Organic Chemistry NEET MCQs
NEET Chemistry For Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in pent-2-en-4-yne is
- 13 σ bonds and no π bond
- 10 σ bonds and 3π bonds
- 8 σ bonds and 5π bonds
- 11 σ bonds and 2π bonds.
Answer: 2. 10 σ bonds and 3π bonds

Question 2. Which of the following molecules represents the order of hybridisation sp², sp², sp, sp from left to right atoms?
- HC ≡ C — C ≡ CH
- CH2 = CH — C ≡ CH
- CH2 = CH — CH = CH2
- CH3 — CH = CH — CH3
Answer: 2. CH2 = CH — C = CH
⇒ \(\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{CH}_2}=\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)
Question 3. The total number of π-bond electrons in the following structure is
- 12
- 16
- 4
- 8
Answer: 4. 8
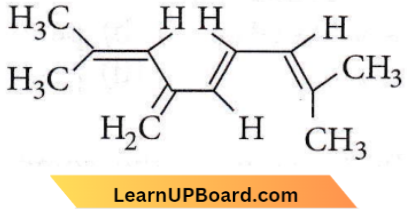
There are four double bonds. Hence, no. of E-electrons =2×4=8.
Organic Chemistry NEET MCQs
Question 4. The state of hybridisation of C2, C3, C5 and C6 of the hydrocarbon,
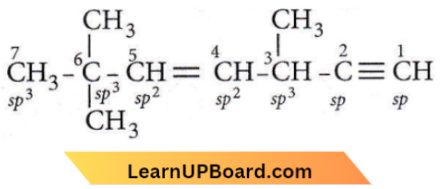
is in the following sequence
- sp³, sp², sp² and sp
- sp, sp², sp² and sp³
- sp, sp², sp³ and sp²
- sp, sp³, sp² and sp³
Answer: 4. sp, sp³, sp² and sp³
∴ \(\mathrm{C}_2-s p, \mathrm{C}_3-s p^3, \mathrm{C}_5-s p^2 \text { and } \mathrm{C}_6-s p^3\)
Question 5. In the hydrocarbon, \(\underset{6}{\mathrm{CH}_3}-\underset{5}{\mathrm{CH}}=\underset{4}{\mathrm{CH}}-\underset{3}{\mathrm{CH}_2}-\underset{2}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \underset{1}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\) the state of hybridisation of carbons 1, 3 and 5 are in the following sequence
- sp, sp², sp³
- sp³, sp², sp
- sp², sp, sp³
- sp, sp³, sp²
Answer: 4. sp, sp³, sp²
The state of hybridisation of carbon in the 1,3 and 5 positions are sp, sp³ and sp².
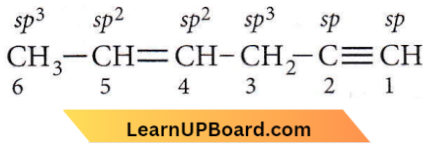
Question 6. In which of the following compounds there is more than one kind of hybridisation (sp, sp², sp³) for carbon?
- CH2 = CH-CH = CH2
- H – C ≡ C – H
- CH3CH2CH2CH3
- CH3-CH = CH-CH3
Answer: 4. CH3-CH = CH-CH3
Question 7. A straight-chain hydrocarbon has the molecular formula C8H10. The hybridisation of the carbon atoms from one end of the chain to the other is respectively sp³, sp², sp², sp³, sp², sp², sp and sp. The structural formula of the hydrocarbon would be
- CH3C ≡ CCH2-CH = CHCH = CH2
- CH3CH2 – CH = CHCH CHC ≡ CH
- CH3CH = CHCH2-C ≡ CCH = CH2
- CH3CH = CHCH2 – CH = CHC ≡ CH
Answer: 4. CH3CH = CHCH2 – CH = CHC ≡ CH
A straight-chain hydrocarbon has the molecular formula C8H10. The hybridisation of the carbon atoms from one end of the chain to the other is respectively sp³, sp², sp², sp³, sp², sp², sp and sp.
⇒ \(\stackrel{s p^3}{\mathrm{CH}_3} \stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C H}}=\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C H}}-\stackrel{s p^3}{\mathrm{C H}}_2-\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C H}}=\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C H}} -\stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C H}}\)
NEET questions on Organic Chemistry
Question 8. Which of the following possesses a sp-carbon in its structure?
- CH2=CCl-CH = CH2
- CCl2 = CCl2
- CH2 = C= CH2
- CH2 = CH-CH=CH2
Answer: 3. CH2 = C= CH2
⇒ \(\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C H}}_2=\stackrel{s p}{\mathrm{C}}=\stackrel{s p^2}{\mathrm{C H}_2}\)
Question 9. The Cl-C-Cl angle in 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrachloro-ethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about
- 120° and 109.5°
- 90° and 109.5°
- 109.5° and 90°
- 109.5° and 120°
Answer: 1. 120° and 109.5°
Tetrachloroethene being an alkene has sp²-hybridised C-atoms and hence the angle CI-C-CI is 120° while in tetrachioromethane is, carbon is sp³ hybridised, therefore the angle Cl-C-Cl is109°28′.
Question 10. The number of σ bonds, π bonds and lone pair of electrons in pyridine, respectively are
- 11,3, 1
- 12,2,1
- 11,2,0
- 12,3,0
Answer: 1. 11,3, 1
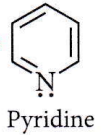
σ bonds:11
π bonds : 3
Lone pair: 1
Question 11. An organic compound X(molecular formula C6H7O2N) has six carbon atoms in a ring system, two double bonds and a nitro group as a substituent, X is
- Homocyclic but not aromatic
- Aromatic but not homocyclic
- Homocyclic and aromatic
- Heterocyclic and aromatic.
Answer: 1. Homocyclic but not aromatic
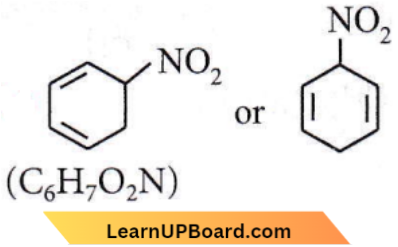
Hence, it is homocyclic (as the ring system is made of one thee of atoms, i.e., carbon) but not aromatic.
