UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
- Explain the need for cell division;
- Describe the cell cycle and list its various phases;
- Describe two types of cell division and list their phases;
- Draw diagrams to explain the sequence of events in the two types of cell divisions;
- Tabulate the differences between mitosis and meiosis;
- State the significance mitosis and meiosis;
- Explain how chromosome number is maintained during mitosis while it is halved during meiosis;
- Recognize homologous chromosomes and crossing over as a means of variations.
All living beings are made up of cells. A cell is the structural and functional unit of life. New cells arise from the pre-existing cells by the process of cell division.
Cell division occurs in all living organisms. In unicellular organisms, cell division directly produces two individuals. In multicellular organisms, life begins from a single cell, the zygote, which divides and redivides into a number of cells to form a complete organism.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
In multicellular organisms, there are two types of cells.
- The somatic cells or the body cells – They form the body of an organism.
- The reproductive cells or sex cells – They are gamete-producing cells. They take part in reproduction of the organism.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Why Do Cells Divide?
The cells divide to produce new cells.
The new cells are produced for:
- Growth: During cell division, a single cell divides to produce new cells that in turn devide and redivide to form a cluster of similar cells. These cells form tissues and organs. Cell division is essential for the growth of an organism.
- Replacement of dead cells: The existing cells in our body a destroyed regularly. These cells should be replaced by new cells for the normal functioning of the body. Cell division of the parent cells in the bone marrow helps in the replacement of dead cells with the new cells.
- Repair of tissues: In case of injuries or normal wear and tear of tissues, cells divide and new cells fill up the broken cut ends to heal wounds. Thus, cell division is essential for the repair of the tissues.
- Reproduction: The sex cells (sperms and eggs) are formed because of cell division (meiosis). These sex cells contain only half the normal number of chromosomes. During fertilization, these sex cells combine to form zygote. Thus, cell division is essential for reproduction.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division The Cell Cycle
A cell cycle or a cell division cycle is a series of events in a cell, leading to its division and duplication of its DNA to produce two daughter cells. Mitosis is only one phase of the cell cycle.
A cell cycle starts from the time a new cell is formed and ends when it completes its own division. Then the cell cycle starts again for each new daughter cell formed. A cell cycle has two basic phases:
- Interphase
- M phase or Mitosis
A cell cycle may be defined as a series of events in a cell leading to an increase in the mass and cytoplasmic components of the cell, duplication of DNA, and then division of nucleus and cytoplasm of the cell and finally forming two daughter cells. A cell cycle extends from the time a cell is formed till the time it completes division.
Interphase
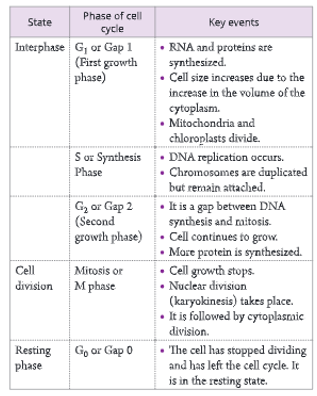
During interphase, a cell prepares itself for cell division. The interphase is the longest phase of a cell cycle. It is metabolically the most active phase of the cell cycle. It has three sub-phases:
- G₁ or first growth phase: This is the first ‘Gap’ (interval) phase of the cell growth before DNA replication. During this phase:
- RNA and proteins are synthesized. Cell size increases due to the increase in the volume of the cytoplasm to almost double.
- Mitochondria (in plant and animal cells) and chloroplasts (in plant cells) divide.
- The cell is ready for DNA synthesis.
- Now the cell enters either the resting phase (Go phase) or a synthesis phase (S phase).
- S or synthesis phase: This is the phase of DNA replication. The DNA is synthesized and chromosomes are duplicated during this phase but they remain attached.
- G₂ or second growth phase: It is the second ‘Gap’ phase after DNA replication. It is a shorter phase in which RNA and proteins necessary for cell division continue to be synthesized. Now the cell becomes ready for next the cell division, i.e. mitosis.Go phase (Resting phase): This is the phase when the cell has stopped dividing and left the cell cycle. It is the resting state of a cell. The cell remains metabolically active.
M Phase Or Mitosis
- During M-phase, cell growth stops. Nuclear division (prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase) takes place, which is usually followed by cytoplasmic division. The various phases of cell cycle are given in
The cell cycle does not go on endlessly. It stops permanently at some point of time.
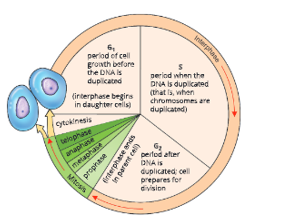
- Its duration differs from one cell type to another. For example, nerve cells (neurons) in our brain once formed in embryo do not divide further. All blood cells form and replace the worn-out cells at an average rate of 2-3 million each second. Surface skin cells are continuously replaced by underlying cells. Liver cells divide once every 1-2 years to replace damaged cells.
