Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Amongst the following, the total number of species not having eight electrons around the central atom in its outermost shell, is NH3, AlCl3, BeCl2, CCl4, PCl5
- 4
- 1
- 3
- 2
Answer: 3. 3
AICl3, BeCl2, and PCl5 do not have eight electrons around the central atom in their outermost shells.

Question 2. In \(\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}\) ion, the formal charge on each oxygen atom and P—O bond order respectively are
- -0.75, 1.25
- -0.75, 1.0
- -0.75,0.6
- -3, 1.25
Answer: 1. -0.75, 1.25
The total charge = -3
So, the average formal charge on each ‘O’ atom is -3/4= -0.75
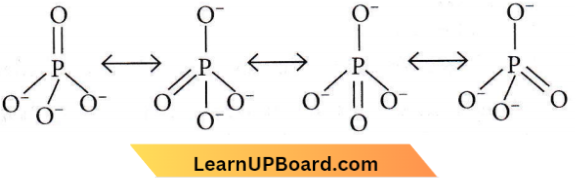
⇒ Average P-O bond order = \(\frac{\text { Total no. of bonds }}{\text { Total no. of resonating structures }}=\frac{5}{4}=1.25\)
Question 3. Among LiCl, BeCl2, BCl3 and CCl4, the covalent bond character follows the order
- \(\mathrm{BeCl}_2>\mathrm{BCl}_3>\mathrm{CCl}_4<\mathrm{LiCl}\)
- \(\mathrm{BeCl}_2<\mathrm{BCl}_3<\mathrm{CCl}_4<\mathrm{LiCl}\)
- \(\mathrm{LiCl}<\mathrm{BeCl}_2<\mathrm{BCl}_3<\mathrm{CCl}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{LiCl}>\mathrm{BeCl}_2>\mathrm{BCl}_3>\mathrm{CCl}_4\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{LiCl}<\mathrm{BeCl}_2<\mathrm{BCl}_3<\mathrm{CCl}_4\)
Along the period, as we move from Li>Be>B>C, the electronegativity increases, and hence the EN difference between the element and Cl decreases and accordingly, the covalent character increases. Thus LiCI < BeCl2 < BCl3 < CCl4 is the correct order of covalent bond character.
Read and Learn More NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 4. Which one of the following formulae does not correctly represent the bonding capacities of the two atoms involved?
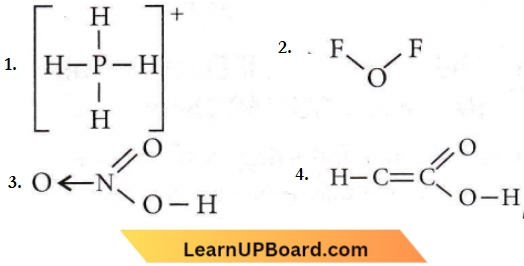
Answer: 4

The asterisk (*) marked carbon has a valency of 5 and hence, this formula is not correct because carbon has a maximum valency of 4.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NEET MCQs
Question 5. Which compound will show the highest lattice energy among the following?
- KF
- NaF
- CsF
- RbF
Answer: 2. NaF
For compounds containing ions of the same charge, lattice energy increases as the size of ions decreases. Thus, NaF has the highest lattice energy
Question 6. Which of the following molecules is non-polar in nature?
- NO2
- POCl3
- CH2O
- SbCl5
Answer: 4. SbCl5
Among the given molecules, SbCl5 is non-polar in nature
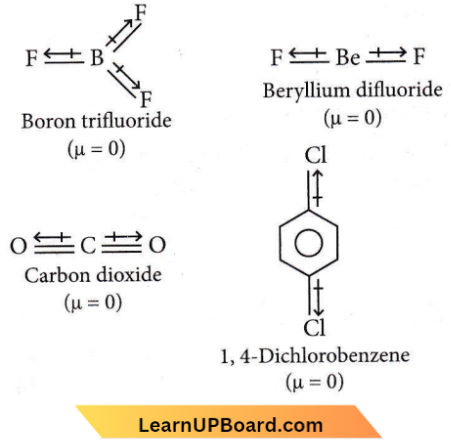
Question 7. Which of the following, set of molecules will have zero dipole moment?
- Ammonia, beryllium difluoride, water, 1, 4-dichlorobenzene
- Boron trifluoride, hydrogen fluoride, carbon dioxide, 1, 3-dichlorobenzene
- Nitrogen trifluoride, beryllium difluoride, water, 1,3-dichlorobenzene
- Boron trifluoride, beryllium difluoride, carbon dioxide, 1, 4-dichlorobenzene
Answer: 4. Boron trifluoride, beryllium difluoride, carbon dioxide, 1, 4-dichlorobenzene
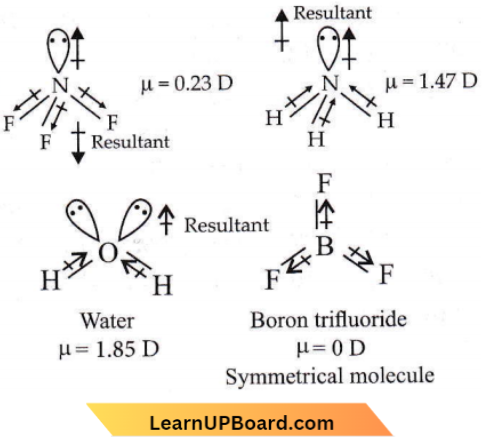
Question 8. Which of the following is the correct order of dipole moment?
