UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Concepts
- Sound and its Production
- Propagation of Sound
- Characteristics of Sound
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Abstract
- Sound is produced by a vibrating object.
- The to-and-fro motion of an object is termed a vibration. Vibration is an example of oscillatory motion.
- In human beings, the sound is produced by the voice box, which is also called the larynx.
- Two cords called the vocal cords, are stretched across the larynx in such a way that there is a narrow slit between them for the passage of air. When air is forced through this slit vocal cords vibrate and sound is produced.
- Sound needs a medium to propagate. It cannot travel in a vacuum.
- Sound is received by our outer ear from where it travels down a canal.
- At the end of the ear canal is a tightly stretched, thin membrane called the eardrum.
- The eardrum is just like a stretched rubber sheet. When sound strikes the eardrum, it vibrates. The eardrum then sends vibrations to the inner ear.
- From the inner ear, the signals are further transmitted to the brain and we can hear.
- The number of oscillations per second is called the frequency. It is measured in hertz (Hz).
- The maximum displacement of a vibrating body from its mean position is called amplitude.
- The time taken to complete one oscillation is called the period.
- Amplitude and frequency are the two important properties of any sound.
- The amplitude of the vibrating body producing the sound determines the loudness of the sound. The larger the amplitude of the vibration, the louder the sound is produced.
- Frequency determines the shrillness or pitch of a sound.
- The higher the frequency of vibration, the higher the pitch.
- Sound can also be classified as audible and inaudible.
- Sound of frequencies less than about 20 vibrations per second (i.e. 20 Hz) and more than about
- 20,0 vibrations per second (i.e. 20 kHz) are not audible to the human ear. Such sounds are called inaudible sounds.
- Thus, for a normal human ear, the audible frequency range is roughly between 20 and 20,000 Hz. A sound that is pleasing to the ear is called a musical sound, while an unpleasant sound is called noise.
- Noise pollution may cause many health-related problems such as lack of sleep, hypertension {high blood pressure), anxiety, etc.
- A person who is continuously exposed to a loud sound may suffer from temporary or even permanent hearing impairment.
- Planting trees along the roadside and in the surroundings can reduce noise pollution.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound And Its Production
- A sound is a form of energy which is produced by a vibrating body. In human beings, the larynx helps in; the production of sound. It is situated in the neck at the upper end of the windpipe. Sound is controlled; by the vocal cords. The quality of sound produced from loose and thick vocal cords is different from the ’ sound produced by tight and thin vocal cords.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 1
Aim: To create and feel vibrations
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Procedure:
1. Take a metal plate (or a shallow frying pan) and hang it at a convenient place in such a way that it does not touch any walls.
2. Now strike it with a stick and touch the plate or pan gently with your finger. Note down your observation.
3. Again strike the plate with the stick and hold it tightly with your hands immediately after striking. Note down your observation again.
4. Touch the plate after it stops producing sound. Note down your observation.

Observations: When the plate was struck, sound and vibrations produced were felt on touching the plate gently. The sound produced vanished on holding the plate tightly. When the plate stopped producing the sound, no vibrations were felt.
Conclusions: When a metal object is struck vibrations are produced. Sound is also produced by a vibrating object.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 2
Aim: To produce sound Dv creating vibrations
Procedure:
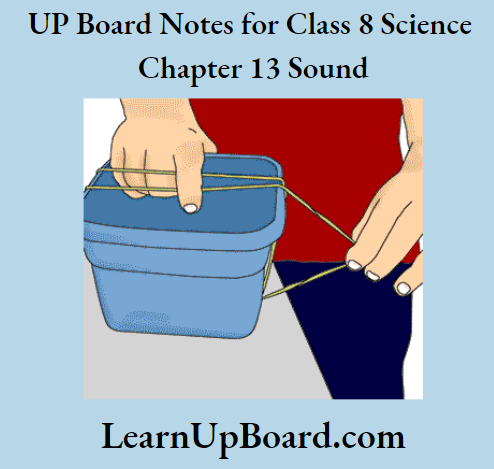
1. Take a rubber band and put it around the longer side of a pencil box
2. Insert two pencils between the box and the stretched rubber and then pluck the rubber band somewhere in the middle. Note down your observations.

