UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Abstract
- The stars, the planets, the Moon, and many other objects in the sky are called celestial objects. They all form part of the universe.
- The Moon revolves around the Earth, and the Earth along with the Moon revolves around the Sun.
- Stars and the Solar System
- Stars are the celestial bodies which emit light of their own. The Sun is also a star.
- The distance between the stars and the Earth is expressed in a unit called a light year.
- A light year is a distance that light travels in one year.
- When seen from the Earth, stars appear to move from east to west.
- Pole Star is situated close to the direction of the axis of the Earth’s rotation; hence, it appears to be stationary when seen from the Earth.
- Groups of stars that appear to form recognizable shapes/patterns in the sky are called
constellations. - The most common constellations are Ursa Major, Orion, and Cassiopeia.
- The Sun, the planets revolving around it and many other celestial bodies comprise the solar system.
- A celestial body revolving around another celestial body is called a satellite. There are two types of satellites: natural and artificial.
- The shape of the Moon changes every day. Different shapes of the moon visible from the Earth are known as the phases of the moon.
- The phases of the Moon occur because only the part of the Moon which reflects sunlight is visible to us. The back of the moon is never visible.
- Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth.
- Artificial satellites are man-made objects launched into the space. Artificial satellites are used for weather forecasting, communication, navigation, transmitting radio and television signals, and military.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Important Terms And Definitions
Asteroids: Numerous small bodies (mainly rocks, metals, etc.) that lie in the large gap existing between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter are known as asteroids.
Comets: The celestial bodies that revolve around the Sun and have very long periods of revolution are known as comets.
Meteors: Small objects that occasionally enter Earth’s atmosphere are known as meteors.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Meteorites: Meteors which reach the Earth are called meteorites.
The Moon
Moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. The surface of the Moon is dusty and infertile. There is complete absence of water and atmosphere on the Moon. Hence, there is absolutely no life on the Moon. The day when the entire Moon is visible, it is known as a full Moon day. The day when the Moon is not visible is known as the new Moon day. The day when only a small portion of the Moon appears in the sky is known as the crescent Moon day. The time period between one full moon day to the next full moon day is slightly longer than 29 days. This period is called a month.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 1
Aim: To observe the shape of the Moon for a few nights
Procedure:
- Observe the Moon continuously for several nights, preferably from one full Moon to the next.
- Make a sketch of the Moon every night in your notebook from the day of the full Moon.
- Also, note the part of the sky (east or west) in which the Moon is seen.
Observations:
- The Moon appears to be perfectly round on the full Moon day.
- After the full Moon day, the size of the Moon decreases every day.
- On the new Moon day, the Moon is not visible even if the sky is clear.
- After the new Moon day, the size the Moon starts increasing each day and the full Moon appears again in another fifteen days.
Conclusion: The crescent-shaped Moon keeps on increasing every day until the full face of the Moon is visible on the fifteenth day. After the full Moon, the size and brightness of the Moon goes on decreasing each night. Subsequently, in another fifteen days, the Moon becomes invisible. This is known as new Moon day.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 2
Aim: To show the positions of the Moon on its orbit and its corresponding phases
Precaution: If you perform this activity in the morning, the white portion of the ball should face east. If this activity is performed in the afternoon, the white portion of the ball should face west. In each case, the line dividing the white and black portions should be kept vertical.
Procedure:
- Take a big ball or a pitcher. Paint half of it white and the other half black.2. Go out into
- The playground with two of your friends. Draw a circle of radius about 2 m on the ground. Divide the circle into eight equal parts as shown in the figure given here.
