NEET Class 12 Biology Multiple Choice Questions – Environmental Issues
Question 1. Carbon monoxide is a major pollutant of
- Water
- Air
- Noise
- Soil
Answer: 2. Air
Carbon monoxide (CO) is major pollutant in air, exhausted by various automobiles.
Question 2. Air pollution is caused by excess of
- Dinitrogen
- Hydrogen
- Water vapour
- None of these
Answer: 1. Dinitrogen
Nitrogen form various oxides such as N2O, NO, NO N2O5, and N2O5 play an important role in the formation of photochemical smog and acid rains. Thus, excess of dinitrogen cause air pollution.
” environmental issues mcqs”
Question 3. Statements given below are pertaining to air pollutants.
- They cause injury to all living organisms.
- They reduce the growth and yield of crops and cause premature death of plants.
- They affect the respiratory system of humans and animals.
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1,2 and 3
- All the given statements are correct as Air pollution has several effects on all living organisms and on climate. Diseases like bronchitis, lung cancer and emphysema are caused by air pollution.
- NO2 causes bronchitis and lowers the resistance to influenza.
- SO2 obstructs breathing and irritates the eyes.
- Nitric acid, nitrous acid and sulphuric acid cause respiratory diseases. Air pollutants reduce the growth and yield of crops and cause premature death of plants.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 4. The Air Prevention and Control of Pollution Act came into force in the year …A… It was amended in …B… to incorporate …C… as an air pollutant.
- A–1980, B–1986, C–water
- A–1981, B–1987, C–noise
- A–1982, B–1988, C–radioactive
- A–1983, B–1989, C–soil
Answer: 2. A–1981, B–1987, C–noise
Question 5. Which of the following is a primary pollutant?
- CO
- HNO3
- H2SO4
- O3
Answer: 1. CO
A primary pollutant is that which persists in the form in which it is released in the environment, e.g. CO.
Question 6. Assertion Secondary air pollutants are formed by interaction among the primary pollutants and are more toxic. Reason (R) DDT is a secondary air pollutant.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false because Secondary air pollutants are produced photochemically from primary pollutants. Smog, photochemical smog, ozone and PAN all are secondary air pollutants. DDT is a primary soil pollutant.
Question 7. Which of the following is a secondary pollutant?
- CO
- O3
- SO2
- CO2
Answer: 2. O3
O3 (ozone) is a secondary pollutant. These are formed by the reaction of primary pollutants. CO is a quantitative pollutant. CO2 and SO2 are primary pollutants.
“global warming can significantly be controlled by “
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 8. One of the following acts as a secondary pollutant.
- Br2
- CI2
- NO2
- HNO2
Answer: 3. NO2
Secondary pollutants are not emitted directly in the air, water or soil, but are synthesised by chemical reactions and the best examples are oxides of nitrogen. They further form ozone, PAN and aldehydes.
Question 9. The secondary pollutant which stops Hill reaction is
- Sulphuric Acid
- Nitric Acid
- Peroxyacetyl Nitrate (Pan)
- Aldehydes
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Peroxyacetyl Nitrate (Pan)
PAN prevents the photolysis of water in photosynthesis or Hill reaction.
Question 10. Match the following columns.
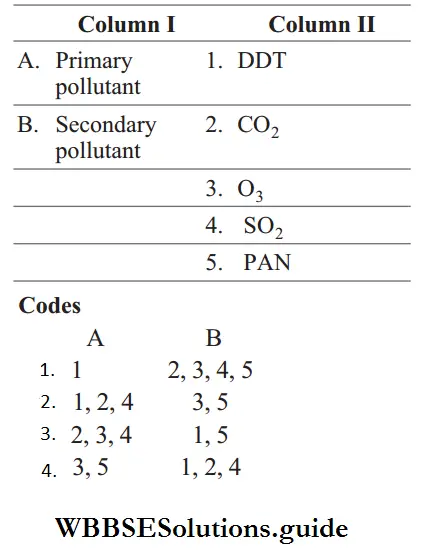
Answer:
1–1, 2, 4
2–3, 5
Question 11. Match the following columns.

Answer:
1–3, 4, 5, 6, 7
2–1, 2, 8, 9
Question 12. Consider the following statements about pollution.
- Pollution is defined as an undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, land, water or soil.
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act was amended in 1987.
- The Environment Protection Act, of 1976 was formed to bring into effect the parameters of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 1 and 2
Statements 1 and 2 are correct, but 3 is incorrect because In order to control environmental pollution, the government of India has passed the Environment Protection Act, 1986 to protect and improve the quality of our environment (air, water and soil). The air act was amended in 1987 to include noise as air pollution.
Question 13. Which of the following is a weightless pollutant?
- Sewage and exhaust emissions
- SO2 and NO2
- Photochemical smog
- Heat, sound and radioactive wastes
Answer: 4. Heat, sound and radioactive wastes
Heat, sound and radioactive wastes are weightless pollutants.
“environmental questions “
Question 14. A scrubber in the exhaust of a chemical industrial plant removes CBSE AIPMT, Karnataka CET
- Gases Like Sulphur Dioxide
- Particulate Matter Of The Size 5 Micrometer Or Above
- Gases Like Ozone And Methane
- Particular matter of the size 2.5 micrometre or less
Answer: 1. Gases Like Sulphur Dioxide
A scrubber can remove gases like sulphur dioxide. In a scrubber, the exhaust is passed through a spray of water or lime
Question 15. In the scrubber, the exhaust is passed through a
- Spray Of Water
- Spray Of Lime
- Both 1 And 2
- Spray Of Electrons
Answer: 3. Both 1 And 2
A scrubber can remove gases like sulphur dioxide. In a scrubber, the exhaust is passed through a spray of water or lime
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 16. Consider the following statements about scrubbers.
