UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Chapter Objectives
- Two objects can be electrically charged by rubbing them with one another.
- American scientist, Benjamin Franklin, showed that clouds have electrical charges on them.
- Electrical charges are of two types Positive charges and Negative charges.
- Like electrical charges repel each other while unlike electrical charges attract each other.
- A charged object can transfer its charge to another object through a metal conductor.
- Earthing protects us from electric shocks that may take place due to leakage of electric current.
- Natural phenomena like lightning, earthquakes, etc. cause large-scale destruction of human life and property.
- Lightning occurs due to electric discharge between the clouds and the Earth or between different clouds.
- The lightning conductor is installed at the highest point of a building to protect them from the damaging effects of lightning.
- During lightning and thunderstorm, we must find a safe place for ourselves.
- During the thunderstorm, we must not travel in open vehicles or try to be in open fields or parks.
- The sudden shaking or trembling of the Earth due to a disturbance caused deep inside the Earth’s crust is known as an earthquake.
- Other reasons of earthquakes are volcanic eruptions, meteor hits or an underground nuclear explosion.
- The outermost layer of the earth is fragmented and each fragment is called a plate.
- Earthquakes generally occur at the boundaries of the Earth’s plates. These boundaries are known as seismic or fault zones.
- A seismograph is used to measure the intensity of an earthquake.
- The power of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale. An earthquake of intensity 7 or more can cause severe destruction of life and property on the Earth.
- Necessary precautions must be taken to protect ourselves from the earthquakes.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Important Terms And definitions
Static charges: Electrical charges produced when two objects are rubbed with one another are known as static charges.
Electroscope: A device used to detect the presence of charge on an object is known as electroscope.
Earthing: The process of transferring charge of a charged object to the Earth is called earthing.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Seismic waves: The waves produced on the Earth’s surface due to the tremors of the earthquake are known as seismic waves.
Seismograph: An instrument used to record the intensity of the earthquake is called seismograph.
Electrical Charges
Two objects acquire static electrical charge when they are rubbed with one another. Static charges do not move by themselves. There are mainly two types of electrical charges positive charges and negative charges. The presence of charge on an object can be detected by an electroscope.
The process of transferring charge of a charged object to the Earth is known as earthing. It is
provided in a tall buildings to protect us from electric shocks that may take place due to the leakage of electric current.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Activity 1
Aim: To show that objects get electrically charged by rubbing them with other objects
Precaution: Do not touch the rubbed end of the refill with your hand or with a metallic object.
Procedure:
- Take a used ball pen refill and rub it vigorously with a piece of polythene.
- Bring the refill close to small pieces of paper.
- Repeat this activity with small pieces of dry leaf, husk, and mustard seeds. Record your observations.
Observation: After rubbing the plastic refill with a piece of polythene, the refill attracts bits of paper.
Conclusion: An object can be charged by rubbing it with another object.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Activity 2
Aim: To charge objects by rubbing them with other objects
Procedure:
- Collect different objects or materials as given in the observation table.
- Try to charge each material by rubbing it with other materials.
- Record your observations in the table.
Observation:
Conclusion: Objects acquire a charge when they are rubbed with other objects.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Activity 3
Aim: To show that like charges repel each other whereas unlike charges attract each other
Procedure:
- Inflate two balloons and hang them such that they do not touch each other.
- Rub both the balloons with a woolen cloth and release them.
- Observe them carefully.
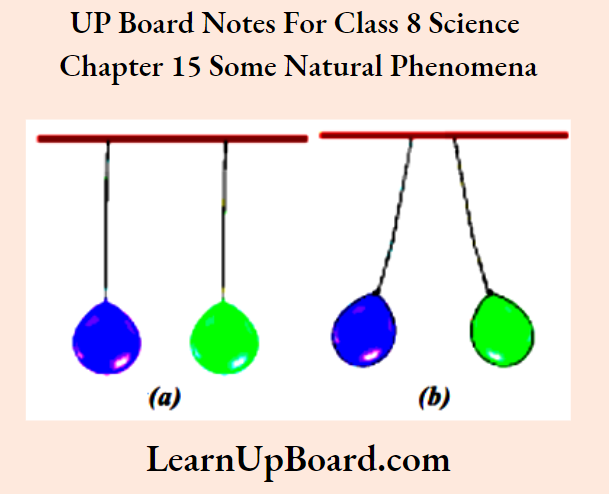
- Interaction between like charges
- Now, take a used pen refill and rub it with polythene.
- Place this refill carefully in a glass tumbler.
- Rub another refill with polythene and bring it close to the charged refill.
- Observe the refills.

Interaction between like charges
8. Now, rub a refill and place it gently in a glass tumbler. Bring an inflated charged balloon near the refill and observe it.

Interaction between unlike charges
Observations:
- The charged balloon repelled the other charged balloon.