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3<\mathrm{BF}_3<\mathrm{NF}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3<\mathrm{NF}_3<\mathrm{NH}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3<\mathrm{NH}_3<\mathrm{NF}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}<\mathrm{NF}_3<\mathrm{NH}_3<\mathrm{BF}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{BF}_3<\mathrm{NF}_3<\mathrm{NH}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NEET MCQs
Question 9. The species, having bond angles of 120° is
- \(\mathrm{ClF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{BCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{PH}_3\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{BCl}_3\)
BCl3-Trigonal planar sp²-hybridised, 120° angle.
Question 10. Consider the molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O. Which of the given statements is false?
- The H — O — H bond angle in H2O is smaller than the H — N — H bond angle in NH3.
- The H — C — H bond angle in CH4 is larger than the H — N — H bond angle in NH3.
- The H — C — H bond angle in CH4, the H — N — H bond angle in NH3, and the H — O — H bond angle in H2O are all greater than 90°.
- The H — O — H bond angle in H2O is larger than the H — C — H bond angle in CH4.
Answer: 4. The H — O — H bond angle in H2O is larger than the H — C — H bond angle in CH4.
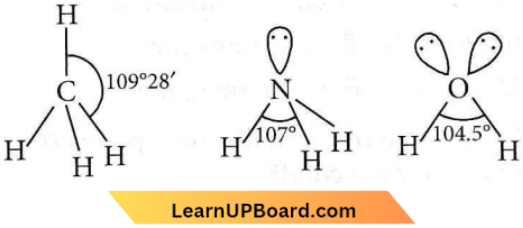
Question 11. Which of the following molecules has the maximum dipole moment?
- CO2
- CH4
- NH3
- NF3
Answer: 3. NH3
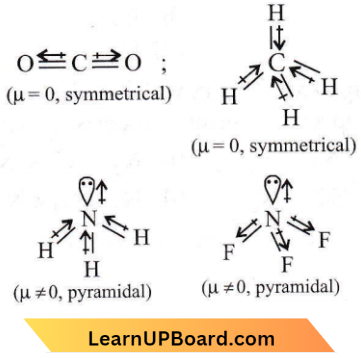
In NH3, H is less electronegative than N and hence dipole moment of each N-H bond is towards N and creates a high net dipole moment whereas in NF3, F is more electronegative than N, the dipole moment of each N-F bond is opposite to that of lone pair, hence reducing the net dipole moment.
NEET questions on Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Question 12. The correct order of increasing bond length of C – H, C – O, C – C and C = C is
- C-H<C=C<C-O<C-C
- C-C<C=C<C-O<C-H
- C-O<C-H<C-C<C = C
- C-H<C-O<C-C<C = C
Answer: 1. C-H<C=C<C-O<C-C
Increasing order of bond length is C-H<C-C<C-O<C-C
Question 13. Which of the following structures is the most preferred and hence of the lowest energy for SO3?
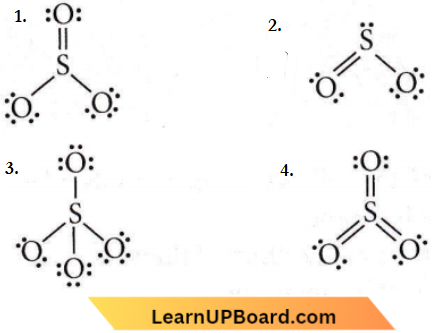
Answer: 4
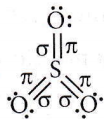
It has a maximum number of covalent bonds involving pπ – dπ bonding also.
Question 14. The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following triatomic species is
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}<\mathrm{NO}_2<\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}<\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}<\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}_2<\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}_2<\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
Structures of \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}, \mathrm{NO}_2\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\) is given as
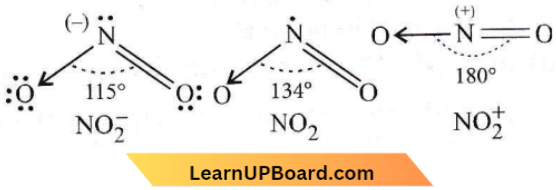
The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following triatomic species is \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}_2<\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
Question 15. The correct order of C – O bond length among CO, CO2-3, CO2 is
- \(\mathrm{CO}<\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{CO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{CO}_2<\mathrm{CO}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}<\mathrm{CO}_2<\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2<\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}<\mathrm{CO}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CO}<\mathrm{CO}_2<\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\)
The more single bond character in resonance hybrid more is the bond length. Hence, the increasing bond length is \(\mathrm{CO}<\mathrm{CO}_2<\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\)
Question 16. The electronegativity difference between N and F is greater than that between N and H yet the dipole moment of NH3 (1.5 D) is larger than that of NF3 (0.2 D). This is because
- In NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the opposite directions whereas in NF3 these are in the same direction
- In NH3 as well as in NF3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction
- In NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction whereas in NF3 these are in opposite directions
- In NH3 as well as in NF3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions.