NEET questions on Organic Chemistry
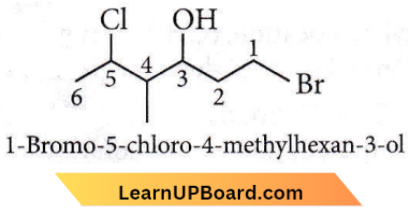
Question 12. The correct IUPAC name of the following compound is
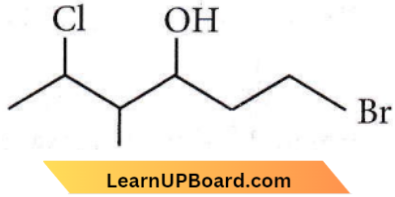
- 1-bromo-5-chloro-4-methylhexan-3-ol
- 6-bromo-2-chloro-4-methylhexan-4-ol
- 1-bromo-4-methyl-5-chlorotoxin-3-ol
- 6-bromo-4-methyl-2-chlorohexan-4-ol.
Answer: 1. 1-bromo-5-chloro-4-methylhexan-3-ol
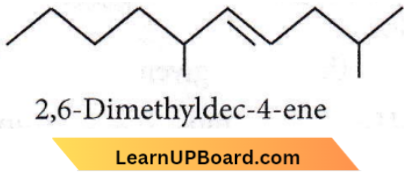
Question 13. The correct Structure of 2, 6-dimethyl-dec-4-ene is
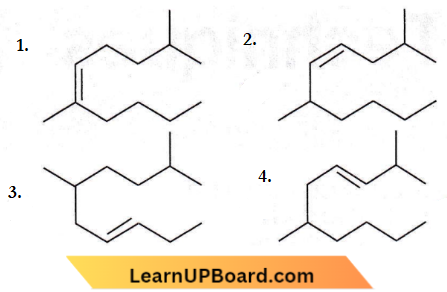
Answer: 2
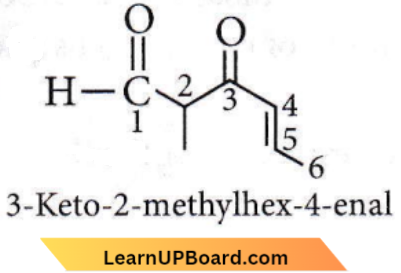
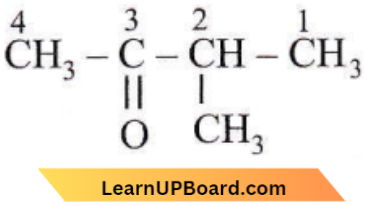
Question 14. The IUPAC name of the compound
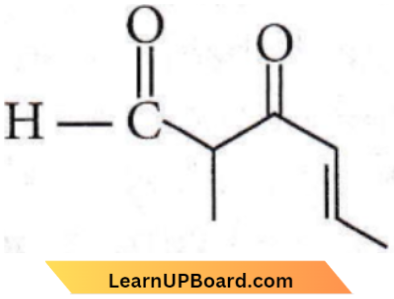
- 5-formylhex-2-en-3-one
- 5-methyl-4-oxohex-2-en-5-al
- 3-keto-2-methylhex-5-enal
- 3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal
Answer: 4. 3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal
Organic Chemistry multiple choice questions NEET
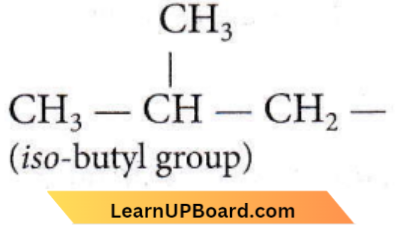
Question 15. The structure of the isobutyl group in an organic compound is
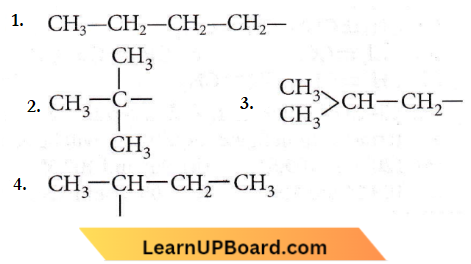
Answer: 3
Question 16. The structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 3-ethyl-2-hydroxy-4-methylhex-3-en-5-yonic acid is
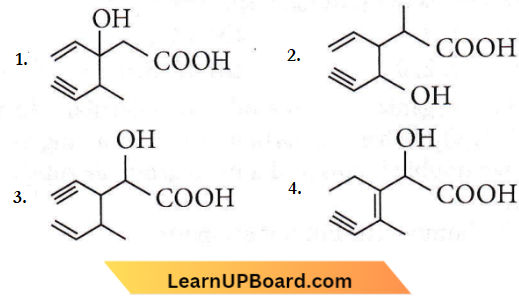
Answer: 4
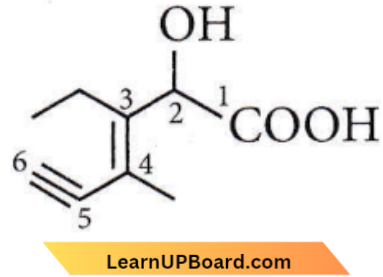
IUPAC name of the compound is 3 -ethyl-2-hydroxy-4-methylhex-3-en-5-ynoic acid.
Question 17. Which nomenclature is not according to the IUPAC system?
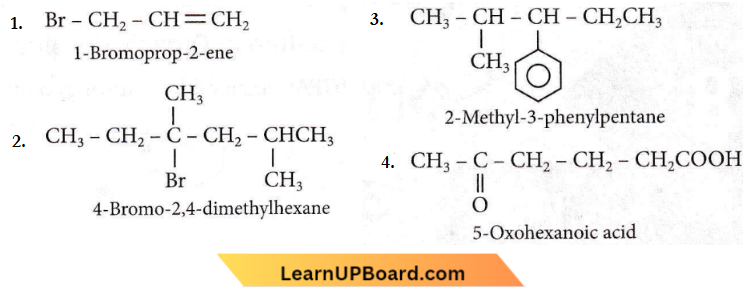
Answer: 1

Organic Chemistry multiple choice questions NEET
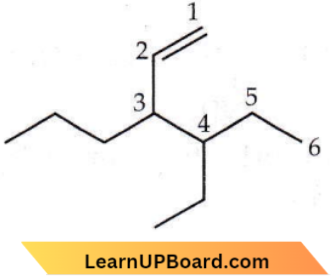
Question 18. The correct IUPAC name for the compound
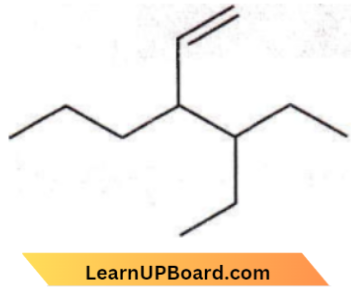
- 4-ethyl-3-propylhex-1-ene
- 3-ethyl-4-ethenyl heptane
- 3-ethyl-4-propylhex-5-ene
- 3-(1-ethylpropyl)hex-1-ene.