- It removes gases like sulphur dioxide from industrial exhaust.
- The exhaust passes through a spray of water or lime.
- Sulphur dioxide reacts with lime to form a precipitate of calcium sulphate and water dissolves gases.
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1,2 and 3
All the given statements are correct for the scrubber. A scrubber can remove gases like sulphur dioxide. In a wet scrubber, a fine spray of water or alkaline fluid like lime is allowed to fall over exhaust emissions. The particles also become heavy and fall down. The lime reacts with sulphur dioxide to produce a precipitate of calcium sulphate or calcium sulphide. Water is used to remove soluble gases and particles.
Question 17. The below diagram shows a scrubber. Identify A, B, C and D.
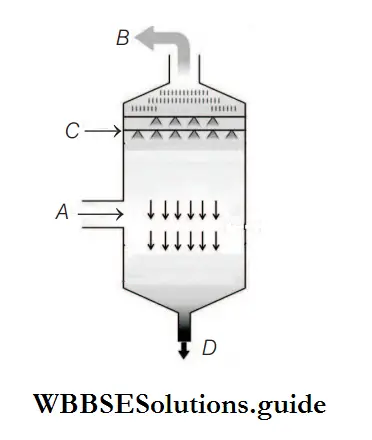
- A–Particulate matter, B–Clean air, C–Dirty air, D–A dust particle
- A–Dirty air, B–Clean air, C–Water lime spray, D–Slurry outlet
- A–Slurry outlet, B–Dirty air, C–Particulate matter, D–Clean air
- A–Dust particle, B–Clean air, C–Particulate matter, D–Water spray
Answer: 2. A– Dirty air, B–Clean air, C–Water spray, D–Slurry outlet.
Question 18. Cyclone collectors are nowadays commonly used to control
- Air Pollution With Special Reference To Dust Particles
- Radioactive Pollution
- Water Pollution In General
- Water pollution with special reference to Ganga Action Plan
Answer: 1. Air Pollution With Special Reference To Dust Particles
The cyclone collector is the device that is used for minimising air pollution by trapping the suspended particles like coarse dust generated due to activities like mining, cement and wood factories. These are dry scrubbers that work on the principle of inertia. Cyclone collector work similar to a centrifuge, but with a continuous feed of dirty air.
Thus, option 1 is correct.
Question 19. Gaseous pollutants can be controlled by
- Arrestors
- Electrostatic Precipitators
- Pyrolysis
- Incineration
Answer: 2. Electrostatic Precipitators
A gaseous pollutant can be controlled by Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP). It is an electrical device that removes particulate matter present in the exhaust of a thermal power plant. More than 99% of particulate matter can be removed by this method.
Question 20. In a coal-fired power plant, electrostatic precipitators are installed to control the emission of
- NOx
- SPM
- CO
- SO2
Answer: 2. SPM
The electrostatic precipitators are installed to control the emission of Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM) as these can cause various respiratory disorders in humans if released into the air.
Question 21. Which one of the following is the most efficient device to eliminate particulate matter from industrial emission?
- Cyclonic separators
- Trajectory separators
- Pyrolysis
- Incineration
- Electrostatic precipitator
Answer: 5. Electrostatic precipitator
An electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) is the most efficient device to eliminate submicron particulates from industrial emissions. It removes the impurities (dust, fibres) by applying a high-voltage electrostatic charge which precipitates the impurities on the charged plates.
” environmental questions and answers pdf”
Question 22. Which of the following is made use in an electrostatic precipitator?
- Catalysts
- Absorbers
- Electrodes
- Chemicals
Answer: 3. Electrodes
An electrostatic precipitator is used to remove particulate matter present in the exhaust of a thermal power plant. It has electrode wires that are maintained at several thousand volts which produce a corona that releases electrons.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 23. In an electrostatic precipitator, very high voltage of electricity is passed through electrodes that produce a corona, which emits …A… . The dust particles present inside the precipitator gains a …B… charge instantly.
- A–electron, B–positive
- A–neutron, B–negative
- A–electron, B–negative
- A–proton, B–positive
Answer: 3. A–electron, B–negative
In an electrostatic precipitator, electrode wires are provided with an electric current of several thousand volts, which produces a corona that releases electrons (A). These electrons attach to dust particles and gives them a negative charge within a very small fraction of a second.
Question 24. Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
- Removes particulate matter from the exhausts of thermal power
plants. - It has a removal efficiency of 99%.
- ESP has thin wires and stack of thick metal plates.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
All the given statements are correct.
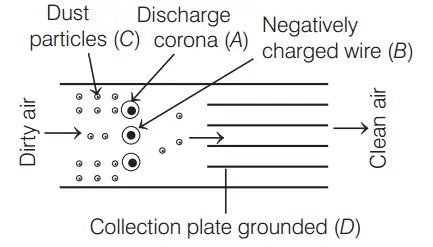
Question 25. The below diagram shows an electrostatic precipitator. Identify A, B, C and D and select the correct option.
- A–Dust particles, B–Negatively charged wire, C–Discharge corona, D–Collection plate grounded
- A–Discharge corona, B–Collection plate grounded, C–Dust particles, D–Negatively charged wire
- A–Discharge corona, B–Negatively charged wire, C–Dust particles, D–Collection plate grounded
- A–Discharge corona, B–Dust particles, C–Negatively charged wire, D–Collection plate grounded
Answer: 3. A–Discharge corona, B–Negatively charged wire, C–Dust particles, D–Collection plate grounded
Question 26. Choose the correct statement regarding the catalytic converters.
- Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters must use leaded petrol
- Platinum, palladium and rhodium are used as catalysts in catalytic converters
- Catalytic converters reduce the particulate matter
- Nitrogen gas in the exhaust is converted to nitric oxide by the catalytic converter
Answer: 2. Platinum, palladium and rhodium are used as catalysts in catalytic converters
The statement in option 2 is correct. Other options are incorrect and can be corrected as Catalytic converters are fitted in vehicles for reducing the emission of poisonous gases. As the exhaust passes through, the catalytic converter, unburnt hydrocarbons are converted into carbon dioxide and water. Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide are changed to carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas, respectively.
Question 27. Catalytic converters are fitted into automobiles to reduce the emission of harmful gases. Catalytic converters convert leftover hydrocarbons into
- Carbon Dioxide And Water
- Carbon Monoxide
- Methane
- Carbon dioxide and methane
Answer: 1. Carbon Dioxide And Water
The statement in option 1 is correct. Other options are incorrect and can be corrected as Catalytic converters are fitted in vehicles for reducing the emission of poisonous gases. As the exhaust passes through, the catalytic converter, unburnt hydrocarbons are converted into carbon dioxide and water. Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide are changed to carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas, respectively.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 28. Catalytic converters
- Fitted into automobiles for reducing emission of poisonous gases.
- Metals like platinum, palladium and rhodium are used as catalysts.
- On passing through a converter, the nitric oxide in the exhaust splits into nitrogen and oxygen. Carbon monoxide is oxidised to carbon dioxide.
- Leaded petrol is harmful to catalytic converters as they can inactivate the catalyst.
Choose the option containing correct statements about converters.
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1,2,3, and 4
Answer: 4. 1,2,3, and 4
All given statements are correct. Catalytic converters are fitted into automobiles for reducing the emission of poisonous gases. Rhodium and platinum, palladium are examples of catalysts used in catalytic converters. They convert unburnt hydrocarbons into CO2 and HO2 and CO and nitric oxide to CO2 and N2 gas, respectively. Use of unleaded petrol is however recommended as the lead petrol causes inactivation of the catalyst.
Question 29. Match the following columns.
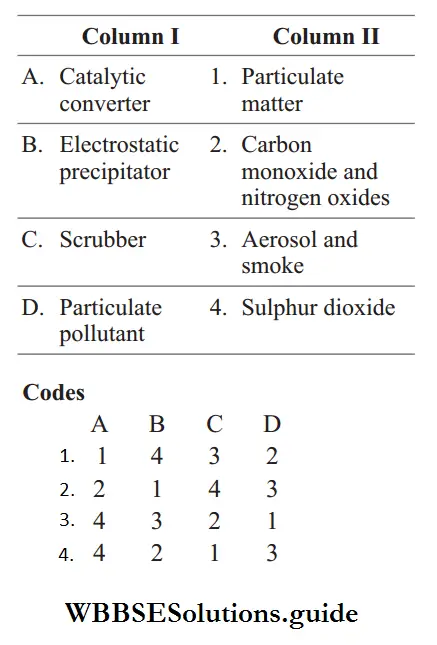
Answer: 2. A–2, B–1, C–4, D–3
Question 30. Which of the following is not an air pollutant?
- NO2
- SO2
- Hydrocarbons
- CO2
Answer: 4. CO2
Carbon dioxide occurs naturally in the atmosphere. It is an essential ingredient in photosynthesis.
Thus, it is not an air pollutant.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 31. Air pollution causing photochemical oxidant production includes
- Carbon Monoxide, Sulphur Dioxide
- Nitrous Oxide, Nitric Acid Fumes, Nitric Oxide
- Ozone, Peroxyacetyl Nitrate, Aldehyde
- Oxygen, chlorine, fuming nitric acid
Answer: 3. Ozone, Peroxyacetyl Nitrate, Aldehyde
Photochemical smog is formed at high temperatures over cities and towns due to still air, emission of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur and hydrocarbon from automobile exhausts and solar energy. Nitrogen dioxide splits into nitric oxide and nascent oxygen. Nascent oxygen combines with molecular oxygen to form ozone. Ozone reacts with hydrocarbon to form aldehyde and ketone. Nitrogen oxides, oxygen and ketones combine to form Peroxyacyl Nitrates (PAN). In areas with intense solar radiation, photoelectrical smog forms brown air.
“environment questions “
Question 32. Smog is a combination of
- Fire And Water
- Smoke And Fog
- Smoke And Water
- Air and water
Answer: 2. Smoke And Fog
Smog is basically derived from the merging of two words; smoke and fog. Smog occurs mainly because of air pollution and can also be defined as a mixture of various gases with dust and water vapour. Smog also refers to hazy air that makes breathing difficult.
Question 33. The basic component of smog may be
- PAN
- ozone
- PBN
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Smog is a highly oxidising polluted atmosphere comprising O3, NO2, PAN (Peroxyacetyl Nitrate) and PBN (Peroxybenzoyl Nitrate).
Question 34. Smog is commonly formed due to JIPMER
- Mixing Of Ozone With NO2
- Deposition Of CO2 On Condensed Vapour Particles
- Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming
- The reaction of oxides of N and S, etc., with sunlight and volatile organic compounds
Answer: 4. Reaction of oxides of N and S, etc., with sunlight and volatile organic compounds
Photochemical smog is formed at high temperatures over cities and towns due to still air, emission of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur and hydrocarbon from automobile exhausts and solar energy. Nitrogen dioxide splits into nitric oxide and nascent oxygen. Nascent oxygen combines with molecular oxygen to form ozone. Ozone reacts with hydrocarbon to form aldehyde and ketone. Nitrogen oxides, oxygen and ketones combine to form Peroxyacyl Nitrates (PAN). In areas with intense solar radiation, photoelectrical smog forms brown air.