Answer: 3. In NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction whereas in NF3 these are in opposite directions
The electronegativity difference between N and F is greater than that between N and H yet the dipole moment of NH3 (1.5 D) is larger than that of NF3 (0.2 D).
The dipole moment of NF3 is 0.24 D, and of NH3 is 1.48 D. The difference is due to the fact that the dipole moment due to N – F bonds in NF3 are in opposite directions to the direction of the dipole moment of the lone pair on N atom which partly cancels out.
The dipole moment of N – H bonds in NH3 are in the same direction as the dipole moment of the lone pair on the N atom which adds up as shown
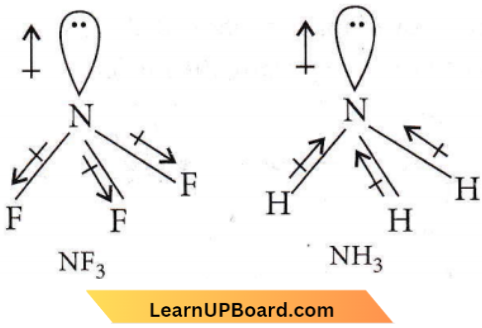
NEET questions on Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Question 17. The correct order in which the O-O bond length increases in the following is
- \(\mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{O}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{O}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{O}_2<\mathrm{O}_3<\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Bond lengths of \(\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{O}\) in \(\mathrm{O}_2\) is 1.21Å, in \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\) is 1.48 Å and in \(\mathrm{O}_3\) is 1.28 Å. Therefore, correct order of the \(\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{O}\) bond length is \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2>\mathrm{O}_3>\mathrm{O}_2\).
Question 18. The correct sequence of increasing covalent character is represented by
- LiCl < NaCl < BeCl2
- BeCl2 < LiCl < NaCl
- NaCl < LiCl < BeCl2
- BeCl2 < NaCl < LiCl
Answer: 3. NaCl < LiCl < BeCl2
The covalent character in a compound is found by Fajan’s rule.
Fajan’s Rule: The smaller the size of the cation and the larger the size of the anion, the greater is the covalent character of an ionic bond. The greater the charge on the cation, the greater is the covalent character of the ionic bond.
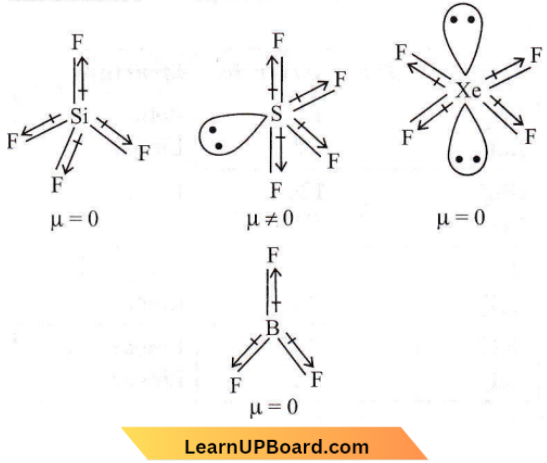
Question 19. Which of the following would have a permanent dipole moment?
- SiF4
- SF4
- XeF4
- BF3
Answer: 2. SF4
For dipole moment, we have to know the hybridization and shape.
Chemical Bonding multiple choice NEET
Question 20. H2O is dipolar, whereas BeF2 is not. It is because
- The electronegativity of F is greater than that of O
- H2O involves hydrogen bonding whereas BeF2 is a discrete molecule
- H2O is linear and BeF2 is angular
- H2O is angular and BeF2 is linear.
Answer: 4. H2O is angular and BeF2 is linear.
The overall value of the dipole moment of a polar molecule depends on its geometry and shape, i.e., vectorial addition of the dipole moment of the constituent bonds. Water has an angular structure with a bond angle of 105°, it has a dipole moment. However, BeF2 is a linear molecule thus, dipole moment summation of all the bonds present in the molecule cancels each other.
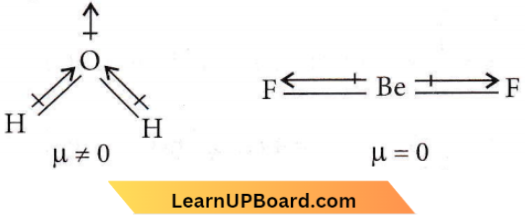
Question 21. Which of the following molecules does not possess a permanent dipole moment?
- \(\mathrm{CS}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_2\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CS}_2\)
The structure of CS2 is linear and therefore it does not have a permanent dipole moment. It is represented as S = C = S.
Question 22. The table shown below gives the bond dissociation energies (Ediss) for single covalent bonds of carbon (C) atoms with elements A, B, C, and D. Which element has the smallest atoms?