Answer: 1. 4-ethyl-3-propyl hex-1-ene
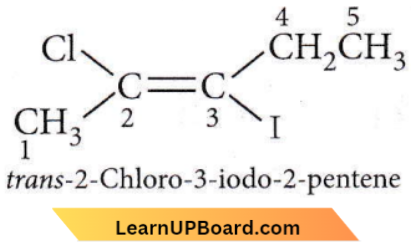
Question 19. The IUPAC name of the following compound is
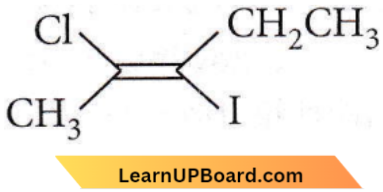
- Trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene
- cis-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentane
- Trans-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
- cis-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene.
Answer: 1. Trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene
Question 20. The IUPAC name of the compound CH3CH=CHC≡CH is
- Pent-4-yn-2-ene
- Pent-3-en-1-yne
- Pent-2-en-4-yne
- Pent-1-yn-3-ene.
Answer: 2. Pent-3-en-1-yne
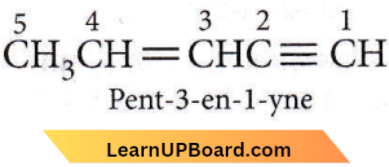
If a molecule contains both carbon-carbon double or triple bonds, the two are treated as seeking the lowest number combination. However, if the sum of numbers turns out to be the same starting from either of the carbon chains, then the lowest number is given to the C=C double bond.
NEET practice questions Organic Chemistry
Question 21. The IUPAC name of the compound having the formula CH≡C—CH=CH2 is
- 1-butyne-3-ene
- but-1-yne-3-ene
- 1-butene-3-yne
- 3-butene-1-yne.
Answer: 3. 1-butene-3-yne
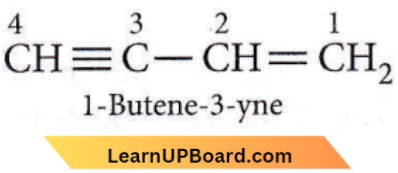
Since the sum of numbers starting from either side of the carbon chain turns out to be the same, so lowest number is given to the C=C end.
Question 22. The IUPAC name is
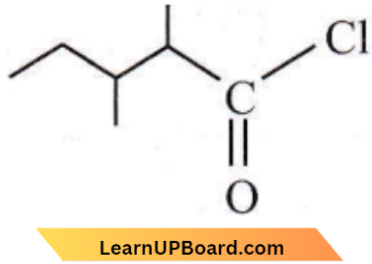
- 1-chloro-1-oxo-2,3-dimethyl pentane
- 2-ethyl-3-methyl butanol chloride
- 2,3-dimethyl pentanol chloride
- 3,4-dimethylpentanoyl chloride.
Answer: 3. 2,3-dimethyl pentanol chloride
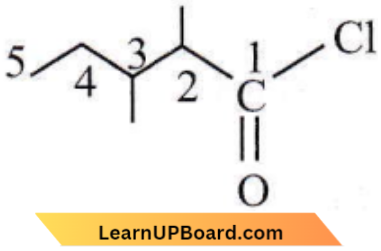
It is 2,3-dimethylpentanoyl chloride.
Question 23. Names of some compounds are given. Which one is not in the IUPAC system?
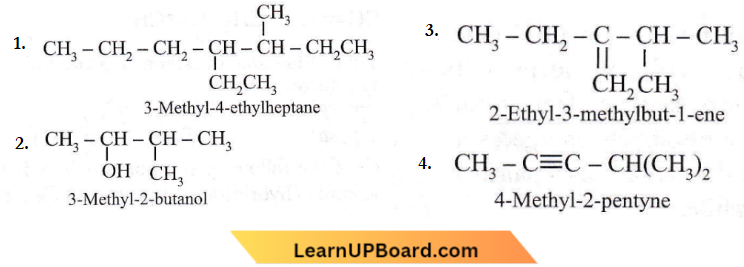
Answer: 1
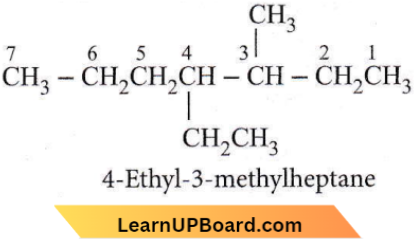
Question 24. The name of the compound given below is
- 4-ethyl-3-methyl octane
- 3-methyl-4-ethylacetate
- 2,3-diethyl heptane
- 5-ethyl-6-methyloctane.
Answer: 1. 4-ethyl-3-methyl octane
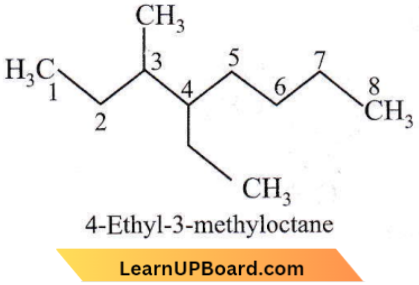
NEET practice questions Organic Chemistry
Question 25. IUPAC name of the following is CH2 = CH – CH2 – CH2 – C ≡ CH
- 1,5-hexene
- 1-hexene-5-yne
- 1-hexyne-5-ene
- 1,5-hexynene.