Question 35. Assertion Smog is commonly formed at places having low temperatures and high pollution of aerosol. Reason (R) It is very common in metropolis cities of India.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Smog is a common problem in many large urban areas, where human activity gives rise to particulates in the air. It can be exacerbated significantly by weather conditions and local geography, which can prevent particulate from being dispersed naturally by wind. It is more closely associated with automobile and industrial emissions, which interact frequently to create the particles that cause smog. Smog is the interaction of light with fine solid or liquid particles in the air, known as aerosols. The most common cause of photochemical smog is the interaction of nitrogen oxides and volatile compounds.
Question 36. Which are the primary constituents of photochemical smog?
- Carbon dioxide and NO2
- Hydrocarbons and CFCs
- SO2 and CO
- NO2 and hydrocarbons
Answer: 4. NO2 and hydrocarbons
Photochemical smog is formed at high temperatures over cities and towns due to still air, emission of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur and hydrocarbon from automobile exhausts and solar energy. Nitrogen dioxide splits into nitric oxide and nascent oxygen. Nascent oxygen combines with molecular oxygen to form ozone. Ozone reacts with hydrocarbon to form aldehyde and ketone. Nitrogen oxides, oxygen and ketones combine to form Peroxyacyl Nitrates (PAN). In areas with intense solar radiation, photoelectrical smog forms brown air.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 37. Which is always present in photochemical smog?
- Ozone
- CO2
- SO2
- CH4
Answer: 1. Ozone
Ozone is generated in the lower atmosphere during the formation of photochemical smog when nitrogen dioxide splits to produce reactive oxygen atoms, which combine with molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecules split under ultraviolet radiations to produce oxygen atoms which combine with molecular oxygen to form ozone. It is always present in photochemical smog.
Question 38. Photochemical smog affects plants by
- Bleaching Of Leaves And Excess Production Of Pigments
- Shedding Of Foliage And Increase Of Transpiration
- Decolourising And Curling Of Leaves
- Degradation of chlorophyll by ozone
Answer: 4. Degradation of chlorophyll by ozone
Ozone is formed by resultant secondary pollutants in smog and degrades the photosynthetic pigments, i.e. chlorophyll of leaves.
Question 39. Choose the correct sequence of air pollution and its components with the effect it produces.
- Chemical factory → NO2 → ozone hole
- Automobile exhausts → NO2 → greenhouse effect
- Heavy industry → CO2 → acid rain
- Incinerators → NOx gases → photochemical smog
Answer: 4. Incinerators → NOx gases → photochemical smog
Nitrogen oxides are produced naturally through biological and non-biological activities. Human activity forms nitrogen oxides in the combustion process of industries, automobiles, incinerators and nitrogen fertilisers. Nitrogen oxides give photochemical smog. Thus, the correct sequence of air pollution and its component with the effect it produces is shown in option 4
Question 40. Match the following columns.
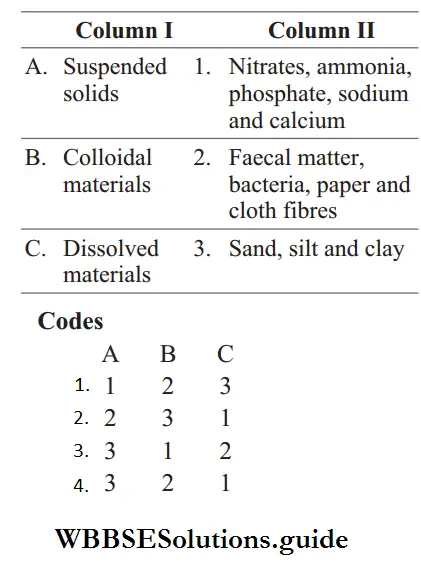
Answer: 4. A–3, B–2, C–1
Question 41. Burning of plastics releases
- CFC
- SO2
- Benzopyrene
- PCB
Answer: 4. PCB
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB) are released from the burning of plastics.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 42. The pollutants emitted by jet aeroplanes in the outer atmosphere are known as
- Smog
- Photochemical Oxidants
- Aerosols
- Loess
Answer: 4. Loess
Chemicals released in the atmosphere with force in the form of mist or vapours are called aerosols. Jet aeroplanes release aerosols which contain CFC.
Question 43. In the ‘wet system’ of removing gaseous pollutants
- Alkali Fluid Is Used
- Acidic Fluid Is Used
- Neutral fluid is used
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Alkali Fluid Is Used
In wet scrubbing processes for gaseous control, a liquid is used to remove pollutants from an exhaust stream. The removal of pollutants in the gaseous stream is done by absorption by the use of scrubbing reagents such as lime or sodium hydroxide (alkaline nature). Thus, the correct answer is 1.
Question 44. Which of the following statements is true?
- Benzene hexachloride is a non-biodegradable pollutant.
- Anthropogenic air pollutants are natural in origin.
- Carbon monoxide is a primary air pollutant.
- Sulphur dioxide causes brown air effects during traffic congestion in cities.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 4
Answer: 1. 1 and 3
Statements I and III are true, but II and IV are false because Non-biodegradable pollutants either do not degrade or degrade extremely slowly in the natural environment, e.g. DDT, BHC (Benzene Hexachloride). Anthropogenic pollutants are man made pollutants, e.g. sewage, pesticides, fertilisers, etc. Primary air pollutants are those which enter the air directly from the source, e.g. carbon monoxide. In traffic congested cities, the brown air effect is caused due to oxides of nitrogen.
