteria.
- Auxin, Cytokinin
- Cytokinin, Auxin
- Auxin, Leghemoglobin
- Nitrogenase, Leg hemoglobin
Answer: 1. Auxin, Cytokinin
Question 38. Conversion of NO3 → NO2 → NH4 is called is catalysed by
- Nitrate assimilation; nitrate and nitrite reductase
- Nitrification; nitrate and nitrite reductase
- Ammonification; glutamate dehydrogenase
- Denitrification; transaminase
Answer: 1. Nitrate assimilation; nitrate and nitrite reductase
Question 39. Transported and storage forms of nitrogen in plants are
- Amides
- Polypeptides
- Amino acids
- α-ketoglutaric acids
Answer: 1. Amides
Question 40. The amino acid which plays a central role in nitrogen metabolism is/are
- Glutamic acid
- α-ketoglutaric acid
- Aspartic acid
- Double-aminated keto acids
Answer: 1. Glutamic acid
Question 41. The amino acid which plays a central role in nitrogen metabolism is/are
- Anthoceros
- Aulosira
- Nostoc
- Groundnut
Answer: 4. Groundnut
Question 42. Nitrite reductase enzyme is used to convert
- Nitrate into nitrite ion
- Nitrogen of the atmosphere into ammonia
- Ammonia into nitrates
- Nitrite to ammonium ion
Answer: 4. Ammonia into nitrates
Question 43. What do hemi parasites absorb from the host?
- Water and minerals
- Sugar
- Both (1) and (3)
- Nothing
Answer: 2. Sugar
Question 44. The small rootless aquatic herb in which a portion of the leaf forms a tiny sac or bladder that traps water insects is
- Dionaea
- Utricularia
- Sarracenia
- Drosera
Answer: 2. Utricularia
Question 45. The process of conversion of NO2, NO3, NH3 to N2 is called and is done by
- Nitrification, Nitrosomouas
- Denitrification, Pseudomonas
- Nitrate assimilation, Nitrogenase
- Ammonification, Bacillus
Answer: 4. Ammonification, Bacillus
Question 46. Which of the following elements are essential for the photolysis of water?
- Ca and Cl
- Mn and Cl
- Zn and I
- Cu and Fe
Answer: 2. Mn and Cl
Question 47. Which of the following is related with the transfer of food material?
- Xylem
- Collenchyma
- Phloem
- Parenchyma
Answer: 3. Phloem
Question 48. Which of the following elements is most mobile in plant metabolism?
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
- Carbon
- Magnesium
Answer: 2. Phosphorus
Question 49. The process of converting ammonia to nitrate by bacteria is known as
- Ammonification
- Nitrification
- Nitrogen fixation
- Denitrification
Answer: 2. Nitrification
Question 50. Root nodules that are present in plants are meant for fertilizers and are found in/on
- Certain leguminous plants
- Casuarina
- Ainas
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 51. Agriculturists have reported about 40-50% higher yields of rice by applying
- Azolla
- Cyanophycean members
- Mycorrhizae
- Thom forest
Answer: 1. Azolla
Question 52. A nutrient element essential for the formation of microtubules of the mitotic spindle apparatus during cell division is
- Phosphorus
- Sulfur
- Calcium
- Zinc
Answer: 3. Calcium
Question 53. The non-symbiotic N2 fixer is
- Anabaena
- Rhizobium
- Azotobactor
- Azolla
Answer: 3. Azotobactor
Question 54. The N2 fixing bacterium associated with root nodules of legumes is known as
- Azotobacter
- Nitrobacter
- Lactobacillus
- Rhizobium
Answer: 4. Rhizobium
Question 55. The bacteria that converts nitrate into molecular nitrogen is called
- Nitrifying bacteria
- Methanobactcria
- Diazotrophic bacteria
- Denitrifying bacteria
Answer: 4. Denitrifying bacteria
Question 56. The bacterium capable of anaerobic N2 fixation is known as
- Clostridium
- Bacillus
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium
Answer: 1. Clostridium
Question 57. Which element is essential for the photolysis of water?