Answer: 2. 1-hexene-5-yne
⇒ \(\stackrel{1}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2=\stackrel{2}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\stackrel{3}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2-\stackrel{4}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2-\stackrel{5}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \stackrel{6}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)
The double bond gets priority over the triple bond. therefore, the correct IUPAC name is 1-hexene-5-yne.
Question 26. The incorrect IUPAC name is
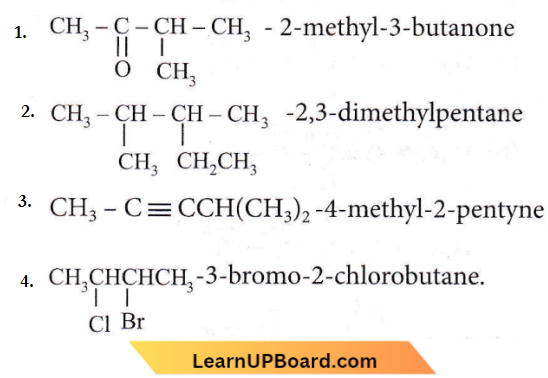
Answer: 1
The  group should get priority over methyl group.;
group should get priority over methyl group.;
Correct IUPAC name is
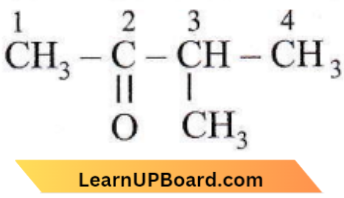
Question 27. The IUPAC name of (CH3)2CH – CH2 – CH2Br is
- 1-bromo-3-methyl butane
- 2-methyl-3-bromopropane
- 1-bromopentane
- 2-methyl-4-bromobutane.
Answer: 1. 1-bromo-3-methyl butane
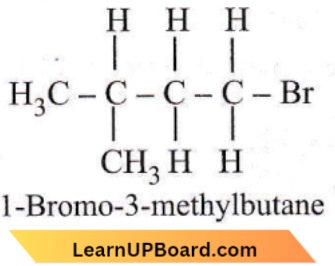
Question 28. The IUPAC name is

- 3-amino-5-heptenoic acid
- β-amino-ε-heptenoic acid
- 5-amino-2-heptenoic acid
- 5-amino-hex-2-enecarboxylic acid.
Answer: 1. 3-amino-5-heptanoic acid
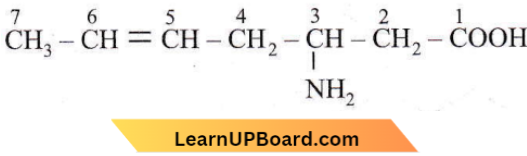
As -COOH group is the highest priority group, it is numbered one. So, the IUPAC name is 3-amino-5-heptenoic acid.
Question 29. 2-Methyl-2-butene will be represented as
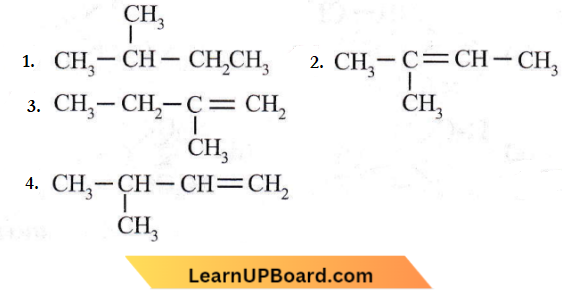
Answer: 2
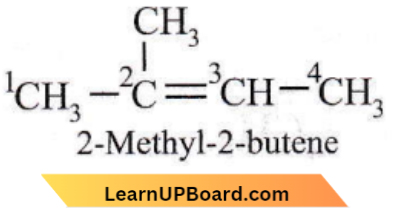
Chemistry MCQs Organic Chemistry NEET
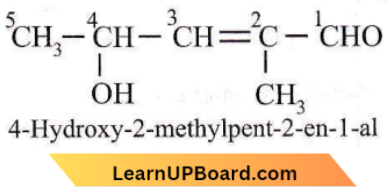
Question 30. The IUPAC name is
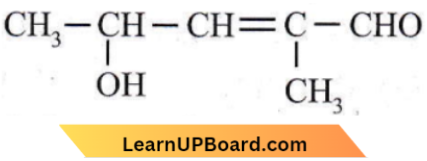
- 4-hydroxy-1-methylpentanal
- 4-hydroxy-2-methyl pent-2-en-1-al
- 2-hydroxy-4-methyl pent-3-en-5-al
- 2-hydroxy-3-methylpent-2-en-5-al.
Answer: 2. 4-hydroxy-2-methyl pent-2-en-1-al
Question 31. The compound which shows metamerism is
- C4H10O
- C5H12
- C3H8O
- C3H6O
Answer: 1. C4H10O
Metamerism occurs when the compound has a different number of carbon atoms on either side of the functional group.
Question 32. Which among the given molecules can exhibit tautomerism?
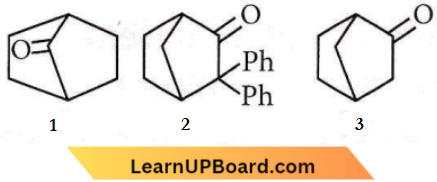
- 3 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 1 and 3
- Both 2 and 3
Which of the given compounds can exhibit tautomerism?
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
Answer: 1. 3 only
α-Hydrogen at bridge carbon never participates in tautomerism. Thus, only (3) exhibit tautomerism.
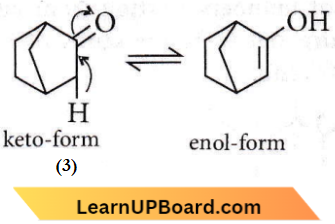
Question 33. Given:
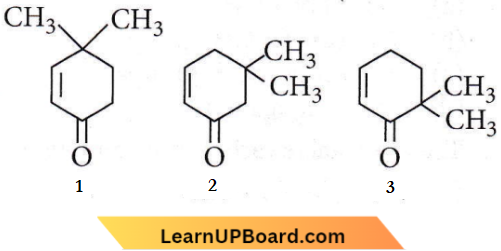
Which of the given compounds can exhibit tautomerism?