Question 45. Which of the following is most poisonous?
- CO
- CO2
- C
- SO2
Answer: 1. CO
Carbon monoxide is produced due to incomplete combustion, metallurgical operations and naturally by plants as well as animals. CO combine with haemoglobin and produce carboxy haemoglobin. At 50 ppm carbon monoxide convert 7.5% of haemoglobin into carboxy haemoglobin. It impair oxygen transport resulting in giddiness, headache, decreased vision, cardiovascular malfunctioning and asphyxia. Thus, CO is most poisonous.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 46. CO is more toxic than CO2 because
- It Affects The Nervous System
- It Damages Lungs
- It Reduces The Oxygen Carrying Capacity Of Haemoglobin
- It forms acid with water
Answer: 3. It Reduces The Oxygen Carrying Capacity Of Haemoglobin
CO is more toxic because it reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of haemoglobin.
Question 47. According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), particles that are responsible for causing great harm to human health are of diameter
- 2.5 micrometres
- 5.00 micrometres
- 10.00 micrometres
- 7.5 micrometres
Answer: 1. 2.5 micrometres
According to Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), particulate size 2.5 micrometres or less in diameter (PM 2.5) are responsible for causing the greatest harm to human health. These fine particulates can be inhaled deep into the lungs and can cause breathing and respiratory symptoms, irritation inflammations and damage to the lungs and premature deaths.
Question 48. Examples of regional pollution are
- Acid Rain
- Smog
- Both 1 and 2
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Regional pollutants are those which have been emitted from all sources in a region and have had time to mix, diffuse from their peak concentration and undergo physical, chemical and photochemical reactions. The size of a region is indeterminate, but usually incorporates one or more cities and is on the order of 100 to 10, 000 km2. Examples of regional pollution are acid rain, smog, etc.
Question 49. Rain is called acid rain when its pH is below
- 7
- 6.5
- 6
- 5.6
Answer: 4. 5.6
Acid rain refers to precipitation with a pH of less than 5.
Question 50. Acid rain is caused by increase in the atmospheric concentration of
- CO2 and CO
- O2 and dust
- SO2 and NOv
- SO3 and CO
Answer: 3. SO2 and NO2
Acid rain is rainfall and other forms of precipitation with a pH of less than 5. Acid rain is caused by large scale emission of acidic gases into the atmosphere from thermal power plants, industries and automobiles. The common ones are sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides (NO2), Volatile Organic carbon (VOCs) and hydrogen chloride.
Question 51. The acid rain destroys vegetation because it contains
- Nitrates
- H2SO4
- O2
- CO
Answer: 2. H2SO4
Acid rain contains acidic components, such as sulphuric acid or nitric acid. The type of acid rain that contains water is called wet deposition. Acid rain formed with dust or gasses is called dry deposition. When these rain falls on the soil the soil become acidic. Also the leaves
Question 52. Acid rain occurs above the areas where
- There Is Excess Production Of Nh3 And Coal Gas
- Factories Are Expelling SO2 In Air
- There Is an Excess Release Of CO2 Due To Increase In Combustion And Respiration
- Excess production of gaseous hydrocarbons
Answer: 2. Factories Are Expelling SO2 In Air
Acid rain occurs above the area where factories are expelling of sulphur dioxide into the air. These oxides react with water and precipitate in the form of the acid rain. For example, around the Taj Mahal the presence of the Mathura refinery has caused multiple events of acid rain.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 53. In acid rain, sulphuric acid accounts for
- 100% of acid
- 70% of acid
- 50% of acid
- 30% of acid
Answer: 2. 70% of acid
Acid rain is caused by a chemical reaction. Sulphur dioxide on reaction with water and oxygen forms sulphur trioxide which is rapidly converted into sulphuric acid in the presence of water. It accounts for 70% volume in acid rain. Hence, the correct answer is option 2.
Question 54. It is said that Taj Mahal is getting destroyed due to
- Flood In Yamuna River
- Decomposition Of Marble As A Result Of High Temperature
- Air pollutant released from oil refinery of Mathura
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Air pollutant released from oil refinery of Mathura
Threat to Taj Mahal from the Mathura refinery is due to pollutant gases comprising SO2, H2S and nitrogen oxides. They would convert CaCO3 (marble) into calcium sulphate and calcium nitrate.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 55. Which of the following is the most serious pollutant among sulphur compounds?
- Oxides of sulphur
- Carbonyl sulphide
- Carbon disulphide
- Sulphates
Answer: 1. Oxides of sulphur
Oxides of sulphur react with water in the atmosphere and form sulphuri cacid which cause rainwater to get acidic and thus oxides of sulphur cause acid rain. Carbonyl sulphide is a colourless gas which decomposes into carbon dioxide and carbon disulphide. Carbon disulphide is a colourless volatile liquid in its pure form. It is not considered to cause any type of pollution. Sulphates are polyatomic ions derived from sulphur and oxygen. Sulphates generally cause water pollution. So, the correct answer is oxides of sulphur.
Question 56. SO2 pollution affects
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Ribosome
- Vacuole
Answer: 2. Mitochondria
SO2 pollution affects the respiratory system mostly, thus it affects the mitochondria. Higher concentrations of SO2 can result in temporary breathing impairment for children and adults who are active outdoors. Short-term exposures of individuals to elevated SO2 levels while at moderate exertion may result in reduced lung function that may be accompanied by such symptoms as wheezing, chest tightness or shortness of breath.