- Nitrogen
- Manganese
- Carbon
- Oxygen
Answer: 2. Manganese
Question 58. Which of the following can utilise molecular nitrogen (N2) as a nutrient for growth?
- Rhizobium
- Spirogyra
- Mucor
- Methancoccus
Answer: 1. Rhizobium
Question 59. Sinks are related to
- Transport of organic solutes
- Stomata
- Enzymes
- Phytochrome
Answer: 1. Transport of organic solutes
Question 60. Supply ends in the transport of solute are
- Green leaves and storage organs
- Root and stem
- Xylem and phloem
- Hormones and enzyme
Answer: 1. Green leaves and storage organs
Question 61. Which of the following is a biofertilizer?
- Funaria
- Fern
- Anabaena
- Fungus
Answer: 3. Anabaena
Question 62. Mo is related with
- N2 fixation
- Flower induction
- Chromosome contraction
- Carbon collection
Answer: 1. N2 fixation
Question 63. Which one of the following elements is present in chlorophylls?
- Manganese
- Magnesium
- Copper
- Iron
Answer: 2. Magnesium
Question 64. Which one of the following bacteria has the potential for nitrogen fixation?
- Nitrosomonas
- Nitrobacter
- Nitrosococcus
- Rhizobium
Answer: 4. Rhizobium
Question 65. For nitrogen fixation, the pigment useful is
- Nitrogenase
- Hemoglobin
- Myoglobin
- Leghemoglobin
Answer: 4. Leghemoglobin
Question 66. Which of the following is a symbiotic bacteria?
- Rhizobium
- Azotobacter
- Clostridium
- Streptomyces
Answer: 1. Rhizobium
Question 67. The metal ion involved in stomatal regulation is
- Fe
- Mg
- Zn
- K
Answer: 4. K
Question 68. Legume plants are important for crop production because they
- Help in NO2 fixation
- Do not help in NO2 fixation
- Increase soil fertility
- All of these
Answer: 3. Increase soil fertility
Question 69. Which of the following is a nitrogen-fixing organism?
- Some BGA
- Rhizobium
- Both (1) and (2)
- Aspergillus
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 70. Which of the following bacteria is involved in the two-step conversion of NH3 into nitrate?
- Azotobacter and Nitrosomonas
- Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter
- Azotobacter and Achromobacter
- Pseudomonas and Nitrobacter
Answer: 2. Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter
Question 71. A metal ion involved in stomatal regulation is
- Iron
- Potassium
- Zinc
- Magnesium
Answer: 2. Potassium
Question 72. The plant ash is an indication of
- Organic matter of plant
- Waste product
- Mineral salts absorbed by plants
- None of these
Answer: 3. Mineral salts absorbed by plants
Question 73. Plant ash has a maximum content of
- Mg
- Fe
- K
- B
Answer: 1. Mg
Question 74. Which of the following is a part of cytochrome?
- Mg
- Zn
- Fe
- Ca
Answer: 3. Fe
Question 75. Food in plants is translocated in the form of
- Glucose
- Starch
- Sucrose
- Fructose
Answer: 3. Sucrose
Question 76. Which of the following is not related to N2 fixation?
- Rhizobium
- Anabaena
- Pseudomonas
- Azotobacter
Answer: 3. Pseudomonas
Question 77. Which of the following is not caused by a deficiency of minerals?
- Chlorosis
- Etiolation
- Shortening of internodes
- Necrosis
Answer: 2. Etiolation
Question 78. The mineral present in cell walls is
- Na
- Ca
- K
- Mg
Answer: 2. Ca
Question 79. What happens when we inoculate Rhizobium in wheat fields?
- No increase in production (nitrogen content of soil remains same)
- A lot of increase in production (nitrogen content of soil increase)
- Fertility of soil decreases
- Fertility of soil increases
Answer: 1. No increase in production (nitrogen content of soil remains same)
Question 80. Nitrifying bacteria are able to
- Convert atmospheric nitrogen into soluble form
- Convert ammonia to nitrate
- Ammonia to nitrogen
- Nitrate to nitrogen
Answer: 2. Convert ammonia to nitrate
Question 81. Magnesium is found in
- Chlorophyll
- Carotenoid
- Phycobilin
- Cytochrome
Answer: 1. Chlorophyll
Question 82. Which of the following is a trace element?