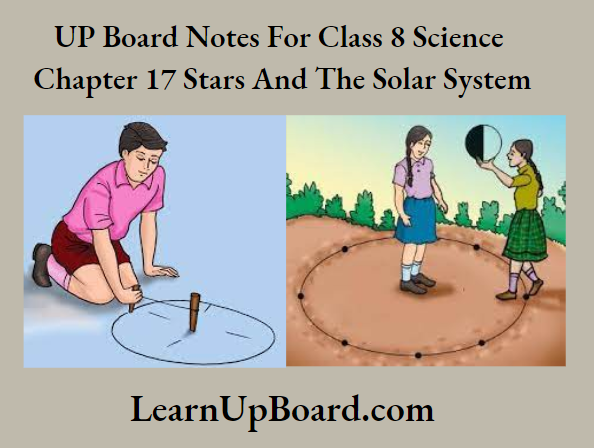
- Stand at the center of the circle. Ask your friend to hold the ball at different points of the circle. Ask her to keep the white portion of the ball towards the Sun.
- Standing at the center of the circle, observe the visible white portion of the ball while your friend stands at the points on the circle marked earlier. Draw the shape of the white portion as you see it.
- Compare your drawings with the different phases of the Moon as shown in the figure given below.
Observation: On the new Moon day, the Moon lies between the Sun and the Earth. However, on the full Moon day, the Earth comes between the Moon and the Sun.
Conclusion: After the new Moon day, the size of the illuminated part of the Moon, visible from the Earth, increases each day. However, the Sun-lit part of the Moon visible from the Earth decreases in size every day after the full Moon day.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The shape of the Moon changes every month rather than daily.
- Sound cannot be heard on the Moon.
- There is no human life existing on the Moon; however, the growth of plants and other microorganisms is possible on its surface.The Moon produces light on its own.
- After the full moon day, the visible part of the Moon starts decreasing.
Answers:
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. Who was the first person to land on the Moon?
- Galileo
- Neil Armstrong
- Isaac Newton
- Edwin Aldrin
Question 2. When the Moon is not visible at night on a clear sky, what is the day called?
- Full Moon day
- Eclipsed Moon day
- Crescent Moon day
- New Moon day
Question 3.What is the reason that it is possible to observe phases of the Moon from the Earth?
- The Moon revolves around the Earth.
- The Moon’s axis is tilted.
- The Moon spins on its axis.
- The Moon’s distance from Earth changes at a particular rate.
Answers:
- Neil Armstrong
- New Moon
- The Moon revolves around the Earth
3. Fill in the blanks.
- The day when only a small portion of the Moon appears in the sky is called the_____ Moon day.
- The day of the full Moon is popularly known as_____while the day of New Moon is popularly called____
- The surface of the Moon is dry, rocky and _____
Answers:
- Crescent
- Purnima, Amavasya
- Infertile/Barren
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Short Answer Type Questions
A. Why does the shape of the Moon change every day?
Answers: The Moon appears bright and shiny because it reflects the sunlight that falls on its surface. The Moon along with the Earth revolves around the Sun. As a result, the relative position of the moon keeps changing every day.
B. Why there is no life on the Moon?
Answers: The two essential factors, which are required for the survival of living beings are air and water. These are not available on the Moon’s surface. Hence, no life exists on the Moon.
Stars and Constellations
Answers: Stars emit their own light. Generally, stars are very far (many millions of kilometers) away from the Earth. This is why they appear too small in the sky. The Sun is the star closest to the Earth. This is why it appears to be very big while other stars seem so small, almost like dots or points in the sky. A group of stars forming a certain pattern with a recognizable shape is called a constellation. The shape of a constellation never changes. Like stars, constellations also appear to move from east to west.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System System Activity 4
Aim: To show that if the stars appear to move from east to west, the Earth rotates from the west to the east
Procedure:
- Stand in the center of a big room.
- Now, start rotating and observe the direction in which the objects in the room appear to move.
Observation: The objects in the room appear to be moving in the direction opposite to our motion.
Conclusion: If the stars appear to move from east to west, the Earth rotates from west to east.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System System Activity 5
Aim: To show that the Pole Star lies close to the axis of the rotation of the Earth
Procedure:
- Take an umbrella and open it. Make about 10-15 stars out of white paper. Paste one star at the position of the central rod of the umbrella and others at different places on the cloth near the end of each spoke as shown in the figure given below.
- Now rotate the umbrella by holding its central rod in your hand. Observe the stars on the umbrella.

Observation: The star situated at the central rod of the umbrella does not appear to move.