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
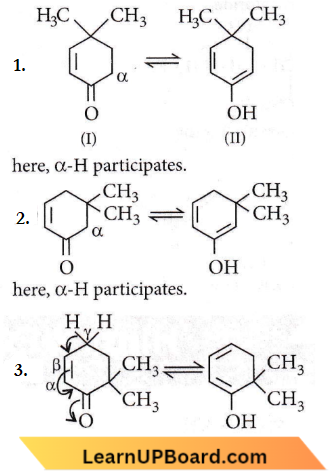
Answer: 2. 1, 2 and 3
In keto-enol tautomerism,
Chemistry MCQs Organic Chemistry NEET
Question 34. The enolic form of ethyl acetoacetate as shown below has
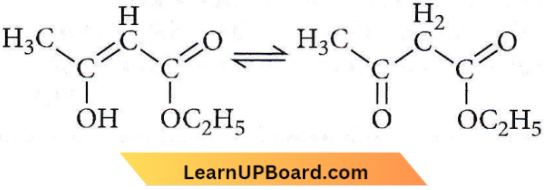
- 9 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
- 9 sigma bonds and 1 pi-bond
- 18 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
- 16 sigma bonds and 1 pi-bond.
Answer: 3. 18 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
The enolic form of ethyl acetoacetate has 18 σ-bonds and 2π-bonds.
Question 35. Which one of the following pairs represents stereoisomerism?
- Structural isomerism and geometrical isomerism
- Optical isomerism and geometrical isomerism
- Chain isomerism and rotational isomerism
- Linkage isomerism and geometrical isomerism
Answer: 2. Optical isomerism and geometrical isomerism
Question 36. The molecular formula of diphenylmethane,
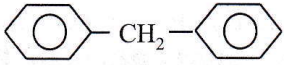
How many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom?
- 6
- 4
- 8
- 7
Answer: 2. 4
Only four structural isomers are possible for mono-chlorinated diphenylmethane.
Question 37. Tautomerism is exhibited by
- R3CNO2
- RCH2NO2
- (CH3)3CNO
- (CH3)2NH
Answer: 2. RCH2NO2
It is a special type of functional isomerism, in which both the isomers are represented by one and the same substance and are always present in equilibrium. It is exhibited by nitroalkane (RCH2NO2) and isonitroalkane.
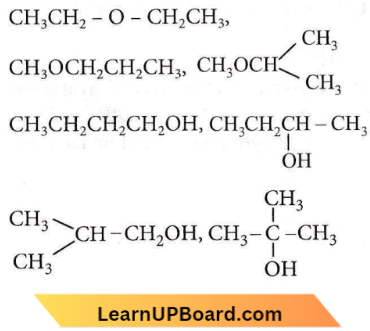
Question 38. The number of isomers in C4H10O will be
- 7
- 8
- 5
- 6
Answer: 1. 7
There are 7 isomers in C4H10O. Out of these, 4 are alcohols and 3 are ethers.
Question 39. Isomers of a substance must have the same
- Structural formula
- Physical properties
- Chemical properties
- Molecular formula.
Answer: 4. Molecular formula.
Isomers must have the same molecular formula but a different structural formula.
Organic Chemistry quiz for NEET
Question 40. How many chain isomers could be obtained from the alkane C6H14?
- Four
- Five
- Six
- Seven
Answer: 2. Five
5-chain isomers are obtained from alkane C6H14
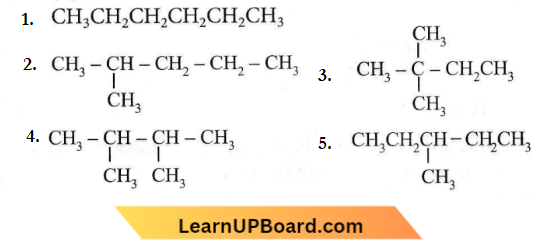
Question 41. A tertiary butyl carbocation is more stable than a secondary butyl carbocation because of which of the following?
- -I effect of – CH3 groups
- +R effect of – CH3 groups
- -R effect of – CH3 groups
- Hyperconjugation
Answer: 4. Hyperconjugation
tert-Bttylcarbocation, (CH3)2C+ is more stable than sec-butyl carbocation (CH3)2C+H due to hyperconjugation.
⇒ \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\) has nine C – H bonds while \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\) has six C – H bonds. Thus, there are more hyperconjugative structures in tert-butyl carbocation.
Question 42. The most stable carbocation, among the following, is
- (CH3)3 C—CH—CH3
- CH3—CH2—CH—CH2—CH3
- CH3—CH—CH2—CH2—CH3
- CH3—CH2—CH2
Answer: 3. CH3—CH—CH2—CH2—CH3
Among the given carbocations, \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3\) is most stable carbocation.
As is consists of a maximum number of u-hydrogens and is stabilised by hyperconjugation.
Organic Chemistry quiz for NEET
Question 43. Which of the following is correct with respect to- I effect of the substituents? (R = alkyl)
- – NH2 < – OR < – F
- – NR2 < – OR < – F
- – NH2 > – OR > – F
- – NR2 > – OR > – F
Answer: 1. – NH2 < – OR < – F and 2. – NR2 < – OR < – F
I-effect increases on increasing the electro negativity of the atom.
∴ -NH2<-OR<-F (-I effect)
Also, – NR2 < – OR < – F (-I effect)
Question 44. Which of the following carbocations is expected to be most stable?
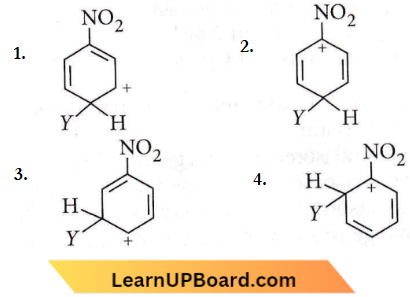
Answer: 3
-NO2 group is meta-directing, thus will stabilize an electrophile at m-position.
Question 45. The correct statement regarding electrophiles is
- Electrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from another electrophile
- Electrophiles are generally neutral species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile
- Electrophiles can be either neutral or positively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile
- Electrophiles is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile.
Answer: 3. Electrophiles can be either neutral or positively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile
Question 46. Which of the following statements is not correct for a nucleophile?
- Ammonia is a nucleophile.
- Nucleophiles attack low-density sites.
- Nucleophiles are not electron-seeking.
- A nucleophile is a Lewis acid.
Answer: 4. Nucleophile is a Lewis acid.