- S
- Mg
- Cu
- P
Answer: 3. Cu
Question 83. Which one of the following organisms may respire in the absence of oxygen?
- Azotobacter
- Clostridium
- Rhizobium
- Lactobacillus
Answer: 2. Clostridium
Question 84. Which of the following is not a trace element?
- Zn
- Mn
- Mg
- Cu
Answer: 3. Mg
Question 85. Symbiotic microorganism is
- Clostridium
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium
- Chromatium
Answer: 3. Rhizobium
Question 86. Essential mineral nutrients are the elements
- In the absence of this plants cannot complete their life cycle
- Which cannot be replaced by another element in its function
- Which are directly associated with the plant metabolism
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 87. Stomatal movement is controlled by
- Na
- Mg
- K
- P
Answer: 3. K
Question 88. Which of the following enzymes fixes nitrogen?
- Nitrate reductase
- Nitrogenase
- PEP carboxylase
- RuBisCo
Answer: 2. Nitrogenase
Question 89. The bacterium capable of anaerobic nitrogen fixation is
- Azatobacter
- Rhizobium
- Bacillus
- Clostridium
Answer: 4. Clostridium
Question 90. In plant metabolism, phosphorus plays a major role to
- Evolve oxygen during photosynthesis
- Create aerobic condition
- Generate metabolic energy
- Evolve carbon dioxide during respiration
Answer: 3. Generate metabolic energy
Question 91. Photosynthetic food material is transported in the form of
- Glucose
- Sucrose
- Starch
- Fructose
Answer: 2. Sucrose
Question 92. Chlorosis is caused due to the deficiency of
- Mg
- Ca
- B
- Mn
Answer: 1. Mg
Question 93. The major portion of the dry weight of plants comprises
- Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
- Calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
- Carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen
- Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Answer: 4. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Question 94. Which one of the following mineral elements plays an important role in biological nitrogen fixation?
- Copper
- Manganese
- Zinc
- Molybdenum
Answer: 4. Molybdenum
Question 95. Stomata of CAM plants
- Are always open
- Open during the day and close at night
- Open at night and close during the day
- Never open
Answer: 3. Open at night and close during the day
Question 96. Stomata of a plant open due to
- The influx of potassium ions
- Efflux of potassium ions
- Influx of hydrogen ions
- The influx of calcium ions
Answer: 1. Influx of potassium ions
Question 97. Plants deficient of the element zinc show its effect on the biosynthesis of plant growth hormone
- Auxin
- Cytokinin
- Ethylene
- Abscisic acid
Answer: 1. Auxin
Question 98. In which one of the following is nitrogen not a constituent?
- Idioblast
- Bacteriochlorophyll
- Invertase
- Pepsin
Answer: 1. Idioblast
Question 99. Gray spots of oats are caused by the deficiency of
- Cu
- Zn
- Mn
- Fe
Answer: 3. Mn
Question 100. The most abundant element present in the plants is
- Iron
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Manganese
Answer: 2. Carbon
Question 101. The ability of Venus flytrap to capture insects is due to
- Chemical stimulation by the prey
- A passive process requiring no special ability on the part of the plant
- Specialized muscle-like cells
- Rapid turgor pressure changes
Answer: 4. Rapid turgor pressure changes
Question 102. The deficiencies of micronutrients not only affect the growth of plants but also vital functions such as photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron flow. Among the list given below, which group of three elements shall affect both photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron transport the most?
- Cu, Mn, Fe
- Co, Ni, Mo
- Mn, Co, Ca
- Ca, K, Na
Answer: 1. Cu, Mn, Fe
Question 103. Potometer works on the principle of
- The amount of water absorbed equals the amount that transpired
- Osmotic pressure
- Root pressure
- The potential difference between the tip of the tube and that of the plant
Answer: 1. Amount of water absorbed equals the amount that transpired
Question 104. Farmers in a particular region were concerned that the premature yellowing of leaves of a pulse crop might cause a decrease in the yield. Which treatment could be the most beneficial to obtain maximum seed yield?