Conclusion: The Pole Star lies close to the axis of the rotation of the Earth, thus, it does not appear to move.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 6
Aim: To show that a constellation appears to move in the sky from east to west
Procedure:
- Locate a constellation (e.g. Ursa Major) in the sky.
- Observe this constellation for a few hours.
Observation: The shape of the constellation remains the same. However, the constellation appears to be moving.
Conclusion: The constellation appears to move in the sky from east to west.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 7
Aim: To locate the Pole Star in the sky
Precaution: This activity should be performed on a clear Moonless night during summer at around 9 pm.
Procedure:
- Look towards the northern part of the sky and identify Ursa Major.
- Look at the two stars at the end of Ursa Major.
- Imagine a straight line passing through these stars as shown in the figure given below.
- Extend this imaginary line towards the north direction. (About five times the distance between the two stars).
- This line will lead to a star.
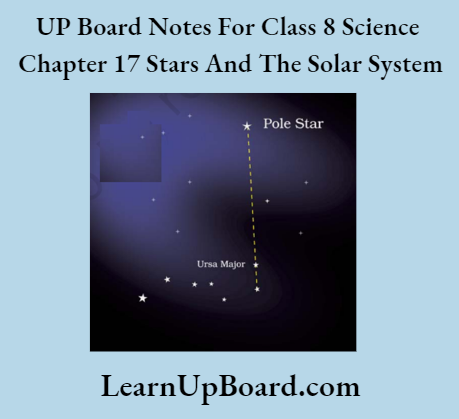
Observation: The imaginary line will lead to a star, that is not too bright. This is the pole star.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 8
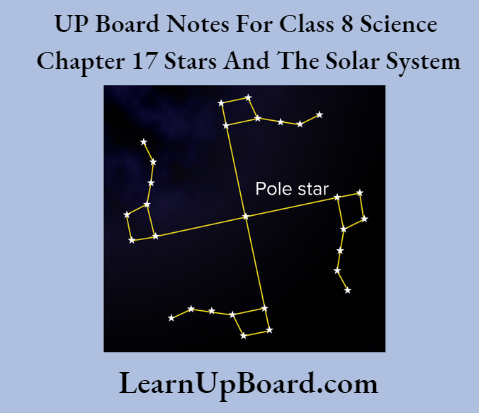
Aim: To show that the Ursa Major constellation moves around the Pole Star
Procedure:
- 1. During a summer night, observe Ursa Major 3-4 times at an interval of 2 to 3 hours.
- Locate the Pole Star each time.
- Compare your observations with those in the figure given below.
Observation Ursa Major appears to move from east to west.
Conclusion: The Ursa Major constellation moves around the Pole Star.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The North Star which indicates the north direction is also called the Pole Star.
- Stars always seem to move in the same direction as the axis of Earth’s rotation.
- Stars are present in the sky at night only.
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
B. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1. Which of these constellations resembles the shape of a hunter’s body?
- Orion
- Ursa Major
- Leo Major
- CassiopeiaAnswers: 1) Orion
Question 2. Which of these stars is located closest to the Earth?
- Pole Star
- Alpha Centauri
- Sirius
- Sun
Answers: 4) Sun
Question 3. Which is the brightest star in the sky?
- Alpha Centauri
- Sun
- Sirius
- Pole Star
Answers: 1) Alpha Centauri
C. Fill in the blanks.
- The distance between the Earth and the Sun is measured in_____.
- There are stars present in the sky.
Answers:
- Light years
- Infinite/Countless
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Short Answer Type Questions
A. Do all the stars of a constellation lie really close together?
Answers: The different stars that form a constellation are not related and lie at widely varying distances from the Earth. However, they all appear to our eye as close together but are not so.
B. Why are stars not visible during the day?
Answers: During the day, the light of the Sun is very bright and the brightness of stars becomes relatively dim in comparison to that of the Sun. Hence, they are not visible during the day.