- The charged refill repelled the other charged refill.
- However, the charged balloon attracted the charged refill.
Conclusion: Like charges attract each other whereas unlike charges repel each other.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Activity 4
Aim: To show that electrical charge can be transferred from a charged object to another object through a metal conductor
Procedure:
- Take an empty jam bottle and a piece of cardboard slightly bigger than the mouth of the bottle.
- Pierce a hole in the cardboard and insert a metal paper clip in it.
- Now, open the paper clip as shown below.
- Cut two strips of aluminum foil of size about 4 cm x 1 cm each.
- Hang these aluminum foil strips on the paper clip.
- Insert the paper clip in the cardboard lid such that, it is perpendicular to it.
- Charge a refill and touch it with the end of the paper clip.
- Observe aluminum strips carefully.

A simple electroscope
Observations: The strips acquire the same charge from the charged refill and repel each other. They become wide open.
Conclusion: Electrical charge can be transferred from a charged object to another object through a metal conductor.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Objects made up of the same materials acquire different electrical charges.
- The negative charge is acquired by a glass rod when it is rubbed with silk.
- Positive charges will always attract negative charges.
- The motion of electrical charges constitutes an electric current.
Answers:
- False
- False
- True
- True
2. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1. Which of the following will charge an object?
- Rubbing with another object
- Wetting with water
- Drying the object in the Sun
- All of these
Answers: 1) Rubbing with another object
Question 2. Which of these instruments is used to test whether an object is carrying charge or not?
- Kaleidoscope
- Microscope
- Telescope
- Electroscope
Answers: 4) Electroscope
3. Fill in the blanks.
- A body or an object possessing charge is said to be a______ object.
- The electrical charges generated by rubbing are________in nature.
- Electrical charge can be transferred from a charged object to another object through a____ conductor.
- ______is the process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth.
Answers:
- Charged
- Static
- Metal
- Earthing
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Short Answer Type Questions
1. What do you mean by ‘static charge’?
Answers:
‘Static Charge’ Definition
The electrical charges that are generated by rubbing two objects with one another are known as static charges. This means that these charges do not move by themselves.
2. When you rub an air-filled balloon with your dry hair and press it against the wall, it sticks to the wall. Explain why?
Answers: When an air-filled balloon is rubbed with dry hair, it gets charged. Therefore, the presence of electrical charge on the surface of the balloon makes it stick to the wall.
3. What are the two types of electrical charges? What happens when a glass rod is rubbed with silk?
The two types of electrical charges are positive charges and negative charges. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it gets electrically charged. The glass rod acquires a positive charge on it.
Lightning: Causes, Effects, and Safety Measures
Lightning occurs due to the electric discharge between the clouds and the Ear or between different clouds. During the lightning and thunderstorms, it is recommended to rush to a safer place like a building, a car with closed windows, etc. If no shelter is available, we must stay far away from all the trees and squat down on our knees with our heads between our hands. Inside the house, the electrical appliances like computers, TVs, etc., should be unplugged. Taking a shower or bath must be avoided.
Lightning conductors protect buildings from the damaging effects of lightning. The lightning conductor consists of a metallic rod at the top of the building connected to an aluminum or copper cable. The cable connects to a copper plate buried in the Earth. The metallic rod acts as a medium to easily transfer electric charge to the ground.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- You should avoid taking a bath during a thunderstorm.
- It is advised to use an umbrella during lightning.
- The phenomenon of lightning takes place due to the accumulation of electrical charges in the clouds.
Answers:
- true
- False
- True
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. The process of electric discharge can occur between which of the following?
- Two or more clouds
- A building and a tree
- Two buildings on the Earth
- Either a) or b)
Answers: 1) Two or more clouds
Question 2. Which of these should be done during a thunderstorm?
- Taking a bath
- Staying inside a building
- Using wired phones
- Standing under the trees
Answers: 2) Staying inside a building
3. Fill in the blanks.
- During the development of a thunderstorm, the air currents move_____while the water droplets move_____
- When the negative charges of the clouds and the positive charges of the earth meet, they produce
streaks of bright light in the form of_____
Answers:
- Upwards, downwards
- Lightning
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Short Answer Type Questions
1. Which places are safe for taking shelter during a thunderstorm?
Covered vehicles like cars and buses (with windows and doors closed), buildings, and houses are safe places for taking shelter during a thunderstorm.
2. Which position is recommended during a thunderstorm – lying on the ground or squatting?
Squatting is a safer position during a thunderstorm. While squatting, place your hands on your knees with your head between your hands.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Long Answer Type Questions
1. Explain how lightning occurs between two clouds during a storm.
Answers:
Occurrence Of lightning between two clouds during a storm:
During a thunderstorm, the air currents move upward while the drops of water move downwards. These movements cause the separation of charges such that the positive charges are collected near the upper surface of the clouds and the negative charges are collected near the lower surface of the
cloud. At the same time, a positive charge is accumulated near the ground. When the accumulated charges become large in magnitude, the positive and negative charges meet and produce lightning.