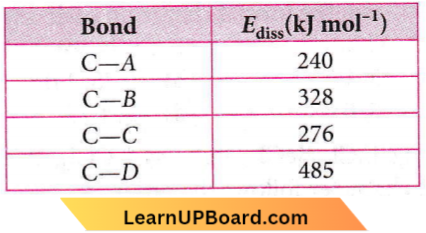
- C
- D
- A
- B
Answer: 2. D
The smaller the atom, the stronger the bond, and the greater the bond dissociation energy. Therefore, the bond C-D has the greatest energy or D has the smallest atoms.
Chemical Bonding multiple choice NEET
Question 23. The strongest bond is in between
- CsF
- NaCl
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. CsF
According to the Fajans rule, ionic character increases with an increase in the size of the cation, (Cs > Rb > K > Na) and with a decrease in the size of the anion (F > CI > Br > I). Thus, CsF has a higher ionic character than NaCl and hence, the bond in CsF is stronger than in NaCl.
Question 24. Which of the following bonds will be most polar?
- N – Cl
- O – F
- N – F
- N – N
Answer: 3. N – F
The polarity of the bond depends upon the electronegativity difference of the two atoms forming the bond. The greater the electronegativity difference, the more is the polarity of the bond.
⇒ \(\begin{array}{cccc}
\mathrm{N}-\mathrm{Cl} & \mathrm{O}-\mathrm{F} & \mathrm{N}-\mathrm{F} & \mathrm{N}-\mathrm{N} \\
3.04-3.16 & 3.5-4.0 & 3.04-4.0 & 3.04-3.04
\end{array}\)
NEET practice questions Chemical Bonding
Question 25. Amongst the following which one will have the maximum lone pair lone pair electron
- \(\mathrm{ClF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{IF}_5\)
- \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{XeF}_2\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{XeF}_2\)
ClF3, IF3, SF4, and Xe2, contain 2, 1, 1, and 3 lone pairs of electrons on the central atom respectively. Hence, XeF2 has maximum lone pair – lone pair repulsions.
Question 26. Match List-A with List-B
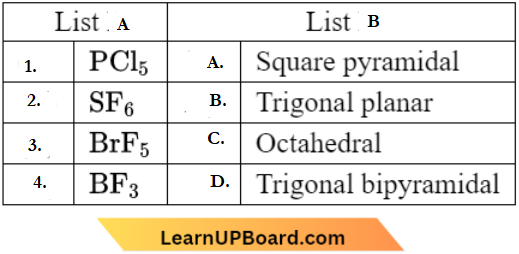
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
- (1) – (D), (2) – (C), (3) – (B), (4) – (A)
- (1) – (D), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (B)
- (1) – (B), (2) – (C), (3) – (D), (4) – (A)
- (1) – (C), (2) – (A), (3) – (A), (4) – (B)
Answer: 2. (1) – (D), (2) – (C), (3) – (A), (4) – (B)
PCl5: Trigonal bipyramidal
SF6: Octahedral
BrF5: Square pyramidal
BF3: Trigonal planar
Question 27. In the structure of ClF3, the number of lone pairs of electrons on the central atom ‘Cl’ is
- One
- Two
- Four
- Three
Answer: 2. Two
The structure of CIF3 is

Hence, Cl has 2 lone pairs of electrons
NEET practice questions Chemical Bonding
Question 28. Predict the correct order among the following:
- Bond pair – bond pair > lone pair-bond pair > lone pair – lone pair
- Lone pair – bond pair > bond pair-bond pair > lone pair – lone pair
- Lone pair – lone pair > lone pair-bond pair > bond pair-bond pair
- Lone pair – lone pair > bond pair-bond pair > lone pair-bond pair
Answer: 3. Lone pair – lone pair > lone pair-bond pair > bond pair-bond pair
According to VSEPR theory, the repulsive forces between lone pair and lone pair are greater than between lone pair and bond pair which are further greater than bond pair and bond pair.
Question 29. Which of the following species contains three bond pairs and one lone pair around the central atom?
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{PCl}_3\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{PCl}_3\)
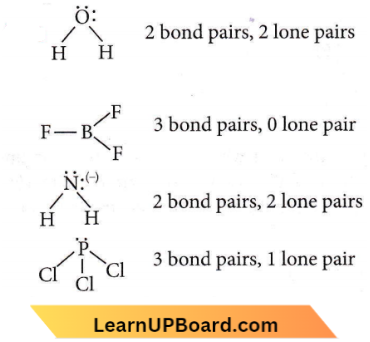
NEET practice questions Chemical Bonding
Question 30. Which of the following is not a correct statement?
- Multiple bonds are always shorter than corresponding single bonds.
- The electron-deficient molecules can act as Lewis acids.
- The canonical structures have no real existence.
- Every AB5 molecule has have square pyramid structure.
Answer: 4. Every AB5 molecule does in fact have a square pyramid structure
For AB5 molecules, there are three possible geometries i.e. plantar pentagonal, square pyramidal, and trigonal bipyramidal.