C. How can you identify Ursa Major?
Answers: The constellation Ursa Major is seen during summer. It is also called the Great Bear or the Saptarishi. There are seven prominently shining stars in the constellation which are arranged in the shape of a question mark. The Pole Star lies at the tail of this constellation.
Solar System: Planets and Other Members
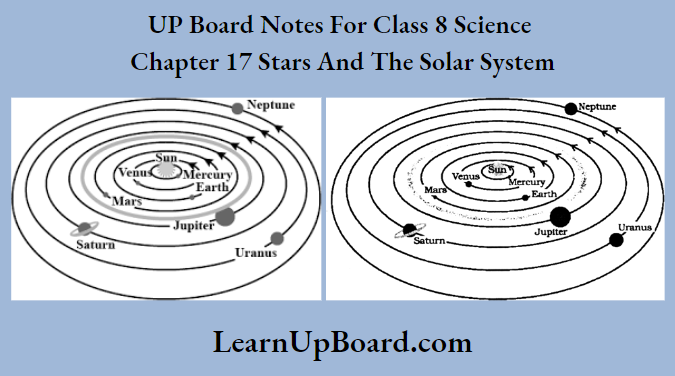
The solar system comprises the Sun, the planets, and various other members such as asteroids, comets, meteors/meteorites, and artificial satellites. There are eight planets in the solar system. These are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. All planets revolve around the Sun in a fixed path called orbit. The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution is called its period of revolution. In addition to the Sun and the eight planets, many other celestial bodies form the part of the solar system.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 9
Aim: To confirm that planets move in their own orbits
Procedure:
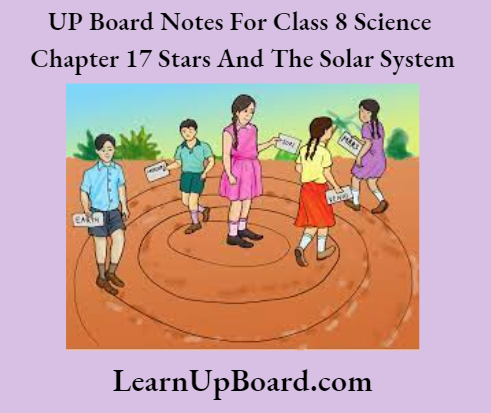
- 1. Go out into the playground with four or five friends. Draw four circles of radii 1 m, 1.8 m, 2.5 m, and 3.8 m, all having a common center as shown in the given figure.
- Ask one of your friends to stand in the centre and represent the Sun. Your other four friends may represent Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
- Ask your friends to move around the Sun in anti-clockwise direction in their own orbits and observe whether they collide with one another or not.
Observation: They do not collide because they are moving in their own fixed orbits.
Conclusion: Planets move in their own fixed path called orbits.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Activity 10
Aim: To observe the planet Venus
Procedure:
- Find out from a newspaper or from an almanac the time when Venus is visible in the sky.
- Observe Venus either 1-3 hours before sunrise or 1-3 hours after sunset.
Observation: Venus can be easily recognized by its brightness. However, it cannot be seen very high in the sky.
Conclusion: Venus is the brightest planet in the night sky. It rotates from the east to the west. Since Venus is close to the Sun, it can also be seen just before sunrise and just after sunset.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Until 2006, Pluto was also a planet (ninth planet) in the solar system.
- Mercury and Venus have rings around them, which can be seen through a telescope.
- The outer planets have very few moons.
- Saturn is the least dense among all the planets.
- The appearance of a comet is a natural phenomenon and it is not an indicator of any forthcoming disaster.
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of these planets is also called the morning star or the evening star?
- Mercury
- Venus
- Mars
- NeptuneAnswers: 2) Venus
Question 2. Which planet in the solar system appears yellowish in color?
- Jupiter
- Uranus
- Satum
- MercuryAnswers: 3) Saturn
Question 3. The axis of the Earth is inclined to its orbital plane at what angle?
- 23.5°
- 25.5°
- 60.5°
- 66.5°Answers: 4) 66.5°
Question 4. Which of these celestial bodies is visible only through large telescopes?