Question 57. A component of living cell affected by pollutant SO2 is
- Nucleus
- All Cell Membrane Systems
- Cell wall
- None of the above
Answer: 2. All Cell Membrane Systems
The component of living cell affected by pollutant SO2 is cell membrane. SO2 replaces oxygen in cellular materials. It affects structural proteins in the membrane and these changes the membrane permeability.
Question 58. The ciliary passage of the respiratory tract gets damaged by
- Oxides Of Sulphur
- Oxides Of Nitrogen
- Oxides of carbon
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Oxides Of Sulphur
Oxides of sulphur irritate the respiratory epithelium and impair normal breathing or cause asthma. Thus, oxides of sulphur can damage ciliary passage of respiratory tract.
Question 59. Which of the following are the most suitable indicators of SO2 pollution in the environment?
- Algae
- Fungi
- Lichens
- Conifers
Answer: 3. Lichens
Lichens are very sensitive to SO2 pollution. They are completely destroyed at places where there is SO2 pollution in the atmosphere. Therefore, they act as very good indicators of SO2 pollution.
Question 60. SO2 of the atmosphere combines with water to form H SO2 4. When this reaches the soil
- It Increases Of Ph Of The Soil
- It decreases the pH of the soil
- pH remains the same
- Soil texture changes
Answer: 2. It decreases the pH of the soil
When sulphur dioxide combines with water and air, it forms sulphuric acid, which is the main component of acid rain. When the rain falls on the soil, the soil become acidic resulting in the lower pH of the soil.
Question 61. Which one of the following statements is incorrect in case of the Bhopal tragedy?
- Methyl isocyanate gas leakage took place
- Thousands of human beings died
- Radioactive fallout engulfed Bhopal
- It took place in the night of December 2/3, 1984
Answer: 3. Radioactive fallout engulfed Bhopal
All options are correct except option 3 because the Bhopal gas tragedy took place in the night of December 2/3, 1984, which was worst chemical disaster in history. People started dying within hours and more than 2000 lives were lost in first few days. Methyl isocyanate gas was the main chemical released that engulfed Bhopal that day.
Question 62. The effect of hydrogen sulphide on man leads to which of the following disease?
- Paralysis
- Sterility
- Blindness
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
HS2 does not accumulate in the body, but repeated/prolonged exposure to moderate levels can cause low blood pressure, headache, loss of appetite and weight. Repeated exposure over time to high levels of HS2 may cause convulsions, coma, brain and heart damage or even death. So, option 4 is correct.
Question 63. In 1984, Bhopal gas tragedy was caused due to leakage of
- Potassium Isocyanate
- Methyl Isocyanate
- Sodium monoxide
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Methyl Isocyanate
Bhopal gas tragedy occurred on 2/3 December, 1984 in which a storage tank containing 36 tonnes of Methyl Isocyanate (MIC) burst in the pesticide manufacturing plant of Union Carbide in Bhopal. MIC is one of the deadliest toxins which when inhaled even in very small doses can kill the animal. It is highly irritating to skin, eyes or mucous membranes and causes death by lung oedema. It is also a carcinogenic agent.
Question 64. What were the effects of the Bhopal gas tragedy?
- Death of newborn babies
- Newborn babies were born with deformities
- Vegetation in the radius of 3.5 sq km around the Union Carbide factory was affected
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Approximately 3598 deaths have resulted from the Bhopal Gas tragedy. Chronic inflammatory damage to the eye and lungs is the main cause. Other effects of this tragedy are the death of newborns and babies were born with deformities and the vegetation in the radius of 3.5 sq. km around the Union Carbide factory was affected.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 65. The TLY (Threshold Limit Value) of methyl isocyanate responsible for the Bhopal gas tragedy is
- 0.002 ppm
- 0.02 ppm
- 0.2 ppm
- 0.005 ppm
Answer: 2. 0.02 ppm
Methyl isocyanate is a volatile, toxic chemical used to manufacture carbamate pesticides. Bhopal gas tragedy (2/3 December 1984) is a case of air pollution in which MIC (Methyl Isocyanate) gas released from a fertiliser manufacturing plant of Union Carbide caused the death of approximately 3598 persons. MIC causes irritation in the eyes which may result in blindness, various lung diseases may result in death. Workers exposed to the MIC 8-hours threshold limit value of 0.02 ppm (46) are exposed to approximately 460 mg MIC in a workday.
Question 66. Various atmospheric air borne pollutants may cause
- Pneumonia
- Diarrhoea
- Respiratory Diseases And Allergies
- Cholera
Answer: 3. Respiratory Diseases And Allergies
Airborne pollutant enters via the respiratory tract in humans and cause respiratory diseases and allergies on the skin.
Question 67. Sulphur dioxide causes
- Emphysema
- Bronchitis
- Asthma
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Sulphur dioxide causes respiratory tract diseases like asthma, bronchitis, cancer, emphysema, etc.
Question 68. Accumulation of fluoride in plant leaves causes
- Chlorosis
- Stem Rot
- Tip burn
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Stem Rot
Fluoride is an accumulative poison in plant foliage. Accumulation may be gradual over time and causes tip burn in leaves.
Question 69. Which of the following is pollution-related disorder?
- Silicosis
- Pneumoconiosis
- Fluorosis
- Leprosies
Answer: 1. Silicosis and 3. Fluorosis
(1 & 3) Fluorides are given out during the refining of metals. Fluorides cause fluorosis. This is a pollution-related disorder. When the level of fluoride content in drinking water becomes as high as 3-12 mg/L, the water becomes polluted. It affects teeth as well as bones. Silicosis is caused by inhalation of dust containing free silica or silicon dioxide, especially by workers engaged in mining, pottery, ceramic industry, sandblasting, and building and construction industries. So, both fluorosis and silicosis are pollution-related disorders.