- Removal of all yellow leaves and spraying the remaining green leaves with 2,4,5-trichloro phenoxy acetic acid
- Application of iron and magnesium to promote the synthesis of chlorophyll
- Frequent irrigation of the crop
- Treatment of plants with cytokinins along with a small dose of nitrogenous fertilizer
Answer: 2. Application of iron and magnesium to promote the synthesis of chlorophyll
Question 105. Sulfur is an important nutrient for optimum growth and productivity in
- Fiber crops
- Oil seed crops
- Pulse crops
- Cereals
Answer: 2. Oil seed crops
Question 106. A plant requires magnesium for
- Cell wall development
- Holding cells together
- Protein synthesis
- Chlorophyll synthesis
Answer: 4. Chlorophyll synthesis
Question 107. Which of the following is a flowering plant with nodules containing filamentous nitrogen-fixing microorganisms?
- Cicer arietinum
- Casuarina equisetifolia
- Crotalaria juncaea
- Cycas revolute
Answer: 2. Casuarina equisetifolia
Question 108. About 98% of the mass of every living organism is composed of just six elements including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen.
- Calcium and phosphorus
- Phosphorus and sulfur
- Sulfur and magnesium
- Magnesium and sodium
Answer: 2. Phosphorus and sulfur
Question 109. Which one of the following elements is not an essential micronutrient for plant growth?
- Ca
- Mn
- Zn
- Cu
Answer: 1. Ca
Question 110. Carbohydrates are commonly found as starch in plant storage organs. Which of the following five properties of starch (1-5) make it useful as a storage material?
- Easily translocated
- Chemically non-reactive
- Easily digested by animals
- Osmotically inactive
- Synthesized during photosynthesis
- (1), (3), and (5)
- (1) and (5)
- (2) and (3)
- (2) and (4)
Answer: 4. (2) and (4)
Question 111. Nitrogen fixation in the root nodules of Anlus is brought about by
- Frankia
- Azorhizobium
- Bradyrhizobium
- Clostridium
Answer: 1. Frankia
Question 112. Guard cells help in
- Fighting against infection
- Protection against grazing
- Transpiration
- Guttation
Answer: 3. Transpiration
Question 113. Manganese is required in
- Chlorophyll synthesis
- Nucleic acid synthesis
- Plant cell wall formation
- Photolysis of water during photosynthesis
Answer: 4. Photolysis of water during photosynthesis
Question 114. An element playing an important role in nitrogen fixation is
- Manganese
- Zinc
- Molybdenum
- Copper
Answer: 3. Molybdenum
Question 115. Which one of the following is not a micronutrient?
- Zinc
- Boron
- Molybdenum
- Magnesium
Answer: 4. Magnesium
Question 116. The chief water-conducting elements of xylem in gymnosperms are
- Transfusion tissue
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Fibers
Answer: 2. Tracheids
Question 117. Which one of the following structures between two adjacent cells is an effective transport pathway?
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Plasmalemma
- Plasmodesmata
- Plastoquinones
Answer: 3. Plasmodesmata
Question 118. One of the free-living, anaerobic nitrogen fixers is
- Rhizobium
- Azotobacter
- Beijerinckia
- Rhodospirilium
Answer: 4. Rhodospirilium
Question 119. The common nitrogen fixer in paddy fields is
- Oscillatoria
- Frankia
- Rhizobium
- Azospirillum
Answer: 4. Azospirillum
Question 120. The transport of food material in higher plants takes place through
- Transfusion tissue
- Tracheids
- Sieve elements
- Companion cells
Answer: 3. Sieve elements
Question 121. Study the cycle and select the option that gives the correct words for all four blanks A, B, C, and D.