Types Of Cell Division
There are two types of cell division in higher organisms.
- Mitosis – Occurs in somatic cells, leading to growth and development.
- Meiosis – Occurs in reproductive cells or sex cells, leading to gamete formation.
Karyokinesis and cytokinesis The cell division has two phases. First is the nuclear division or karyokinesis, leading to division of the parent nucleus into daughter nuclei. This is followed by the division of cytoplasm or cytokinesis, leading to the division of the parent cell into daughter cells.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Mitosis
- (Gk. mitos: thread)
Mitosis or mitotic cell division is an equational division in which one parent cell divides to form - Two daughter cells. The daughter cells formed areidentical to each other and also to the parent cell inevery respect. In mitosis, the same chromosome number of the parent cell is maintained at eachstage of the mitotic division of the cell and henceit is referred to as equational division or homotypic division I
Interphase – The Resting Phase
- Interphase is the growth period between two successive divisions of a cell. Thus, it is a preparatory phase just before the cell starts dividing. This stage is said to be a resting phase because no external change in chromosomes is visible. However, the
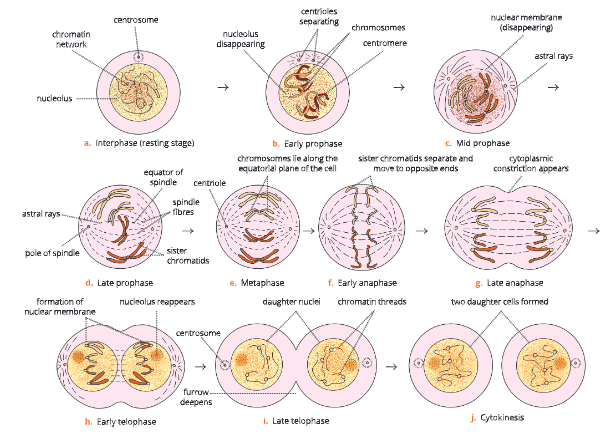
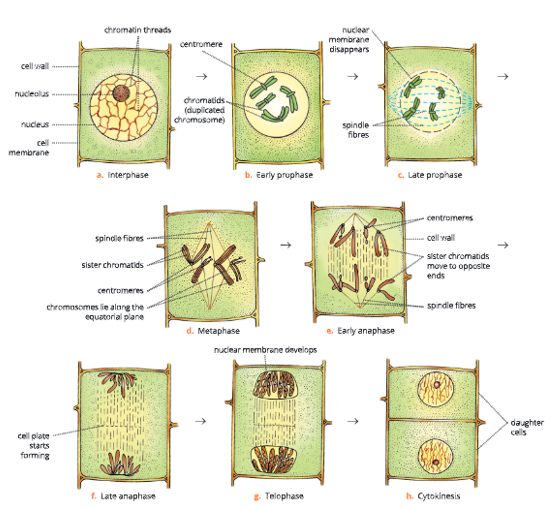
- cell is metabolically most active and prepares itself for the division by synthesizing almost the double amount of DNA (the genetic material) and RNA. The volume of cytoplasm and nucleus increases during this stage. However, chromosomes are not yet distinguished.
Karyokinesis – Phases of mitosis
- The nuclear division or karyokinesis during mitosis occurs in four phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- Somatic cells are body cells (like skin cells, brain cells, etc.) that contain normal number of chromosomes (called diploid number, 2n).
- Gametes are sex cells (sperm and ova) that contain half the normal number of chromosomes (called haploid number, n).
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Prophase (Gk. pro: first, phasis: stage)
- This is the first and the longest phase of mitosis.
- The chromatin material undergoes condensation (becomes short and thick) and changes into thread-like structures called chromosomes.
- Each chromosome duplicates to form two sister chromatids. The two sister chromatids lie close to each other and remain attached at a point called centromere.
- As prophase advances, the chromosomes become shorter and thicker (condensed).
- In animal cells, the centrosome initiates and regulates the cell division. The centrosome splits into two small round bodies called centrioles. The two centrioles migrate to the opposite poles of the cell.
- Soon two radiating fibres known as Between the separating centrioles, spindle fibres asters are formed around the centriole at each pole. are formed by the aster.
- Towards the end of the prophase, the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane disappear.
- The duplicated chromosomes start moving towards the equator.
Spindle formation in plant cell
- In plant cells, no centrosome (centriole) is there and asters are not formed. However, spindle formation still occurs and spindle fibres are formed by microtubules (cytoplasmic strands).
