UP Board Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Force And Laws Of Motion Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The resultant force acting on a body is zero, then a
- The body is in unequilibrium
- The body is in equilibrium
- The body moves with constant acceleration
- Body moves with retardation
Answer: 2. Body is in equilibrium
When the resultant force acting on a body is zero, then the body will be in equilibrium.
Question 2. If a ball thrown up in a moving car comes back to the boy’s hands, then it explains
- Newton’s first law of motion
- Newton’s second law of motion
- Newton’s third law of motion
- law of conservation of momentum
Answer: 1. The balls come back to the boy’s hand due to the law of inertia (Newton’s first law of motion). During the period, when the ball is in the air, the ball covers the same horizontal distance as the train and so it comes back to the boy’s hand.
Question 3. A thrust of 200 N is applied on the surface of the wall, then the normal reaction on the wall is
- 200 N
- 100 N
- 400 N
- 300 N
Answer: 1. 200 N
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction, therefore the normal reaction is 200 N.
Question 4. A bus of mass 500 kg is moving with a velocity of 5 m/s and is acted upon by a forward force of 500 N due to the engine and retarding force of 200 N due to friction velocity of the bus after 20 s will be
- 15 m/s
- 17 m/s
- 19 m/s
- 21 m/s
Answer: 2. 17 m/s
Given, m = 500 kg,
u=5 m/s and t=20 s
Resultant force, F=500-200=300 N
Acceleration, a=\(\frac{F}{m}=\frac{300}{500}=0.6 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\)
By equation of motion,
v=u+a t=5+0.6 \(\times 20=17 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
Question 5. 1 dyne is equal to
- \(10^5 \mathrm{~N}\)
- \(10^7 \mathrm{~N}\)
- \(10^{-5} \mathrm{~N}\)
- \(10^{-7} \mathrm{~N}\)
Answer: 3. \(10^{-5} \mathrm{~N}\)
Dyne is the unit of force in the CGS system.
1 N = \(\frac{1 \mathrm{~kg}-\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{s}^2}=\frac{1000 \mathrm{~g} \times 100 \mathrm{~cm}}{1 \mathrm{~s}^2}\)
1 dyne =\(\frac{1}{10^5} \mathrm{~N}=10^{-5} \mathrm{~N}\)
Question 6. 1 kg-wt is equal to
- 9.8 kg
- 1 kg
- 9.8 N
- 98 N
Answer: 3. 9.8 N
1 kg-wt = mg N = 1 x 9.8 N = 9.8 N
Question 7. A truck moving with a speed of 54 km/h. The truck driver applied brakes suddenly and brings the truck to rest in 5 s, then the average retarding force on the truck, if the mass of the truck and driver is 400 kg, will be
- 1200 N
- 600 N
- 800 N
- 500 N
Answer: 1. 1200 N
Given, u=54 \(\mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}=54 \times \frac{5}{18} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
=15 m/s, v=0 and t=5 s
Retardation, a=\(\frac{v-u}{t}=\frac{0-15}{5}=-3 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\)
Average retarding force, F=m a=400 \(\times\) 3=1200 N
Question 8. Two forces acting on a body in different directions, then acceleration produced in the body is due to
- Resultant of both forces
- The sum of both forces
- Difference between both forces
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Resultant of both forces
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the resultant force on a body is responsible for its acceleration.
Question 9. Two forces F1 and F2 are acting on a body as shown in the figure, then acceleration in the body is
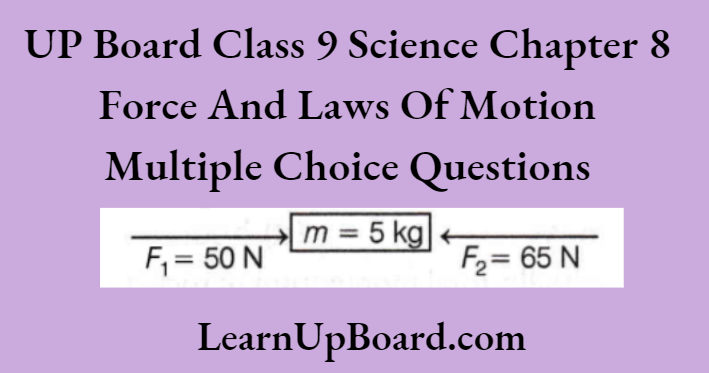
- 23 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2 \)
- 3 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2 \)
- 2 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2 \)
- 22 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2 \)
Answer: 2. 3 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2 \)
The resultant force on a body,
F=\(F_2-F_1=65-50=15 \mathrm{~N}\)
By Newton’s second law of motion,
F=m a \(\Rightarrow\) 15=5 a
a=3 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\)
Question 10. The dirty Blanket is beaten with a stick to remove dust particles. Which law holds good for this?