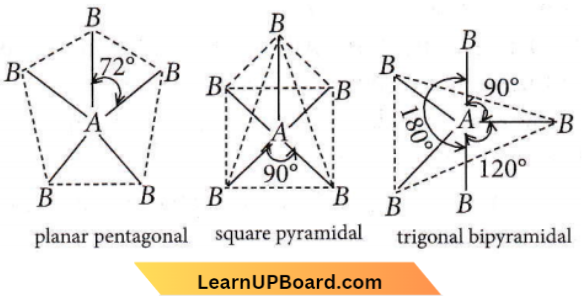
Out of these three geometries, it is only a trigonal bipyramidal shape in which bond pair-bond pair repulsions are minimal and hence, this geometry is the most probable geometry of AB5 molecule.
Question 31. Which of the following is not isostructural with SiCl4?
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{SCl}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{SCl}_4\)
∴ \(\mathrm{SiCl}_4, \mathrm{NH}_4^{+}, \mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\) and \(\mathrm{PO}_4^{3-}\) ions are the examples of molecules/ions which are of AB, type and have tetrahedral structures. SCl4 is AB4 (lone pair) type species.
Although the arrangement of five sp³d hybrid orbitals in space is trigonal bipyramidal, due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons in the basal hybrid orbital, the shape of AB5 (lone pair) species gets distorted and trichomes distorted tetrahedral or see-saw.
Chemistry MCQs Chemical Bonding NEET
Question 32. In which of the following molecules all the bonds are not equal?
- \(\mathrm{NF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{ClF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{AlF}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{ClF}_3\)
The Cl – F (Cl – Feq) bond length is equal to 1.60 Å while each of the two axial CI – F (Cl – Fa) bond lengths is equal to 1.70 Å.
Question 33. Which of the following molecules has trigonal planar geometry?
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{PCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{IF}_3\)
Answer: 1
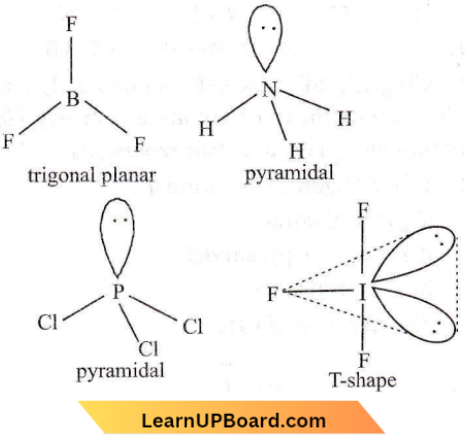
Question 34. In a regular octahedral molecule, MX6 the number of X- M -A bonds at 180° is
- Three
- Two
- Six
- Four.
Answer: 1. Three
In an octahedral molecule, six hybrid orbitals direct towards the corners of a regular octahedron with a bond angle of 90°.
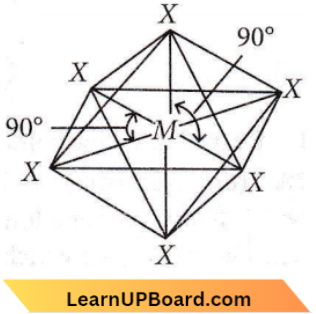
According to this geometry., the X number of X – M – X bonds at 180° must be three
Question 35. In BrF3 molecule, the lone pairs occupy equatorial positions to minimize
- Lone pair – bond pair repulsion only
- Bond pair – bond pair repulsion only
- Lone pair-lone pair repulsion and lone pair-bond pair repulsion
- Lone pair – lone pair repulsion only
Answer: 4. Lone pair – lone pair repulsion only
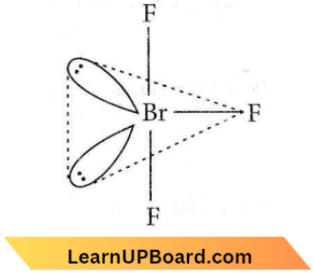
Bent T-shaped geometry in which both lone pairs occupy the equatorial positions of the trigonal bipyramid. Here (lp – lp) repulsion = 0, (lp – bp) repulsion = 4, and (bp – bp) repulsion = 2.
Chemistry MCQs Chemical Bonding NEET
Question 36. In \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\) ion, the number of bond pair and lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom are
- 2,2
- 3, 1
- 1,3
- 4,0
Answer: 4. 4,0
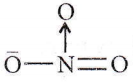
In NO3– ion, nitrogen has 4 bond pairs of electrons and no lone pair of electrons.
Question 37. In which of the following bond angles is maximum?
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{PCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SCl}_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
The bond angle is maximum in NH4+ tetrahedral molecules with a bond angle of 109º.
Question 38. BCl3 is a planar molecule whereas NCl3 is pyramidal because
- The nitrogen atom is smaller than the boron atom
- BCl3 has no lone pair but NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons
- B—Cl bond is more polar than N—Cl bond
- The N-Cl bond is more covalent than the B—Cl bond.
Answer: 2. BCl3 has no lone pair but NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons
There is no lone pair on boron in BCl3. hence, no repulsion takes place. There is a lone pair of nitrogen in NCl3, hence, repulsion takes place. Therefore, BCl3 is a planar molecule but NCl3 is a pyramidal molecule.