Nucleophiles are electron-rich species hence, they are Lewis bases.
NEET MCQs on Organic Chemistry
Question 47. Treatment of cyclopentanone 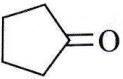 with methyl lithium gives which of the following species?
with methyl lithium gives which of the following species?
- Cyclopentanonyl radical
- Cyclopentanonyl biradical
- Cyclopentanonyl anion
- Cyclopentanonyl cation
Answer: 3. Cyclopentanonyl anion
Question 48. Which of the following is the most correct electron displacement for a nucleophilic reaction to take place?
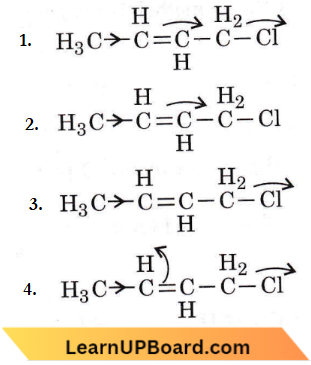
Answer: 1. Nucleophiles will attack a stable carbocation (SN1 reaction).
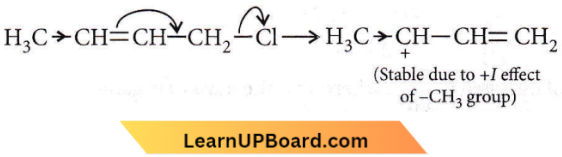
Question 49. Consider the following compounds:
Hyperconjugation occurs in
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
- 1 only
- 2 only.
Answer: 1. 3 only
Hyperconjugation can occur only in compound 3 as it has an α-hydrogen atom.
NEET MCQs on Organic Chemistry
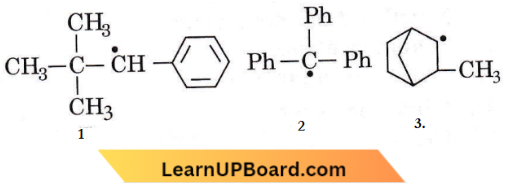
Question 50. In which of the following compounds, does the C—Cl bond ionisation give the most stable carbonium ion?
Answer: 4
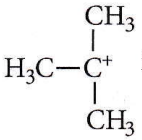 is most stable due to hyperconjugation.
is most stable due to hyperconjugation.
Question 51. The radical 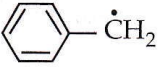 is aromatic because it has
is aromatic because it has
- 7 p-orbitals and 7 unpaired electrons
- 6 p-orbitals and 7 unpaired electrons
- 6 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons
- 7 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons.
Answer: 3. 6 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons
Question 52. Arrange the following in increasing order of stability.
- 5< 4<3<1<2
- 4<5<3<1<2
- 1<5<4<3<2
- 5<4<3<2<1
Answer: 1. 4<3<1<2
The greater the number of electron-donating alkyl groups (+1 effect), the greater the stability of carbocations.
+I effect is in the order:
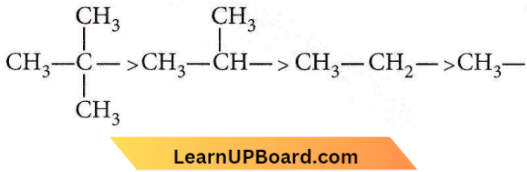
NEET MCQs on Organic Chemistry
The more the number of hyperconjugation structures of carbocations, the more is the stability.
Hence, the order of stability of carbocations is 5<4<3<1<2.
Question 53. What is the hybridization state of benzyl carbonium ion ![]()
- sp²
- spd²
- sp²d
- sp³
Answer: 1. sp²
Question 54. Homolytic fission of the following alkanes forms free radicals CH3 — CH3, CH3 — CH2 — CH3, (CH3)2 CH — CH3, CH3 — CH2 — CH(CH3)2. Increasing the order of stability of the radicals is
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \dot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)\(<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \dot{\mathrm{C}}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)\(<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \dot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \dot{\mathrm{C}}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)\(<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \dot{\mathrm{C}}<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \dot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \dot{\mathrm{C}}<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \dot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3\)\(<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2<\mathrm{CH}_3-\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)\(<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \dot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_3<\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \dot{\mathrm{C}}\)
Homolytic fission of the following alkanes forms free radicals CH3 — CH3, CH3 — CH2 — CH3, (CH3)2 CH — CH3, CH3 — CH2 — CH(CH3)2.
The more the number of hyperconjugation structures, the greater is the stability.
Question 55. Which one is a nucleophilic substitution reaction among the following?
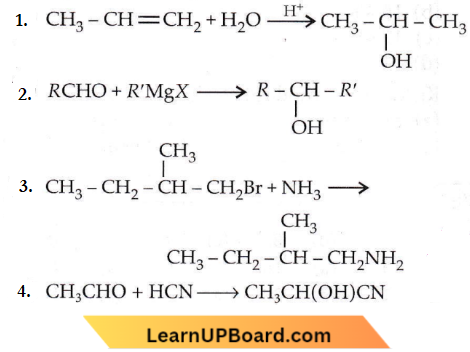
Answer: 3
A nucleophilic substitution reaction involves the displacement of a nucleophile by another.
Question 56. Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic reagents?
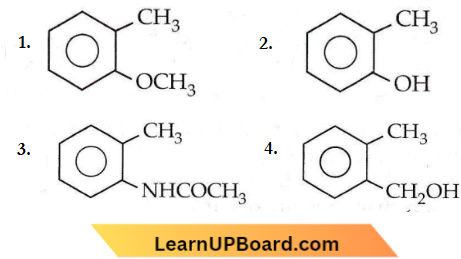
Answer: 2
+R effect of the -OH group is greater than that of the -OCH3 group.
Question 57. Which of the following species is not electrophilic in nature?