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Metaphase (Gk. meta: between, phasis: stage)
- The chromosomes arrange themselves on the equatorial plane.
- Each chromosome is attached by a spindle fibre at its centromere.
- Small disc-shaped structures are present at the surface of centromere. These are called kinetochores. Chromosomes lie at the equator with one chromatid connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibres from one pole and another chromatid connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibres of opposite pole.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Anaphase (Gk. ana: back, phasis: stage)
- This is the shortest phase of mitosis.
- The centromere of each chromosome divides into two halves (sister chromatids) so that each chromatid has its own centromere.
- The sister chromatids separate and begin to move towards the opposite poles due to the contraction of spindle fibres, and due to the repelling force developed between the sister chromatids.
- Depending on the position of the centromere, the chromosomes appear as U, V or J-shaped.
- The anaphase ends when all the chromatids (now behaving like chromosomes) reach the opposite poles.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Telophase (Gk. telo: end, phasis: stage)
- This is the last phase in karyokinesis (nuclear division). The events of prophase occur in reverse sequence during telophase.
- The chromatids (daughter chromosomes) uncoil, elongate and change into network of chromatin threads.
- The nuclear membrane reappears around the chromatin network at each pole.
- Nucleolus reappears in each daughter nucleus.
- Spindle fibres disappear.
- In animal cells, centrosome organizes itself above the nucleus, thus completing karyokinesis.
The karyokinesis (mitosis proper) is followed by the division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Cytokinesis (Gk. cyto: cell, kinesis: movement)
- It is the division of the cytoplasm to form two daughter cells. It begins during late anaphase and is completed soon after telophase. At the end of the telophase, a furrow appears in the middle of the cell membrane which splits the cytoplasm into two halves to form two daughter cells. Cytokinesis is different in animal and plant cells.
How is cytokinesis different in animal and plant cells?
- In animal cells, a constriction (or furrow) appears in the cell(or plasma) membrane. This constriction deepens by theend of the telophase, finally completing the division ofcytoplasm.
- In plant cells, a cell plate is formed in the centre of thecell at the equator. The cell plate extends on either sideuntil it completely divides the cell into two daughter cellsIn animal cells, cytokinesis starts from the periphery andproceeds towards the centre, but in plant cells, cytokinesisstarts from centre due to the cell plate formation, andextends towards the periphery.
Differences between mitosis in an animal cell and a plant cell is given in
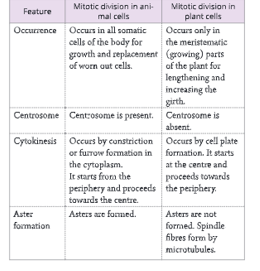
Significance of mitosis
- Mitosis maintains the same number of chromosomes in all the cells of an individual.
In other words, mitosis is an equational division in which two daughter cells produced are identical to each other and even to their parent cell. This type of cell division usually takes place in the somatic cells such as tips of roots, stems, etc. In animals, zygote develops into mature organism through mitotic cell divisions. - It plays a significant role in the replacement of cells lost during wear and tear, and in wound healing.
- It is responsible for the growth of an organism.A fertilized cell develops into an embryo and finally into an adult as a result of mitotic cell division.
- Mitosis helps the cells in maintaining the proper size.
- It is a method of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
- If mitotic cell division becomes uncontrolled, it may cause tumours or cancerous growth.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Meiosis-The ReductionDivision (Gk. meioun: to diminish)
Meiosis takes place in the reproductive cells that produce gametes, i.e. sperms and ova. Meiosis is a modified mitosis in which chromosomes divide once and the nucleus divides twice. As a result of this the number of chromosomes is reduced to half. Thus, the four cells resulting from a meiotic division have a haploid number of chromosomes It means that the number of chromosomes of parent cell (diploid) becomes half in each sex cell. This is because when the male and female gametes fuse during fertilization, the diploid (double) number of chromosome pairs is restored. Meiosis is a reductional division.
Meiosis has two nuclear divisions.
- First meiotic division (reduction division)
- Second meiotic division (mitotic division/ equational division)
Thus, in a meiotic cell division, all the stages, i.e.prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase are repeated twice.
During meiosis, the diploid cells are reduced to haploid cells (number of chromosomes is halved).
Diploid → Haploid
(2n) (n)
In the absence of meiosis, the number of chromosomes will double and the offspring will not be able to survive.