Question 70. Bagassosis is
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Due To Exposure To Fibrous Cellulose Part Of Crushed Sugarcane
- Is An Asthma Like Condition Produced Due To Exposure To Flax Or Cotton Fibres
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Due To Exposure To Damp Hay Or Grain
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to exposure to paprika
Answer: 1. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Due To Exposure To Fibrous Cellulose Part Of Crushed Sugarcane
Bagassosis is an interstitial lung disease, is a type of hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to exposure to the fibrous cellulose part of crushed sugarcane.
Question 71. Which of the following diseases is caused or aggravated by pollution?
- Bronchitis
- Rheumatism
- Scurvy
- Haemophilia
Answer: 1. Bronchitis
Inflammation of the lining of bronchial tubes causes bronchitis. Particulate matter, a prominent source of air pollution causes pneumoconiosis, byssinosis, emphysema, bronchitis and severe coughing. Rheumatism is a disease of joints. Scurvy is a deficiency disease caused due to the deficiency of vitamin C. Haemophilia is a genetic sex-linked disorder in which blood fails to clot normally.
Question 72. Black foot disease occurs due to
- Cadmium
- Mercury
- Arsenic
- Copper
Answer: 3. Arsenic
Black foot disease is caused by excessive consumption of arsenic in water. Black foot disease, with gangrene-like symptoms, affects the feet and sometimes the fingers. It is a rare peripheral vascular disease found mainly in the Province of Taiwan (China). The best prevention for this disease is avoidance of exposure to arsenic by ingesting clean drinking water.
Question 73. ‘Knock knee’ syndrome occurs due to the pollution of
- Nitrates
- Phosphates
- Fluorides
- Heavy metals
Answer: 3. Fluorides
Fluorides are given out during the refining of minerals (e.g. aluminium) and can contaminate groundwater. Excess fluorides in drinking water causes teeth deformity, hardened bones and stiff and painful joints (skeletal fluorosis) or knock knee disease.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 74. Black lung disease is common in
- Coal Miners Odisha Jee 2005
- Refinery Workers
- Petrochemical Industry
- Farmers
Answer: 1. Coal Miners Odisha Jee 2005
Black lung is a man-made, occupational lung disease that is contracted by prolonged breathing of coal mine dust. The disease is called ‘black lung’ because it causes the lungs to look black instead of pink. Medically, it is a type of pneumoconiosis called coal worker’s pneumoconiosis.
Question 75. Assertion Fluorides destroy vegetation. Reason (R) Fluorosis hinders respiration.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false because, In plants, fluorides combine chemically with Mg 2+ of chlorophyll and hence inhibit photosynthesis. It causes the abscission of leaf and fruit and hence destroy vegetation. In human beings, the typical symptom of excess fluorine (fluorosis) is the mottling of teeth.
Question 76. In a small town, pasture is contaminated with airborne fluorides. Grazing animals in that area will suffer from
- Dental And Bone Diseases
- Goitre Disease
- Thyroid Disease
- Beriberi
Answer: 1. Dental And Bone Diseases
Fluorides cause fluorosis. It is a disease which is defined by mottling of teeth, and abnormal bones that are liable to fracture because fluorine replaces Ca²+ and makes the bones brittle. Fluoride is light airborne particulate matter.
Question 77. Fly-ash is a/an
- Insectivorous Plant
- Light Airborne Particulate Matter
- New Name Of Orchid Plant
- Causal organisms of various diseases
Answer: 2. Light Airborne Particulate Matter
Fly ashes are finely divided residues resulting from the combustion of ground or powdered coal. It is discharged as an airborne emission. It is a light airborne particulate matter.
Question 78. Assertion COPD disease is very common in Kanpur. Reason (R) It is disease of respiratory tract occurring due to pollution.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Kanpur is the most polluted city in the country, with high quantities of Respirable Suspended Particulate Matter (RSPM) in the air according to the results of a survey carried out by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in 2002. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a condition characterised by narrowing of the air ways, but these changes are permanent rather than reversible. COPD is caused by exposure to pollutant that produce inflammation.
Question 79. Fibrosis of lung is due to
- Asbestos And Cement Particles
- Mercury
- China Clay
- Rubber Particles
Answer: 1. Asbestos And Cement Particles
The asbestos and cement particles from industries are added to the air and these are inhaled by workers and people living nearby. These particles form a coating on the internal lining of lungs and bronchioles causing very serious fibrosis which may later lead to cancer.
Question 80. In silicosis, the silica particles can be seen
- As Needle Shaped Crystal By Light Microscopy
- As Needle Shaped Crystals Under Polarised Light
- As Maltese Cross Shaped Crystal By Light Microscopy
- As Maltese Cross Shaped Crystals Under Polarised Light
Answer: 2. As Needle Shaped Crystals Under Polarised Light
Silicosis is a lung disease caused by breathing-in tiny bits of silica. It is characterised by the fibrotic nodules with the concentric onion skinned arrangement of collagen fibres, central hyalinisation and a cellular peripheral zone with light birefringent particle seen under polarised light.
Question 81. Which of the following ailments is a result of inhalation of fine particulate matter?
- Irritation
- Inflammation
- Damage of lungs and premature deaths
- All of the above
Answer: 4. Damage of lungs and premature deaths
Fine particulates can be inhaled deep into the lungs and can cause breathing and respiratory symptoms, irritation, inflammations and damage of the lungs and premature deaths.