- Law of conservation of momentum
- Law of inertia
- Law of impulse
- Law of conservation of energy
Answer: 2. Law of inertia
When we beat a blanket with the help of a stick, then it comes into motion. However, the dust particles continue to rest due to inertia and get detached from the blanket.
Question 11. A bullet of 20 g strikes a sandbag at a speed of 200 m/s and gets embedded after traveling 2 cm, then the resistive force exerted by sand on the bullet is
- 2 \(\times 10^3 \mathrm{~N}\)
- 2 \(\times 10^4 \mathrm{~N}\)
- 2 \(\times 10^6 \mathrm{~N}\)
- 2 \(\times 10^5 \mathrm{~N}\)
Answer: 2. 2 \(\times 10^4 \mathrm{~N}\)
Given, u=200 \(\mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\), v=0, s=0.02 m
and m=20 \(\mathrm{~g}=20 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~kg}\)
From the third equation of motion,
⇒ \(v^2 =u^2+2 a s\)
a =\(\frac{v^2-u^2}{2 s}\)
=\(\frac{(0)^2-(200)^2}{2 \times 0.02}\)
=-\(10^6 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\)
Negative sign indicates retardation.
Resistive force, F =m a=20 \(\times 10^{-3} \times 10^6\)
=2 \(\times 10^4 \mathrm{~N}\)
Question 12. Impulse is equal to
- Rate of change in momentum
- Rate of change in force
- Change in reaction force
- Change in momentum
Answer: 4. Change in momentum
Impulse, I =F \(\times \Delta t\)
= \(\frac{\Delta p}{\Delta t} \cdot \Delta t=\Delta p\) = Change in momentum.
Question 13. Jetplanes and rockets work on the principle of conservation of
- Energy
- Momentum
- Mass
- Heat
Solution: 2. Momentum
Initially, the total momentum of the rocket and its fuel is zero, when the fuel is exploded. The burnt gases are allowed to escape through a nozzle with very high downward velocity and with large momentum in a downward direction.
To conserve this momentum, the rocket acquires an equal momentum in the upward direction and hence starts moving upwards.
Question 14. A Bullet Of Mass 30g is fired horizontally with a velocity of 120 m/s from a pistol of mass 2 kg, the recoil velocity of the pistol is
- 1.6 m/s
- 2.8 m/s
- 2.4 m/s
- 1.8 m/s
Answer: 4. 1.8 m/s
By the law of conservation of momentum,
Initial momentum = Final momentum 0=0.03×120 + 2xv
where v is recoil velocity.
0 = 3.6 + 2v
v=\(\frac{-3.6}{2}=-1.8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
Question 15. An object of mass 4 kg moves with a velocity of 4 m/s, then its momentum will be
- 16 m/s
- 4 m/s
- 16 kg-m/s
- 4 kg-m/s
Solution: 3. 16 kg-m/s
Momentum,p = mv = 4x 4 = 16kg-m/s
Question 16. A force acts on a body of mass 5 kg and changes its velocity from 8 m/s to 12 m/s in 4s, then the magnitude of the force is
- 8 N
- 4 N
- 5 N
- 6 N
Answer: 3. 5 N
According to Newton’s second law of motion, Force = Rate of change in momentum
F=\(\frac{m(v-u)}{t}=\frac{5(12-8)}{4}=5 \mathrm{~N}\)
Question 17. When a person jumps down from a tower into a stretched tarpaulin, then receives
- Greater injury
- Less injury
- No injury
- None of the above
Answer:
When a person jumps, the tarpaulin gets depressed at the place of impact, therefore impact time interval increases, As a result, a person experiences a very small force, and hence he receives no injury.
Question 18. A cricket ball of mass 0.25 kg moving with a velocity of 10 m/s is brought to rest by a player in 0.1 seconds, and then the impulse exerted by the player is
- 2.5 N-s
- 1.5 N-s
- 25 N-s
- 30 N-s
Answer: 1. 2.5 N-s
Impulse = Change in momentum -m{v -u)
= 0.23 (0-10) = -2.3 N-s
A negative sign indicates the direction of the impulse is opposite to the motion of the ball.