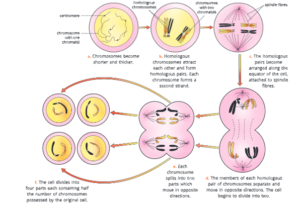
First meiotic division (Meiosis I)
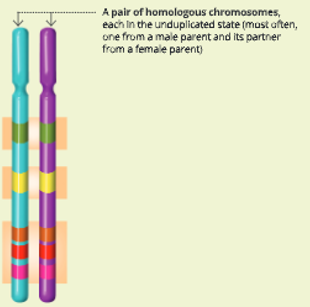
Homologous chromosomes
- These are chromosome pairs, with each pair containing one chromosome from the father and one from the mother. They are not identical. They are similar in length, gene position and location of centromere. The gene, however, contains different alleles.
- Homologous chromosomes come together (associate) and subsequently segregate into daughter cells during meiosis I. Thus, the number of chromosomes is reduced from diploid (double) to the haploid (single) state. That is why it is known as reduction division.
The following events take place during this division.
Pairing of homologous chromosomes
- During prophase I, the longest part of meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes attract each other and come to lie in pairs. The pairing of homologous chromosomes is known as synapsis and the pair is known as bivalent.
Chiasmata formation or crossing over
- Chromosome continues to shorten and thicken. Each chromosome splits lengthwise into two chromatids (sister chromatids) so that each homologous pair now has four chromatids and is termed as tetrad.
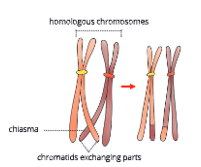
- The non-sister chromatids of a tetrad break open and rejoin each other. This is known as crossing over or chiasmata (singular: chiasma) formation.
- Exchange of some genes or portions of chromatids takes place between paternal and maternal chromatids of a pair of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. This is known as crossing over
- Homologous pairs arrange themselves at equator during metaphase I, the second phase of meiosis I. Nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear.
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Separation Of Homologous Pairs
- The members of homologous chromosomes completely separate from each other and move. towards the opposite poles during anaphase-I. Nuclear membrane reappears, leading to the formation of two daughter nuclei at telophase I.
Second meiotic division (Meiosis 2)
- It is similar to mitosis. During this division, the two chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles. Nuclear membrane reappears and four cells are formed. Finally each cell formed is haploid (n), i.e. it contains half the number of chromosomes of the original cell (diploid, 2n).
Significance of meiosis
- The number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the daughter cells.
- It results in the formation of haploid sex cells (sperms and ova), which after fertilization restore the diploid number of chromosomes in the zygote.
- During crossing over, that occurs in meiosis, parts of chromatids are exchanged between homologous chromosomes which brings about variations in the offspring.
- The four chromatids of a homologous pair of chromosomes are passed on to four different daughter cells. This also causes gametic variation.
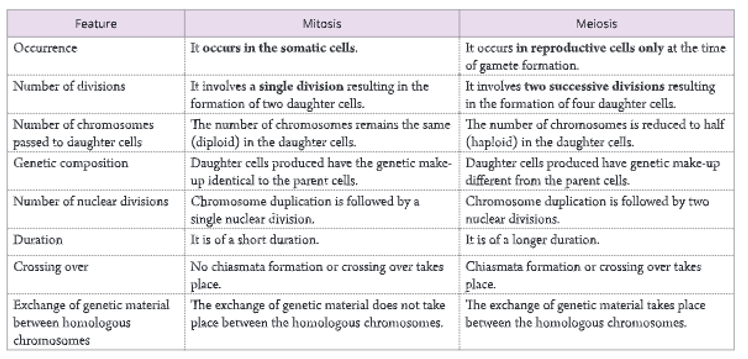
- It prevents the multiplication of chromosomes, and thus maintains the stability of species.Differences between mitosis and meiosisThe major differences between mitosis and meiosis are given in
UP Board Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Summary
- New cells arise from pre-existing cells by the process of cell division.
- Cell division is necessary for growth, replacement of dead cells, healing of wounds, and reproduction.
- A cell division starts when a new cell forms. It proceeds through interphase and ends when the cell reproduces by mitosis and cytokinesis. The cell prepares itself for division during interphase.
- There are two types of cell divisions mitosis and meiosis.
- Mitosis is an equational division required for growth and development. A diploid cell divides to form two genetically identical diploid cells in mitosis.
- Mitosis maintains the same number of chromosomes in all the cells of an individual.
- Meiosis is a special type of cell division which produces sex cells or gametes. It is known as reduction division. One diploid cell divides to produce four genetically different haploid cells as a result of melosis.
- Meiotic division prevents the multiplication of chromosomes, and thus maintains the stability of species
- The cell cycle has following two basic phases – Interphase [first growth phase (G₁), synthesis phase (S) and second growth phase (G₂)] and mitosis.
- Mitosis has four phases prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Meiosis has two nuclear divisions – first meiotic division and second meiotic division.