Observations: On plucking, the band vibrates and a sound is produced.
Conclusion: Sound is produced by a vibrating object.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 3
Aim: To create waves by producing vibrations
Procedure:
1. Take a metal dish and pour water into it. Strike it at its edge with a spoon
2. Note down your observations.

2. Strike the plate again and then touch it. Note down your observations.
3. Strike the dish again and look at the surface of the water.
4. Then hold the dish and note down your observations.
Observations: In steps I and 2, both sound and vibrations were produced. In step 3, waves were seen on the water’s surface. But on holding the dish, vibrations stopped and there were no waves.
Conclusion: Vibrations produce sound as well as waves.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 4
Aim: To make an Ektara and identify its vibrating part
Procedure:
1. Take a hollow coconut shell or an earthen pot and make a musical instrument Ektara.
2. Play this instrument and identify its vibrating part.

Observations: The vibrating part is its strings.
Conclusion: The vibrating part of an Ektara is its string, which produces sound vibrating.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 5
Aim: To make a Jaitarang
Procedure:
1. Take 6-8 metal bowls or tumblers and fill them with water up to different levels, increasing gradually from one end to the other.
2. Then take a pencil and strike the bowls gently, in succession. Note down your observation.

Observations: Different types of sounds are produced on vibrating bowls filled with water up to different levels.
Conclusion: Vibrations produce sound. The sound produced varies with the amount of water present in a bowl.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 6
Aim: To find out how vocal cords produce sound
Procedure:
1. Take two rubber strips of the same size. Place them one above the other and stretch them tight.
2. Now blow air through the gap between them
3. Record your observation.

4. You can also take a piece of paper with a narrow slit and hold it between your fingers
5. Now’ blow’ through the slit and listen to the sound.
Observation: As the air blows through the stretched rubber strips or the piece of paper, a sound is produced.
Conclusion: In human beings, sound is produced by the voice box or the larynx. Two cords called the vocal
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The to-and-fro motion of an object is called vibration.
- In human beings, the sound is produced by vocal cords.
- ‘When we pluck the string of an instrument, like the sitar, not only its string but the whole instrument vibrates.
- Women have longer vocal cords than men.
Answer
- True
- True.
- True
- False
2. Multiple choice questions.
1. What does a vibrating body transfer to the adjacent molecules in a medium?
- Energy
- Force
- Speed
- Pressure
Answer: 1. Energy
2. What is the length of the vocal cord in men?
- 10 mm
- 15 mm
- 20 mm
- 25 mm
Answers: 3. 20mm
3. Fill in the blanks.
- Sound is a form of_________
- Sound is produced when objects__________
- The voice box is also called the_________
- The voice box is situated in the neck at the upper end of the________
Answers:
- Energy
- Vibrate
- Larynx
- Windpipe
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How do human beings produce voices?
Answer
In human beings, the sound is produced by the voice box, which is also called the larynx. Two cords called the vocal cords, are stretched across the larynx in such a way that there is a narrow slit between them for the passage of the air. When air is forced through this slit, the vocal cords vibrate and sound is produced.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Propagation of Sound
Sound needs a medium for its propagation. Sound can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum. The outer part of the ear, which is shaped like a funnel, – receives the sound. From here, the sound travels through the middle ear and reaches the inner ear; which transmits signals to the brain. That is how we hear.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 7
Aim: To observe that sound needs a medium to travel
Procedure:
1. Take a dry metal tumbler and place a cell phone inside it
2. Ask your friend to call you on that cell phone from another cell phone. Listen to the ring carefully.
3. surround the nim of the tumbler with your hands and put your mouth on the opening between your hands.