- \(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{Cl}}\)
- BH3
- H3O+
Answer: 3. H3O+
Organic Chemistry NEET question bank
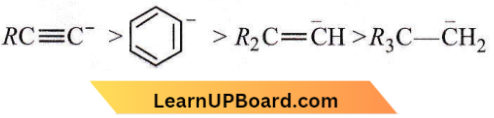
Question 58. The stability of carbanions in the following:

is in the order of
- (4) > (2) > (3) > (1)
- (1) > (3) > (2) > (4)
- (1) > (2) > (3) > (4)
- (2) > (3) > (4) > (1)
Answer: 3. (1) > (2) > (3) > (4)
The higher the no. of electron-releasing groups lower be stability of carbanion, and vice-versa. So, the order of stability of carbanions is
Question 59. For (1) I–, (2) Cl–, and (3) Br–, the increasing order of nucleophilicity would be
- CI– < Br– < I–
- I– < Cl– < Br–
- Br– < Cl– < I–
- I– < Br– < Cl–
Answer: 1. Cl– < Br– < I–
In the case of different nucleophiles, but present in the same group in the periodic table, the larger is the atomic mass, the higher is the nucleophilicity. Hence, the increasing order of nucleophilicity of the halide ions is F–<Cl–<Br–<I–.
Question 60. Which amongst the following is the most stable carbocation?
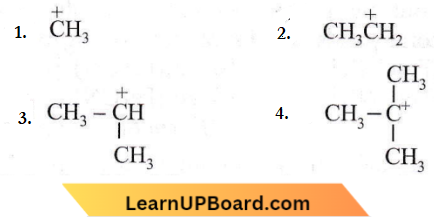
Answer: 4
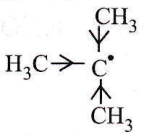
3° carbon is more stable due to the stabilization of the charge by three methyl groups (or +I effect). It can also be explained on the basis of hyperconjugation. The greater the number of hyper conjugative α-H atoms, the more the hyperconjugation structures and the more will be stability.
Question 61. Which of the following is the most stable carbocation (carbonium ion)?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{CH}}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{C}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
Answer: 3. \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{C}\)
3° > 2° > 1° The more the delocalisation of the positive charge, the more is its stability.
Question 62. Cyclic hydrocarbon ‘A’ has all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in the plane. All the carbon-carbon bonds have the same length, less than 1.54 Å, but more than 1.34 Å. The bond angle will be
- 109°28′
- 100°
- 180°
- 120°
Answer: 4. 120°
Cyclic hydrocarbon ‘A’ has all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in the plane. All the carbon-carbon bonds have the same length, less than 1.54 Å,but more than 1.34 Å.
All the properties mentioned in the question suggest that it is a benzene molecule. Since in benzene, all carbons are sp²-hybridised, therefore, C – C – C angle is 120°
Organic Chemistry NEET question bank
Question 63. Paper chromatography is an example of
- Adsorption chromatography
- Partition chromatography
- Thin layer chromatography
- Column chromatography.
Answer: 2. Partition chromatography
Paper chromatography is a type of partition chromatography.
Question 64. The most suitable method of separation of 1:1 mixture of ortho and para-nitrophenols is
- Chromatography
- Crystallisation
- Steam distillation
- Sublimation.
Answer: 3. Steam distillation
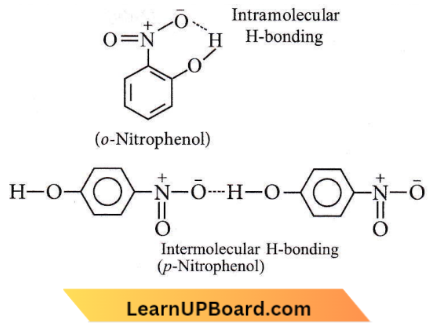
The o- and p-nitrophenols are separated by steam distillation since the o-isomer is steam volatile due to intramolecular H-bonding while-isomer is not steam volatile due to the association of molecules by intermolecular H-bonding.
Question 65. The best method for the separation of naphthalene and benzoic acid from their mixture is
- Distillation
- Sublimation
- Chromatography
- Crystallisation.
Answer: 4. Crystallisation.
Both naphthalene and benzoic acid are sublimable. Hence they cannot be separated by sublimation method. They can be separated by crystallisation with hot water. Benzoic acid dissolves in hot water whereas naphthalene does not.
Question 66. In steam distillation of toluene, the pressure of toluene in vapour is
- Equal to the pressure of a barometer
- Less than the pressure of a barometer
- Equal to vapour pressure of toluene in simple distillation
- More than the vapour pressure of toluene in simple distillation.
Answer: 2. Less than the pressure of the barometer
In steam distillation of toluene, the pressure of toluene in the vapour is less than the pressure of a barometer, because it is carried out when a solid or liquid is insoluble in water and is volatile with steam but the impurities are non-volatile.
Question 67. Which of the following techniques is most suitable for the purification of cyclohexanone from a mixture containing benzoic acid, isoamyl alcohol, cyclohexane and cyclohexanone?
- Sublimation
- Evaporation
- Crystallisation
- IR spectroscopy
Answer: 4. IR spectroscopy
In IR spectroscopy, each functional group appears at a certain peak (in cm-1). So, cyclohexanone can be identified by carbonyl peak.
Organic Chemistry NEET question bank
Question 68. In Lassaignes extract of an organic compound, both nitrogen and sulphur are present, which gives blood red colour with Fe due to the formation of
- \(\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_5 \mathrm{NOS}\right]^{4-}\)
- \([\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{SCN})]^{2+}\)
- \(\mathrm{Fe}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_3 \cdot \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{NaSCN}\)
Answer: 2. \([\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{SCN})]^{2+}\)
In case, nitrogen and sulphur both are present in an organic compound, sodium thiocyanate is formed. It gives a blood-red colour and no Prussian blue since there is no free cyanide.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Na}+\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{N}+\mathrm{S} \longrightarrow \mathrm{NaSCN}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Fe}^{3+}+\mathrm{SCN}^{-} \longrightarrow \underset{\text { Blood red }}{[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{SCN})]^{2+}}\)
Question 69. Nitrogen detection in an organic compound is carried out by the Lassaignes test. The blue colour formed corresponds to which of the following formulae?
- \(\mathrm{Fe}_3\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Fe}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_3\)
- \(\mathrm{Fe}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_2\)
- \(\mathrm{Fe}_5\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_3\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{Fe}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_3\)
⇒ \(\underset{\text { Sodium ferrocyanide }}{3 \mathrm{Na}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]}+2 \mathrm{Fe}_2\left(\mathrm{SO}_4\right)_3 \rightarrow \underset{ \text { Ferric ferrocyanide
(Prussian blue) }}{\mathrm{Fe}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]_3}+6 \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
Question 70. The Lassaignes extract is boiled with a cone. HNO3 while testing for halogens. By doing so it
- Decomposes Na2S and NaCN formed
- Helps in the precipitation of AgCl
- Increases the solubility product of AgCl
- Increases the concentration of NO–3 ions.