- Meteors
- Meteorites
- Asteroids
- CometsAnswers: 3) Asteroids
Question 5. Which of these is the first Indian satellite launched from the Earth?
- INSET
- Aryabhatta
- Kalpana-I
- EDUSAT
Answers: 2) Aryabhatta
3. Fill in the blanks.
- _______ is commonly known as Dhruv Tara.
- The reflection of light from______ and_____ on Earth’s surface makes it appears blue-green when seen from space.
- Mars has_____ small natural satellites.
- The mass of Jupiter is nearly______times that of the Earth.
- _____ are swarms of meteors seen at the time when the Earth crosses the tail of a comet.
Answers:
- The Pole Star
- Water, landmass
- Two
- 318
- Meteor showers
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why is life possible on the Earth?
Answers: Environmental conditions such as appropriate distance from the Sun, the correct level of temperature, the presence of atmosphere and water, together make the existence and continuation of life possible on the Earth. Moreover, the presence of the ozone layer around the Earth prevents organisms from harmful ultraviolet radiation of the Sun.
2. What do you mean by inner planets and outer planets?
Answers:
Inner planets and Outer planets
The four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, which are nearer to the Sun, are called the inner planets. However, the planets outside the orbit of Mars, namely Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are much farther off from the Sun. These planets are called the outer planets.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Textbook Exercises
Choose the correct answer in Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
- An asteroid
- A satellite
- A constellation
- A Comet
Answer: 3) A constellation
Question 2. Which of the following is NOT a planet of the Sun?
- Sirius
- Mercury
- Saturn
- Earth
Answer: 1) Sirius
Question 3. Phases of the Moon occur because
- We can see only that part of the Moon which reflects light toward us.
- Our distance from the Moon keeps changing.
- The shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the Moon’s surface.
- The thickness of the Moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer: 1) We can see only that part of the Moon which reflects light toward us.
Question 4. Fill in the blanks.
- The planet which is farthest from the Sun is______.
- The planet which appears reddish in color is______.
- A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a______.
- A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as_______.
- Shooting stars are actually not_______.
- Asteroids are found between the orbits of_______and_____.
Answer:
- Neptune
- Mars
- Constellation
- Satellite
- Stars
- Mars, Jupiter
Question 5. Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F):
- The Pole Star is a member of our solar system.
- Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system.
- Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system.
- INSAT is an artificial satellite.
- There are nine planets in the solar system.
- Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
Question 6. In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answers: Venus is visible as an evening star in the western part of the sky
Question 7. Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answers: Jupiter
Question 8. What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answers: A groups of stars that appear to form recognisable shapes/patterns are called constellations. The Great Bear and Orion are two constellations.
Question 9. Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in
(a) Ursa Major and (b) Orion
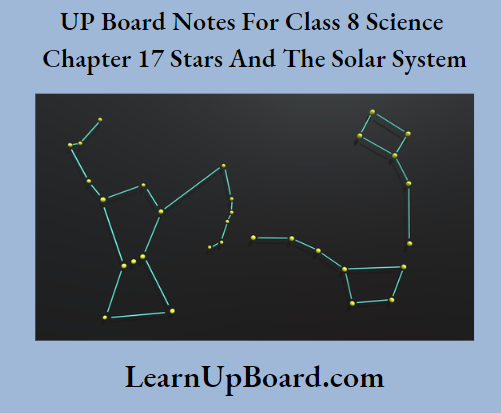
Question 10. Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answers: Asteroids and Meteors
Question 11. Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answers: The Pole Star is located at the end of Ursa Major. A straight line from the last two stars when extended towards the north leads to the Pole Star.
Question 12. Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answers: No, all stars in the sky do not move. However, they appear to move from east to west due to the rotation of the Earth about its axis.
Question 13. Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years away from the Earth?
Answers: Stars are situated very far (many millions of kilometers) away from the Earth. Such large distance cannot be conveniently expressed in kilometers. Hence, it is expressed in a unit called a light year. One light year is the distance traveled by light in one year. One light year is equivalent to 9.46 x 10¹2 km. If we say that a star is eight light years away from earth, it means that the light from the star will reach the earth in eight years.