4. Indicate to your friend to call on that cell phone again. Listen to the ring while sucking air from the tumbler.
5. Remove the tumbler from your mouth. Note down your observation.
Observations: The sound became fainter as the air was sucked from the tumbler. The sound became loud again after removing the mouth.
Conclusion: As the air was sucked, a partial vacuum was created inside the tumbler and the sound became fainter. Once air entered the tumbler again, the sound became louder. This proves that sound needs a medium to travel.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 8
Aim: To determine if sound can travel through liquids
Procedure:
1. Take a bucket or a bathtub and fill it with clean water.
2. Take a small bell in one hand. Shake this bell inside the water to produce sound. Make sure that the bell does not touch the body of the bucket or the tub.
3. Place your ear gently on the water surface and note down your observations.

Observations: The sound of the bell is heard.
Conclusion: Sound can travel through liquids.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 9
Aim: To determine if sound can travel through solids
Procedure:
1. Take a meter scale or a long metal rod and hold its one end to your ear.
2. Ask your friend to gently scratch or tap the other end of the scale.
Observations: The sound of the scratch is heard.
Conclusion: Sound can travel through solids.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 10
Aim: To observe how an eardrum works
Procedure:
1. Take a tin can and cut its ends.
2. Stretch a piece of rubber balloon across one end of the can and fasten it with a rubber band.
3. Put four or five grains of dry cereal on the stretched rubber and ask your friend to speak “Hurray, Hurray’1 from the open end.

Observations: On speaking, grains jump up and down.
Conclusion: Grains jump up and down due to the vibrations. The vibrations produce movements. The eardrum is just like a stretched rubber sheet. Sound vibrations make the eardrum vibrate and thus, we can hear sound.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Sound needs a medium for its propagation.
- The eardrum sends vibrations directly to the brain.
Answers:
- True
- False
B. Multiple-Choice Questions
1. What is the name of the membrane present in the ear?
- Ear foil
- Eardrum
- Ear sheet
- Hammer
Answer: 2. Eardrum
2. In which of the following mediums does sound travel the fastest?
- Water
- Air
- Iron
- Vacuum
Answers: 3. Iron
3. Fill in the blanks.
- The_______sends vibrations to the inner ear.
- Sound travels the_________in solids and_______in gases.
Answers:
- Eardrum
- Fastest, Slowest
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Short Answer Type Question
Question 1. How do we hear?
‘When sound enters into our ear, it travels through a canal at the end of which there is a tightly stretched, thin membrane called the eardrum. When sound strikes the eardrum, it vibrates. The eardrum then sends vibrations to the inner ear. From there, the signal is further transmitted to the brain. That is how we hear.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Characteristics of Sound
Amplitude and frequency are two important properties of sound. Frequency determines the shrillness or pitch of a sound. The male voice has a low pitch, whereas the female voice has a high pitch. Scientifically, a musical sound is produced by regular vibrations, and noise is produced by irregular vibrations. Too much noise in our surroundings is harmful to us and is known as noise pollution.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Activity 11
Aim: To find the relation between the loudness and amplitude of the sound
Procedure:
1. Take a metallic tumbler and a tablespoon.
2. Strike the tablespoon gently at the brim of the tumbler.
3. Hear the sound produced.
4. Now’ Dang the spoon on the tumbler and hear the sound produced again.
5. Next suspend a small thermocol ball touching the rim of the tumbler.
6. vibrate the tumbler by striking it and check how far the ball is displaced.
7. Strike the tumbler gently and then with some force.
8. Compare the displacements (or amplitudes} of vibrations in both cases.