Question 39. In compound X, all the bond angles are exactly 109°28′, and X is
- Chloromethane
- Carbon tetrachloride
- Iodoform
- Chloroform.
Answer: 2. Carbon tetrachloride
As C – Cl bonds are directed towards the corner of a regular tetrahedron
Chemical Bonding quiz for NEET
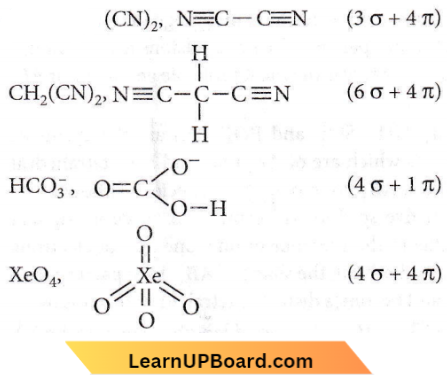
Question 40. Which of the following species contains an equal number of σ and π bonds?
- \((\mathrm{CN})_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2(\mathrm{CN})_2\)
- \(\mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{XeO}_4\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{XeO}_4\)
Question 41. Which one of the following molecules contains no π bond?
- \(\mathrm{SO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 42. Which one of the following statements is not correct for sigma- and pi- bonds formed between two carbon atoms?
- A sigma-bond is stronger than a pi-bond.
- Bond energies of sigma- and pi-bonds are of the order of 264 kJ/mol and 347 kJ/mol, respectively.
- Free rotation of atoms about a sigma bond is allowed but not in the case of a pi bond.
- Sigma-bond determines the direction between carbon atoms but a pi-bond has no primary effect in this regard.
Answer: 2. Bond energies of sigma- and pi-bonds are of the order of 264 kJ/mol and 347 kJ/mol, respectively.
Sigma bond dissociation energy. = 347 kJ/mol
Pi-bond dissociation energy = 264kJ/mol
NEET MCQs on Molecular Structure
Question 43. The main axis of a diatomic molecule is z, molecular orbital px, and py overlap to form which of the following orbitals?
- π molecular orbital
- σ molecular orbital
- δ molecular orbital
- No bond will form
Answer: 1. π molecular orbital
For π overlap, the lobes of the atomic orbitals are perpendicular to the line joining the nuclei.
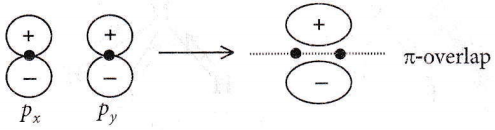
Hence, only sidewise overlapping takes place
Question 44. Which statement is not correct?
- A sigma bond is weaker than a pi bond.
- A sigma bond is stronger than a pi bond.
- A double bond is stronger than a single bond.
- A double bond is shorter than a single bond.
Answer: 1. A sigma bond is weaker than a π bond.
A σ bond is stronger than a t-bond
Question 45. Linear combination of two hybridized orbitals belonging to two atoms each having one electron leads to the formation of
- Sigma bond
- Double bond
- Co-ordinate covalent bond
- Pi bond.
Answer: 1. Sigma bond
Question 46. Which of the following does not apply to metallic bonds?
- Overlapping valence orbitals
- Mobile valence electrons
- Delocalized electrons
- Highly directed bonds
Answer: 4. Highly directed bonds
Metallic bonds have electrostatic attractions on all sides and hence, do not have directional characteristics.
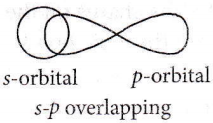
Question 47. The angle between the overlapping of one s-orbital and one p-orbital is
- 180°
- 120°
- 109°28′
- 120°, 60°
Answer: 1. 180°
The type of overlapping between s- and p-orbitals occurs along the internuclear axis and hence, the angle is 180°.
Question 48. Which of the following pairs of compounds is isoelectronic and isostructural?
- \(\mathrm{TeI}_2, \mathrm{XeF}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{IBr}_2^{-}, \mathrm{XeF}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{IF}_3, \mathrm{XeF}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{BeCl}_2, \mathrm{XeF}_2\)
Answer: None
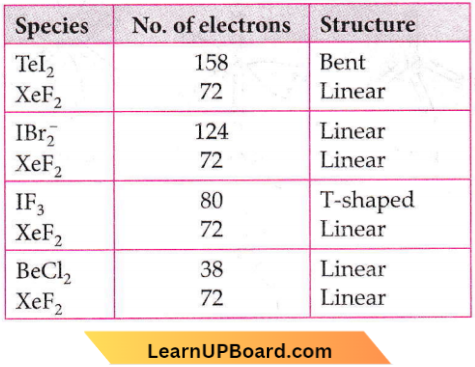
In this question, in place of isoelectronic, there should be the same number of valence electrons.