Answer: 1. Decomposes Na2S and NaCN, formed
In the case of Lassaigne’s test of halogens, it is necessary to remove sodium cyanide and sodium sulphide from the sodium extract if nitrogen and sulphur are present. This is done by boiling the sodium extract with conc. HNO3.
⇒ \(\mathrm{NaCN}+\mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{NaNO}_3+\mathrm{HCN} \uparrow \)
⇒ \(\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{~S}+2 \mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaNO}_3+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S} \uparrow\)
Question 71. In the sodium fusion test of organic compounds, the nitrogen of the organic compound is converted into
- Sodamide
- Sodium cyanide
- Sodium nitrite
- Sodium nitrate.
Answer: 2. Sodium cyanide
Sodium cyanide (Na + C + N → NaCN)
Question 72. Lassaignes test is used in qualitative analysis to detect
- Nitrogen
- Sulphur
- Chlorine
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these.
Organic Chemistry NEET question bank
Question 73. A blue colouration is not obtained when
- Ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate
- Copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6]
- Ferric chloride reacts with sod. ferrocyanide
- Anhydrous CuSO4 is dissolved in water.
Answer: 2. Copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6]
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{CuSO}_4+\mathrm{K}_4\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right] \rightarrow \underset{\text { chocolate ppt. }}{\mathrm{Cu}_2\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]+2 \mathrm{~K}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4}\)
Question 74. Kjeldahl’s method for the estimation of nitrogen can be used to estimate the amount of nitrogen in which one of the following compounds?
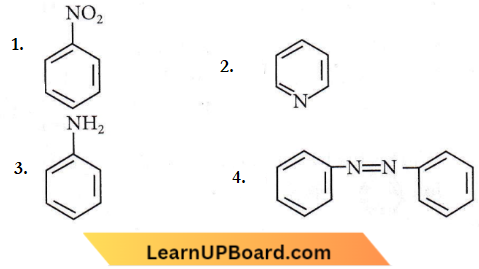
Answer: 3
Kjeldahtr’s method is not applicable to compounds containing nitrogen in the nitro group, azo groups and nitrogen present in the ring (for example, pyridine).
Question 75. In Dumas’s method for estimation of nitrogen, 0.25 g of an organic compound gave 40 mL of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 725 mm pressure. If the aqueous tension at 300 K is 25 mm, the percentage of nitrogen in the compound is
- 16.76
- 15.76
- 17.36
- 18.20
Answer: 1. 16.76
In Dumas’s method for estimation of nitrogen, 0.25 g of an organic compound gave 40 mL of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 725 mm pressure. If the aqueous tension at 300 K is 25 mm,
Mass of organic compound = 0.25 g
Experimental values, At STP
⇒ \(V_1=40 \mathrm{~mL}, V_2=?, T_1=300 \mathrm{~K}, T_2=273 \mathrm{~K}\)
⇒ \(P_1=725-25=700 \mathrm{~mm}, P_2=760 \mathrm{~mm}\)
⇒ \(\frac{P_1 V_1}{T_1}=\frac{P_2 V_2}{T_2} \Rightarrow V_2=\frac{P_1 V_1 T_2}{T_1 P_2}=\frac{700 \times 40 \times 273}{300 \times 760}=33.52 \mathrm{~mL}\)
22400 mL of \(\mathrm{N}_2\) at STP weighs = 28 g
∴ 33.52 mL of \(\mathrm{N}_2\) at STP weighs = \(\frac{28 \times 33.52}{22400}=0.0419 \mathrm{~g}\)
% of \(\mathrm{N}=\frac{\text { Mass of nitrogen at STP }}{\text { Mass of organic compound taken }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{0.0419}{0.25} \times 100=16.76 \%\)
Organic Chemistry NEET question bank
Question 76. In Kjeldahl’s method for estimation of nitrogen present in a soil sample, ammonia evolved from 0.75 g of sample neutralized 10 mL of 1 M H2SO4. The percentage of nitrogen in the soil is
- 37.33
- 45.33
- 35.33
- 43.33
Answer: 1. 37.33
In Kjeldahl’s method for estimation of nitrogen present in a soil sample, ammonia evolved from 0.75 g of sample neutralized 10 mL of 1 M H2SO4.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+2 \mathrm{NH}_3 \rightarrow\left(\mathrm{NH}_4\right)_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\)
10 mL of 1 M H2SO4 = 10 m mol
[M x V(mL) = mmol]
The acid used for the absorption of ammonia = 10 mL of 2 N (or 1 M) H2SO4
% of N = \(\frac{1.4 \times N \times V}{W}=\frac{1.4 \times 2 \times 10}{0.75}=37.33 \%\)
Organic Chemistry NEET question bank
Question 77. In Dumas’ method of estimation of nitrogen 0.35 g of an organic compound gave 55 mL of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 715 mm pressure. The percentage composition of nitrogen in the compound would be (aqueous tension at 300 K = 15 mm)
- 15.45
- 16.45
- 17.45
- 14.45
Answer: 2. 16.45
In Dumas’ method of estimation of nitrogen 0.35 g of an organic compound gave 55 mL of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 715 mm pressure.
Given: V1 = 55mL, V2 = ?
P1 = 715 – 15 = 700 mm, P2 = 760 mm
T1 = 300K, T2 = 273K
General sas equation, \(\frac{P_1 V_1}{T_1}=\frac{P_2 V_2}{T_2}\)
Volume of nitrogen at STP, \(V_2=\frac{P_1 V_1 T_2}{P_2 T_1}=\frac{700 \times 55 \times 273}{760 \times 300}=46.099 \mathrm{~mL}\)
% of nitrogen = Vz , where, W= the mass of organic compound.
% of N = \(=\frac{46.099}{8 \times 0.35}\) = 16.46
Question 78. Kjeldahl’s method is used in the estimation of
- Nitrogen
- Halogens
- Sulphur
- Oxygen.
Answer: 1. Nitrogen