Observation: In steps, I and 2, the sound produced was loud when the tumbler was struck hard. In steps 3 and 4, the vibrations produced were more when force was applied.
Conclusion: The loudness of the sound was more when the amplitude of the vibration of the tumbler was greater. Thus, the loudness of sound is proportional to its amplitude.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The number of oscillations per second is called the amplitude of oscillation.
- Amplitude and frequency are two important: properties of any sound.
- The larger the amplitude of vibrations, the louder the sound produced.
- For a normal human ear, the audible frequency range is roughly between 200 and 20,000 Hz.
Answers:
- False
- True
- True
- False
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following determines the shrillness or pitch of a sound?
- Frequency
- Amplitude
- Period
- None of these
Answer: 1. Frequency
2. ‘Which characteristic of sound distinguishes a male and a female voice?
- Loudness
- Period
- Pitch
- Amplitude
Answers: 3. Pitch
3. Fill in the blanks.
- The higher the frequency of vibration, the__________is the pitch.
- The maximum displacement of a vibrating body from its mean position is called___________.
- Sounds of frequencies less than about___________ GHz are not audible to the human ear.
- A complete to-and-fro motion of a vibrating body about its mean position is called a /an_________.
Answers:
- Higher
- Amplitude
- 20
- Oscillation
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Choose the correct answer.
Sound can travel through
- Gases only
- Solids only
- Liquids only
- Solids, liquids, and gases
Answer 4. Solids, liquids, and gases
Question 2. Voice of which of the following is likely to have a minimum frequency?
- Baby girl
- Baby boy
- A man
- A woman
Answer: 3. A man
Question 3. In the following statements, tick (T) against those which are true, and (F) against those which are false.
- Sound cannot travel in a vacuum.
- The number of oscillations per second of a vibrating object is called its period.
- If the amplitude of the vibration is large, the sound is feeble.
- For human ears, the audible range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
- The lower the frequency of vibration, the higher the pitch.
- An unwanted or unpleasant sound is termed as music.
- Noise pollution may cause partial hearing impairment
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
Question 4. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
- The time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is called.
- Loudness is determined by the vibration.
- The unit of frequency is.
- Unwanted sound is called
- The Shrillness of a sound is determined by the vibration.
Answer:
- Period
- Amplitude
- Hertz (Hz)
- Noise
- Frequency.
Question 5. A pendulum oscillates 40 times in 4 seconds. Find its period and frequency.
Answer
Frequency=Number of oscillations/Time in seconds
Frequency = 40/4
Frequency = 10 Hz
Time period =1/Frequency
Time period = 1/10
Period — 0.1 s
Question 6. The sound from a mosquito is produced when it vibrates its wings at an average rate of 500 vibrations per second. What is the period of the vibration?
Answer
Frequency = 500 vibrations per second – 500 Hz
We know, that time period =1/Frequency
Time period = 1/500
Time period = 2 x 10 3 s
Question 7. Identify the part that vibrates to produce sound in the following instruments:
- Dholak
- Sitar
- Flute
Answer:
- Stretched membrane
- String
- Air column
Question 8. What is the difference between noise and music? Can music become noise sometimes?
Answer:
Differences between noise and music are:
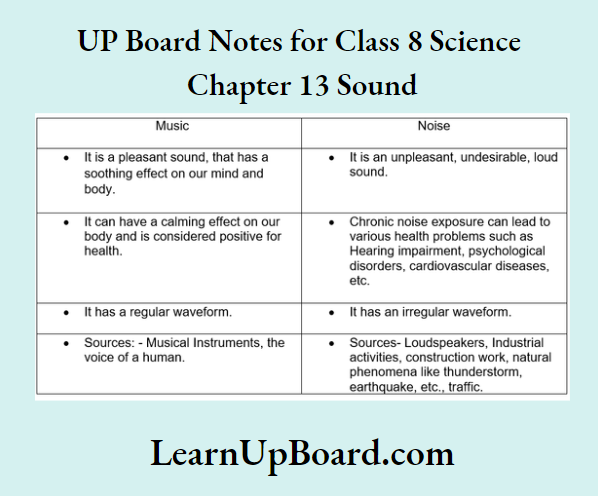
Yes, music can become noise. When music is too loud or the sounds produced by the instruments are not in sync with each other then music becomes noise.
Question 9. List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings.
Answer
Sources of noise pollution are:
- Noise of vehicles
- Loudspeakers
- Working machines
- Bursting of crackers
- Air coolers
- Radios and televisions at high volumes
- Kitchen Appliances
- Hawkers etc.
Question 10. Explain in what ways noise pollution is harmful to humans.
Answer
Noise pollution is harmful to humans in following ways
Too much noise in our surroundings is known as noise pollution. It is very harmful to us and can cause irritability, loss of concentration, high blood pressure, headache, stress, sleep disturbances, etc. It can even damage hearing permanently.
Question 11. Your parents are going to buy a house. They have been offered one on the roadside and another three lanes away from the roadside. Which house would you suggest your parents should buy? Explain your answer.
Answer
My parents should buy the house, which is located three lanes away from the roadside because a roadside house has many disadvantages such as:
- A lot of noise due to passing vehicles.
- Smoke and dust are produced by running vehicles.
- Sound of loud horns of vehicles at the time of traffic jams.
Question 12. Sketch the larynx and explain its function in your own words.
Answer:

Functions of the larynx: When air passes through the vocal cords, they vibrate to produce sound. Vocal cords may become loose/thick or tight/thin on vibration, thus producing different Types of sounds.
Question 13. Lightning and thunder take place in the sky at the same time and the same distance from us. Lightning is seen earlier and thunder is heard later. Can you explain why?
Answer
The speed of light is 3 * 10® m/s, while that of sound is only 330 m/s. So, although lightning and thunder take place simultaneously in the sky and at the same distance from the Earth, lightning is seen first.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Hots Corner
1. Can two people talk on the Moon in the same way as they can on the Earth?
Answer
No, there is no air or atmosphere on the Moon and sound needs a medium to travel. Therefore, the sound from one person will not travel to the ear of the other person. Hence, we cannot talk on the Moon in the same way as we do on the Earth.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Practice Exercise
1. Give one word for the following.
- The position where the bob of a pendulum stops
- Number of oscillations per second
- The sound produced by regular vibrations
- The factor on which the loudness of a sound depends
- Unit in which the loudness of a sound is measured
Answers:
- Mean position
- Frequency
- Music
- Amplitude
- Decibel
2. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Sound travels at different speeds in different substances.
- Scientifically, a musical sound is produced by regular vibrations.
- The male voice has a high pitch.
- The time period is denoted by the letter T.
- Loudness of a sound is inversely proportional to the amplitude of the vibration.
Answers:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum. Why?
Answer
Sound cannot travel through a vacuum.
Sound is a form of energy and is produced by a vibrating body. The vibrating body transfers its energy to the neighboring molecules in the medium, which in turn pass on their energy to the other; molecules. Since no molecules are present in a vacuum, there is no transfer of energy. Thus, sound \ cannot travel in a vacuum.
Question 2. The bob of a pendulum oscillates twice per second. Find its period and frequency.
Answer
Given
The bob of a pendulum oscillates twice per second.
Frequency = Number of oscillations/Time (in seconds)
Frequency = 2/1 = 2 Hz.
Time period = 1/Frequency
Time period = — = 0.5 s
Question 3. Write any three methods to reduce noise pollution.
Answer
Three methods to reduce noise pollution are:
- The use of loudspeakers in public places and residential areas should be banned.
- Vehicles should be fitted with effective silencers and should not be allowed to play loud music.
- Planting more trees on the roadsides reduces noise pollution as they absorb the sound.
Question 4. What are ultrasounds?
Answer
Ultrasounds
Sound frequencies more than 20,000 Hz (20 k Hz) are called ultrasounds. Human beings cannot perceive ultrasonic sounds. Hence, ultrasounds are also called ‘inaudible’ sounds.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