NEET MCQs on Molecular Structure
Question 49. The hybridizations of atomic orbitals of nitrogen in \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}, \mathrm{NO}_3^{-} \text {and } \mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) respectively are
- \(s p, s p^3\) and \(s p^2\)
- \(s p^2, s p^3\) and \(s p\)
- \(s p, s p^2\) and \(s p^3\)
- \(s p^2, s p\) and \(s p^3\)
Answer: 3. \(s p, s p^2\) and \(s p^3\)
X = \(\frac{1}{2}(V E+M A-c+a)\)
For \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}, X=\frac{1}{2}(5+0-1)=2\) i.e., sp hybridisation
For \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}, X=\frac{1}{2}(5+0+1)=3\) i.e., \(s p^2\) hybridisation
For \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}, X=\frac{1}{2}(5+4-1)=4\) i.e, \(s p^3\) hybridisation
Question 50. Which of the following pairs of ions is isoelectronic and isostructural?
- \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}, \mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{ClO}_3^{-}, \mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}, \mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{ClO}_3^{-}, \mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}, \mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\) and 4. \(\mathrm{ClO}_3^{-}, \mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
1. \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}: 6+24+2=32 ; s p^2\); trigonal planar \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}: 7+24+1=32 ; s p^2\); trigonal planar
Hence, these are isoelectronic as well as isostructural.
2. \(\mathrm{ClO}_3^{-}: 17+24+1=42 ; s p^3\), trigonal pyramidal \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}: 6+24+2=32 ; s p^2\), trigonal planar
Hence, these are neither isoelectronic nor isostructural.
3. \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}: 16+24+2=42 ; s p^3\), trigonal pyramidal \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}: 7+24+1=32 ; s p^2\), trigonal planar These are neither isoelectronic nor isostructural.
4. \(\mathrm{ClO}_3^{-}: 17+24+1=42; s p^3\), trigonal pyramidal \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}: 16+24+2=42; s p^3\), trigonal pyramidal Hence, these are isoelectronic as well as isostructural.
NEET MCQs on Molecular Structure
Question 51. The correct geometry and hybridization for XeF4 are
- Octahedral, sp³d²
- Trigonal bipyramidal, sp³d
- Planar triangle, sp³d³
- Square planar, sp³d2.
Answer: 1. Octahedral, sp³d²
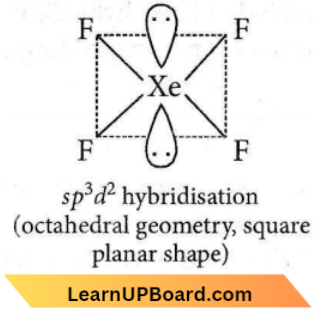
Question 52. In which of the following pairs, both the species are not isostructural?
- Diamond, Silicon carbide
- \(\mathrm{NH}_3, \mathrm{PH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{XeF}_4, \mathrm{XeO}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{SiCl}_4, \mathrm{PCl}_4^{+}\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{XeF}_4, \mathrm{XeO}_4\)
In diamond and silicon carbide, the central atom is sp³ hybridized and hence, both are isostructural.
NH3 and PH3, both are pyramidal and the central atom in both cases is sp³ hybridized. SiCl4 and PCl+4, both are tetrahedral and the central atom in both cases is sp³ hybridized.
![]()
In XeF4, Xe is sp³d² hybridized and the structure is square planar while in XeO4, Xe is sp³ hybridized and the structure is tetrahedra.
Question 53. Maximum bond angle at nitrogen is present in which of the following?
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
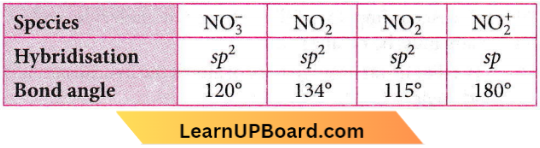
So, \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\) has maximum bond angle.
Question 54. Which one of the following species has a planar triangular shape?
- \(\mathrm{N}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
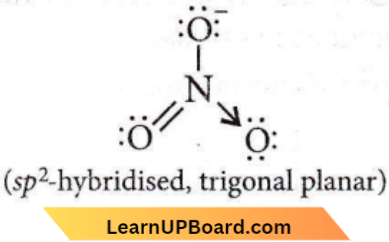
Question 55. XeF2 is isostructural with
- \(\mathrm{SbCl}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{BaCl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{TeF}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{ICl}_2^{-}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{ICl}_2^{-}\)
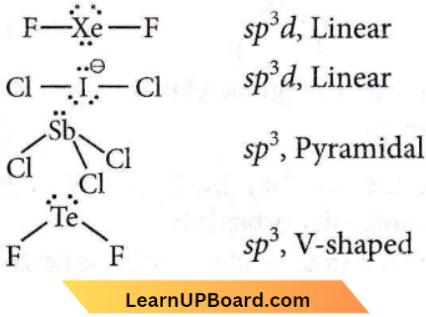
Chemical Bonding NEET question bank
Question 56. Which of the following is a polar molecule?
- \(\mathrm{SiF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{XeF}_4\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{SF}_4\)
SF4 has sp³d-hybridisation and see-saw shape with (4 bp + 1 lp)

Question 57. In which of the following pairs, the two species are isostructural?