Question 82. 3, 4-benzopyrene causes
- Leukaemia
- Cytosilicosis
- Lung Cancer
- Tuberculosis
Answer: 3. Lung Cancer
There are a number of chemicals, which causes lung cancer and one of them is 3,4-benzopyrene. Benzopyrene mutates three positions is the p53 gene, which leads to lung cancer. Hence, the correct option is 3.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 83. What is true about the Euro II norms? It is laid down to
- Control Sulphur At 350 Ppm In Diesel And 150 Ppm In Petrol
- Reduce Sulphur Level To 50 Ppm In Gasoline
- Reduce Sulphur Level To 200 Ppm In Diesel And Petrol
- Reduce sulphur level to 200 ppm in diesel and 100 ppm LPG
Answer: 1. Control Sulphur At 350 Ppm In Diesel And 150 Ppm In Petrol
Euro 2 norms were stipulated to control sulphur content at 350 ppm in diesel and 150 ppm in petrol and aromatic hydrocarbons are to be contained at 42%.
Question 84. All automobiles and fuel (petrol and diesel) were to have met the Euro III emission specification in eleven Indian cities from 1 April 2005 and have to meet the Euro IV norms by
- 1 April 2007
- 1 April 2008
- 1 April 2009
- 1 April 2010
Answer: 4. 1 April 2010
All automobiles and fuel were to have met the Euro III emission specification in eleven Indian cities from 1 April, 2005 and have to meet the Euro IV norms by 1 April 2010.
Question 85. Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act was ammended in 1987 to include among pollutants
- Vehicular Exhaust Neet 2020
- Allergy Causing Pollen
- Noise
- Particulates of size 2.5 micrometers or below
Answer: 3. Noise
Air (Prvention and Control of Pollution) Act was ammended in 1987 to include noise as pollutant.
Question 86. Noise is
- Loud Sound
- Sound Of High Frequency
- Unwanted Sound
- Constant sound
Answer: 3. Unwanted Sound
Noise is defined as an undesired high level of sound. It is a physical form of pollution that affects the receiver directly. Noise or unwanted sound has a value of 80 dB and above.
Question 87. What is the intensity of sound in normal conversation?
- 10-20 dB
- 30-60 dB
- 70-90 dB
- 120-150 dB
Answer: 3. 70-90 dB
The unit of sound level is decibel. Moderate conversation produces 30–60 dB sound.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 88. During day time sound level in the silent zone is about
- 20 dB
- 30 dB
- 40 dB
- 50 dB
Answer: 4. 50 dB
Sound is expressed in decibels (dB). A decibel is one-tenth of bel, a unit of measuring electric or acoustic power. The World Health Organisation (WHO) has recommended a noise of less than 75 decibels for industries. The National Pollution Control Board has recommended the following maximum permissible noise level in Indian cities
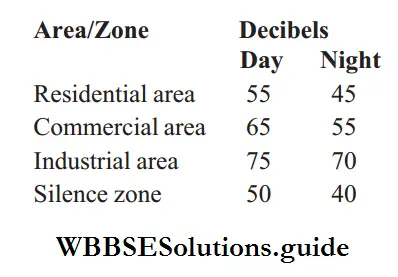
Question 89. Noise pollution is measured in
- Decibels
- Amperes
- Fathoms
- Ohm
Answer: 1. Decibels
Noise pollution is measured in decibels (dB).
Question 90. Sound above what level is considered hazardous noise pollution?
- Above 80 dB
- Above 120 dB
- Above 150 dB
- Below 30 dB
Answer: 1. Above 80 dB
Sound above 80 dB becomes hazardous to humans.
Question 91. Consider the following statements regarding noise.
- Causes psychological disorders in humans.
- Causes physiological disorders in humans.
- Unit of measurement of noise dB.
- 150 dB is tolerable for humans.
Choose an option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 4
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Answer: 3. 1,2, and 3
All statements are correct except IV because Noise pollution causes psychological and physiological disorders in humans. Noise is measured in dB unit. Above 80 dB noise became hazardous for human.
Question 92. The green muffler is used against which type of pollution?
- Air
- Soil
- Water
- Noise
Answer: 4. Noise
Green plants are being planted along road side to check noise pollution. This is known as green muffler.
Question 93. The anxiety and stress reactions are caused by
- Air Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Nuclear pollution
Answer: 2. Noise Pollution
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Noise pollution has several adverse effects on human health as The first effects of noise are anxiety and stress however, in extreme cases it may lead to fright. Noise causes headache by dilating blood vessels of the brain, eye strain by dilating the pupil, digestive spasms through anxiety and high blood pressure by increasing cholesterol level in the blood. Noise can impair the development of nervous system of unborn babies which leads to abnormal behaviour in later life.
Question 94. Assertion Inhabitants close to very busy airports are likely to experience health hazards. Reason (R) Sound level of jet aeroplanes usually exceeds 160 dB.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Noise level up to 65 dB (decibel) in a commercial area and up to 75 dB in industrial areas is permitted as per law. Prolonged exposure to noise level to 80 dB or more leads to loss of hearing ability, fatigue, nervousness, fever, hypertension, gastric disorder, increase in cholesterol level and dilation of pupil of the eye. As the jet aeroplanes have the noise up to 150-160 dB or more, the inhabitants in the vicinity of busy airports are likely to experience above health hazards. Maximum noise level is recorded in rockets, i.e. 180 dB.
Question 95. Which of the following physiological manifestations is the result of noise pollution?
- Dilation of pupil
- Increase in the rate of heartbeat
- Constriction of blood vessels
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Because of noise pollution nervous tension, blood pressure and heart trouble increases. It causes constriction of blood vessels and increases the rate of heartbeat. Noise pollution also increases digestive spasms and causes the dilation of the pupils of the eyes. It causes impairment of night vision and decreases the rate of colour perception.