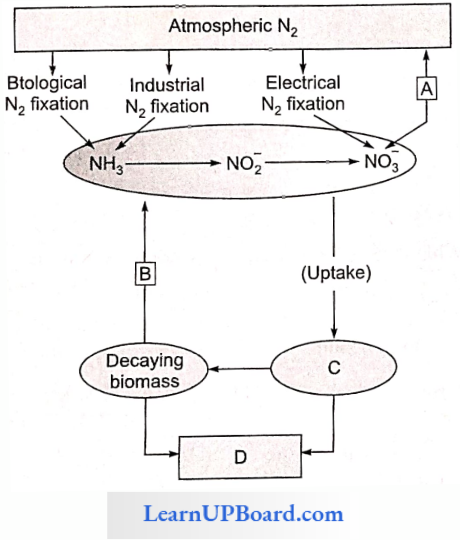
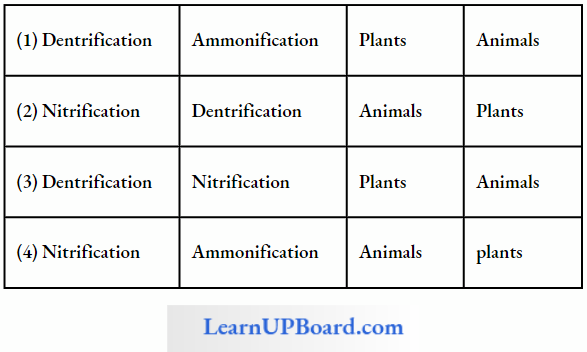
Answer: 1
Question 122. Leguminous plants are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen through the process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Which one of the following statements is not correct during this process of nitrogen fixation?
- Nodules act as sites for nitrogen fixation.
- The enzyme nitrogenase catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NH3.
- Nitrogenase is insensitive to oxygen.
- Leghemoglobin scavenges oxygen and is pinkish in color.
Answer: 3. Nitrogenase is insensitive to oxygen.
Question 123. Which one of the following is correctly matched?
- Apoplast—Plasmodesmata
- Potassium—Readily immobilization
- Balance of rice seedlings—F. Skoog
- Passive transport of nutrients—ATP
Answer: 2. Potassium—Readily immobilization
Question 124. Which one of the following is a wrong statement?
- Root nodule-forming nitrogen fixers live as aerobes under free-living conditions.
- Phosphorus is a constituent of cell membranes, certain nucleic acids, and all proteins.
- Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter are chemoautotrophs.
- Anabaena and Nostoc are capable of fixing nitrogen in a free-living state also.
Answer: 2. Phosphorus is a constituent of cell membranes, certain nucleic acids, and all proteins.
Question 125. The nitrogen-fixing microbe associated with Azolla in rice fields is
- Anabaena
- Frankia
- Tolypothrix
- Spimlina
Answer: 1. Anabaena
Question 126. Best defined function of Manganese in green plants is
- Calvin cycle
- Nitrogen fixation
- Water absorption
- Photolysis of water
Answer: 4. Photolysis of water
Question 127. For its activity, carboxypeptidase requires
- Zinc
- Iron
- Niacin
- Copper
Answer: 1. Zinc
Question 128. For its action, nitrogenase requires
- High input of energy
- Light
- Mn2+
- Super oxygen radicals
Answer: 1. High input of energy
NEET Biology Notes For Mineral Nutrition Assertion Reasoning Question And Answers
In the following questions, an Assertion (A) is followed by a corresponding Reason (R). Mark the correct answer.
- If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- If both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- If Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
- If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question 1. Assertion: Some mineral nutrients are essential.
Reasoning: They can be synthesized by the plants.
Answer: 2. If both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Question 2. Assertion: Ca++ cannot replace H+ adsorbed on clay or humus particles.
Reasoning: The retentive capacity of Ca+2 is more than that of H+.
Answer: 2. If both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Question 3. Assertion: Chelating agents used in improving the availability of some minerals in soil are actually electron acceptors.
Reasoning: They increase the solubility of some minerals in acidic soils.
Answer: 2. If both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Question 4. Assertion: N, P, and K are called critical elements.
Reasoning: They become deficient easily in soil due to leaching and higher requirements.
Answer: 4. If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question 5. Assertion: When cation uptake exceeds anion uptake, certain changes occur in the ionic composition of the cell.
Reasoning: H2O and organic acids produced within cell dissociate and H+ moves outside the cell.
Answer: 1. If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