- \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\) and \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{BF}_3\) and \(\mathrm{NF}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{BrO}_3^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{XeO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{SF}_4\) and \(\mathrm{XeF}_4\)
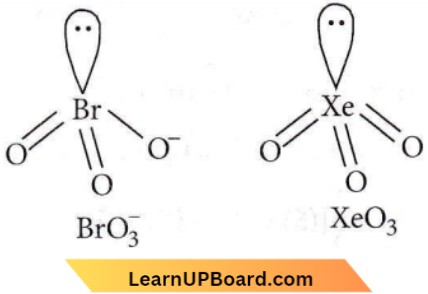
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{BrO}_3^{-}\) and \(\mathrm{XeO}_3\)
Hybridisation of Brin \(\mathrm{BrO}_3^{-}\): H = 1/2(7 + 0 – 0 + 1) = 4 i.e.sp³ hybridisation
Hybridisation of Xe in XeO3 : H = 1/2(8 +0 -0+0)= 4 i.e. sp³ hybridisation
In both BrO–3 and XeO3, the central atom is sp³ hybridized and contains one lone pair of electrons, hence in both cases, the structure is trigonal pyramidal.
Question 58. Which of the following species has a linear shape?
- \(\mathrm{O}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\)
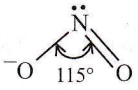
∴ \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\): Due to sp² hybridization of N-atom and the presence of one lone pair on it, \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}\) has an angular shape.
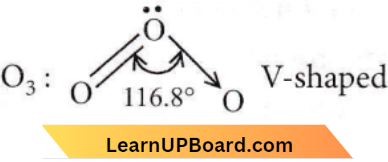
SO2: Due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons in one of the three sp²-hybrid orbitals, the SO2 molecule has an angular (V-shaped) structure.
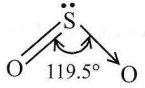
∴ \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\): Due to sp hybridisation of \(\mathrm{N}^{+}, \mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\) ion has linear shape.
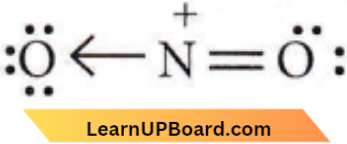
Chemical Bonding NEET question bank
Question 59. The correct order regarding the electronegativity of hybrid orbitals of carbon is
- \(s p<s p^2<s p^3\)
- \(s p>s p^2<s p^3\)
- \(s p>s p^2>s p^3\)
- \(s p<s p^2>s p^3\)
Answer: 3. \(s p>s p^2>s p^3\)
The electronegativity of carbon atom is not fixed. It varies with the state of hybridization. The electronegativity of carbon increases as the s-character of the hybrid orbital increases.
C(sp)>C(sp²)>c(sp³)
Question 60. Four diatomic species are listed below. Identify the correct order in which the bond order is increasing in them.
- \(\mathrm{NO}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{C}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{He}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}<\mathrm{C}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{He}_2^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2^{2-}<\mathrm{He}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}\)
- \(\mathrm{He}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}<\mathrm{C}_2^{2-}\)
Answer: 4. \(\mathrm{He}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}<\mathrm{C}_2^{2-}\)
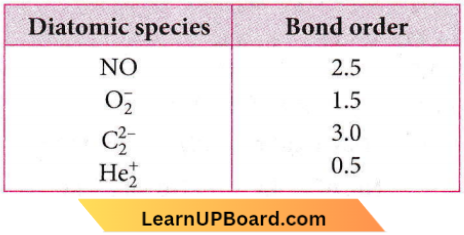
Thus, bond order increases as: \(\mathrm{He}_2^{+}<\mathrm{O}_2^{-}<\mathrm{NO}<\mathrm{C}_2^{2-}\)
Question 61. What is the dominant intermolecular force or bond that must be overcome in converting liquid CH3OH to a gas?
- Dipole-dipole interaction
- Covalent bonds
- London dispersion force
- Hydrogen bonding
Answer: 4. Hydrogen bonding
Methanol can undergo intermolecular association through H-bonding as the -OH group in alcohols is highly polarised.
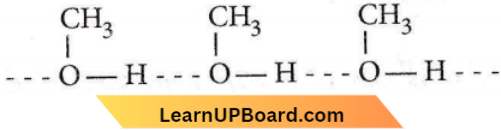
As a result, in order to convert Iiquid CH3OH to a gaseous state, the strong hydrogen bonds must be broken.
Chemical Bonding NEET question bank
Question 62. Which of the following has pπ – dπ bonding?
- \(\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}\)
- \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
- \(\mathrm{BO}_3^{3-}\)
- \(\mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{SO}_3^{2-}\)
In sulfite ion, the central atom sulfur is sp³ hybridisedElectronic structure of S atom in an excited state
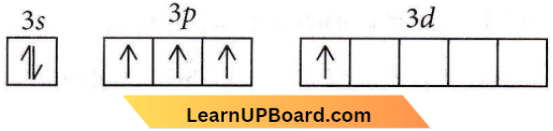
The three p electrons form o bonds with three oxygen atoms with one position (of the tetrahedron) being occupied by a lone pair. The d electron (excluded from hybridization) forms π bond with one oxygen atom. i.e. pπ – dπ bonding occurs.