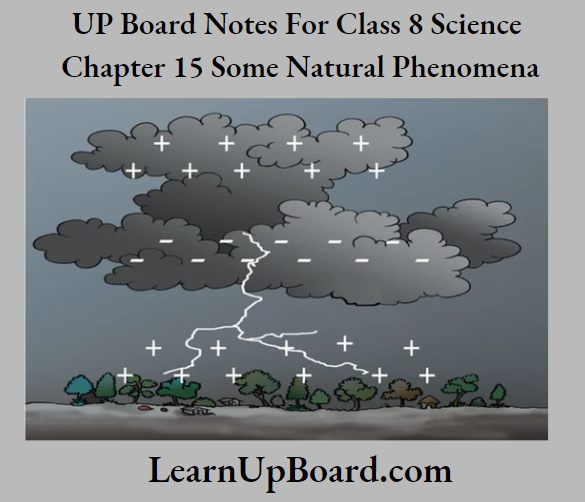
Accumulation of charges leading to lightning
Earthquakes: Causes, Effects, and Protective Measures
Earthquakes cause huge damage to life and property. Earthquake occurs due to the motion of Earth’s plates. The Earth’s plates collide and move past one another or slide over one another.
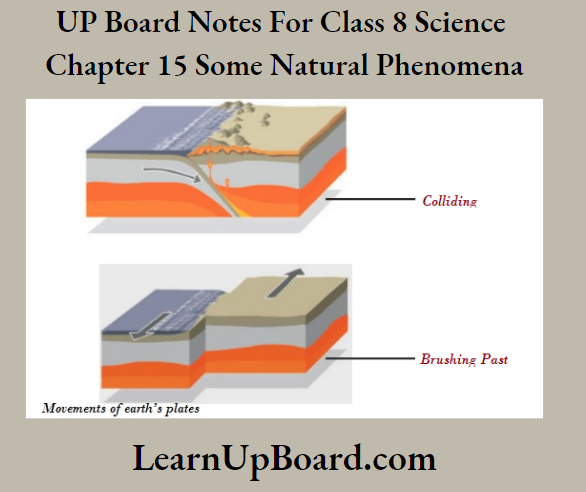
Movement of earth’s plates
A seismograph records the seismic waves produced due to the tremors of the earthquake on the Richter scale. A seismograph consists of a vibrating rod or a pendulum, which vibrates when the tremors of an earthquake occur. The pen attached to the vibrating system records the seismic waves on the paper moving under it.
Necessary precautions must be taken to protect ourselves from earthquakes. We should avoid the use of heavy construction materials in the highly earthquake-prone areas. The buildings constructed must be ‘Quake Safe’. If we are inside the house, we must take shelter under a table and stay away from heavy objects. If we are outside the house, we must move to a clear spot.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- 1Earthquakes can also cause floods, landslides, and tsunamis.
- The fault zones are the most susceptible regions to earthquakes.
- An earthquake measuring 8 on the Richter scale is mild and quite harmless.
Answers:
- True
- True
- False
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following instruments is used to record seismic waves during an earthquake?
- Seismograph
- Richter scale
- Electroscope
- Barometer
Answers: 1)Seismograph
Question 2. Most earthquakes are caused by disturbances in which of these parts of the earth?
- Crust
- Mantle
- Inner core
- All of these
Answers: 1)Crust
C. Fill in the blanks.
- Each fragment of the Earth’s crust is called a____
- The outermost layer of the Earth is known as_____
Answers:
- Plate
- Crust
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Short Answer Type Questions
1. How does a seismograph work?
Answers:
Working Of Seismograph
A seismograph consists of a vibrating rod or a pendulum, which vibrates when tremors occur. The pen attached to the vibrating system records the seismic waves on the paper moving under it. Scientists construct a complete map of the earthquake by studying these waves.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Long Answer Type Questions
1. What is an earthquake? How is the magnitude of an earthquake expressed?
Answers:
Earthquake:
The sudden shaking or trembling of the Earth due to a disturbance caused deep inside the Earth’s crust is known as an earthquake. The magnitude of an earthquake is expressed in the Richter scale. The earthquakes measuring up to 3 on the Richter scale are said to be mild and do not cause any damage. On the other hand, earthquakes measuring 7 or more on the Richter scale are very severe and can destroy the entire area where they occur.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Textbook Exercises
Select the correct option in Questions 1 and 2.
Question 1. Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
- A plastic scale
- A copper rod
- An inflated balloon
- A woollen cloth
Answers: (2) A copper rod
Question 2. When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth the rod
- and the cloth both acquire a positive charge.
- becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
- and the cloth both acquire a negative charge.
- becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
Answers: (2) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
Question 3. Write T against true and F against false in the following statements:
- Like charges attract each other.
- A charged glass rod attracts a charged plastic straw.
- Lightning conductors cannot protect a building from lightning.
- Earthquakes can be predicted in advance.
Answers:
- F
- T
- F
- F
Question 4. Sometimes, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweaters during winter. Explain.
Answers: Woolen clothes get charged when they get rubbed with the human body. When these clothes are taken off, the electric discharge takes place between the sweater and the body. This electric discharge produces a crackling sound.
Question 5. Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
The human body is a conductor of electricity. When we touch a charged body with our hand, the charge of the charged body passes to the Earth through our body. Thus, the charged body loses its charge.
Question 6. Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Answers: The destructive energy of an earthquake is measured in the Richter scale. Yes, an earthquake that measures 3 on the Richter scale will be recorded by a seismograph. Such an earthquake is mild and does not cause any damage to life and property.
Question 7. Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Answers:
Three safety measures to protect ourselves from lightning during a thunderstorm are:
- Stay indoors or under a covered area
- Do not take a shower or bath
- Do not use electrical appliances or wired phones at home
Question 8. Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon.
Answers: The same materials get the same charges on rubbing and the same charges to repel each other. Therefore, balloons on rubbing are similarly charged and they repel each other. The charged and the uncharged balloons do have the same charges on them. Therefore, they attract each other.
Question 9. Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument that can be used to detect a charged body.
Answers: An electroscope can be used to detect if a body is charged or not. When a charged body touches the metal conductor, the metal strips repel each other and open wide. This proves that the body is charged.

A simple electroscope
Question 10. List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Answers: In India, the earthquake-prone areas are Kashmir, Gujarat, and Rajasthan.
Question 11. Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What precautions would you take to protect yourself?
Answers: During an earthquake, if we are outside the home, we should find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees, and overhead power lines. If in a car or a bus, we should not come out and ask the driver to drive slowly to a clear spot.
Question 12. The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Answers: Carrying an umbrella is not a good idea during a thunderstorm because it has metal wires and a metal rod in it which can provide an easy path for the electric discharge from the clouds. Hence, it increases the risk of electrocution in case of lightning strikes.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Hots corner
1. A glass rod can be charged by rubbing when held in hand. However, an iron rod cannot be charged in the same way. Can you explain why?
Answers: A glass rod is an insulator. Hence, it does not transfer the electric charge produced on its surface through our hand and the body to the Earth. However, an iron rod is a good conductor of electricity. As soon as it gets charged by rubbing, the electric charges produced on its surface flow through our hand and body into the Earth. Therefore, the iron rod remains uncharged.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Practice Exercises
Objective Type Questions
1. Circle the odd one out.
- Polythene, silk, woolen cloth, wet hair
- Seismic zone, safe zone, fault zone, weak zone
- Plastic refill, glass rod, balloon, metal rod
Answers:
- Wet hair
- Safe zone
- Metal rod
2. Give one word for the following.
- The device is used to protect buildings from the damaging effects of lightning.
- The device is used for detecting the presence of charge on an object.
- The sudden shaking or trembling of the Earth.
- Waves are produced during an earthquake.
Answers:
- Lightning conductor
- Electroscope
- Earthquake
- Seismic waves
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- If you are indoors during an earthquake, it is best to rush outside immediately.
- We should go to the roof of tall buildings when it is lightning.
- During an earthquake, the Earth’s plates collide with each other.
Answers:
1. True
2. False
3. True
4. Fill in the blanks.
- Earthquakes tend to occur at the_____of the Earth’s plates.
- _____is the rapid flow of charge through air between the two oppositely charged clouds.
- Lightning occurs when____and_____ charges meet.
- Two charged plastic refills will_____each other.
Answers:
- Boundaries
- Electric discharge
- Positive, negative
- Repel
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Short Answer Type Questions
1. Give two common examples of static electricity from your daily life.
Answers:
Two common examples of static electricity are:
- When the television sets are turned on for a long time a layer of charge develops on their screens. This is due to the presence of static electricity.
- When we brush our hair, they start getting attracted to the hairbrush. This is because they have acquired charge in the form of static electricity.
2. Which regions of the Earth are more prone to earthquakes?
Answers: The regions that fall on the boundaries of the Earth’s plates are weak or dangerous zones. Earthquakes are more likely to occur in these zones. These weak zones are also called seismic or fault zones.
3. Do earthquakes bring some changes to the Earth’s surface? Explain.
Answers: Yes, earthquakes can bring some geographical changes to the Earth’s surface. During an earthquake, the Earth starts shaking. Sometimes, deep and large slits appear on the Earth’s surface. Earthquakes with high intensity are so strong that new islands and coral beaches may be formed. Some freshwater springs have also been formed due to earthquakes.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