Question 14. The radius of Jupiter is II times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answers:
Let the radius of Earth = R units
200
Volume of Earth = 4/3xpx R³ cubic units
Radius of Jupiter = ||R units
Thus, volume of Jupiter = 4/3 × px (11R)³ cubic units
= 4/3 × px 1331R³ cubic units
X
Now, ratio of the volume of Jupiter and Earth = Volume of Jupiter/ Volume of Earth
:. 4/3 × px 1331 = R³/4/3 × px R³
= 1331/1 or 331: 1
So, Jupiter can accommodate 1331 Earths.
Question 15. Boojho made the following sketch of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Hots Corner
Question 1. Venus is far away from the Sun as compared to Mercury. Still, Venus is hotter than Mercury. Why is it so?
Answers:
Venus is far away from the Sun as compared to Mercury. Still Venus is hotter than Mercury.
Venus has a thick atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide gas. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse which traps the infrared radiations of the Sun resulting in an increase in the temperature of the planet. In contrast, Mercury has a thin atmosphere with a variety of gases. The atmosphere does not have greenhouse gases which can trap heat. Thus, Venus is much hotter than Mercury.
Question 2. Why do stars twinkle when planets do not?
Answers: Stars are located at a distance from the Earth; so they appear as dots or points in the sky. These points vibrate due to the atmospheric air currents. Hence, when seen from the Earth, they generally seem to twinkle or vibrate. However, planets are not located as far from Earth. They are relatively bigger in size and so their vibrations, due to atmospheric currents, are apparently not visible as twinkling.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Practice Exercise Objective Type Questions
1. Give one word for the following.
- The branch of science that deals with the study of the universe
- The unit of measurement used to measure distance in space
- The name of our galaxy
Answers:
- Astronomy
- Light year
- Milky way
2. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Venus is also called the morning star.
- Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system.
- Aryabhatta is a natural satellite of the Earth.
Answers:
- False
- True
- False
3. Circle the odd one out.
- Orion, Great Bear, Ursa Major, Big Dipper
- Earth, Venus, Moon, Jupiter
Answers:
- Orion
- Moon
4. Fill in the blanks.
- It is not possible to hear any sound on the Moon because of the absence of______.
- Asteroids are found between the orbits of_____ and______.
Answers:
- Atmosphere
- Mars, Jupiter
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is meant by an equatorial plane and orbital plane?
The equatorial plane refers to the plane of the Earth’s equator, and the orbital plane refers to the plane in which the Earth revolves around the Sun.
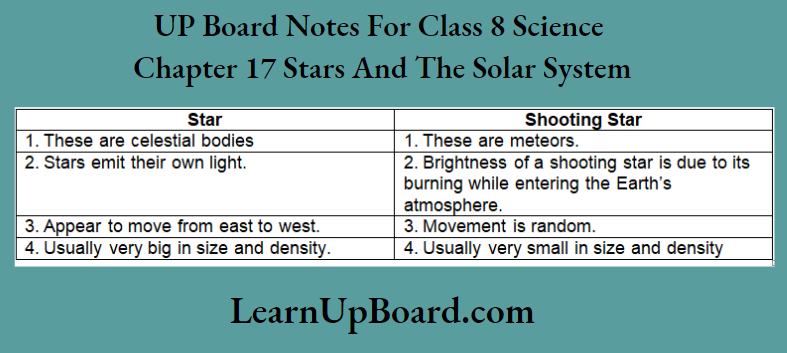
2. What are the differences between a star and a shooting star?
3. Name a periodic comet. Why is it so-called?
Answers: Halley’s comet is a periodic comet. It is called so because it appears at regular intervals of time. Halley’s comet is seen after every 76 years.
4. Why is the Sun classified as a star?
Answers:
The Sun is classified as a star due to the following reasons:
- It has its own source of energy.
- It continuously emits large amounts of light and energy.
- It has a life period.
5. State in which month/season the following constellations are seen:
1. Ursa major
2. Orion
1. Visible in April in the northern part of the sky.
2. Visible during the winter season in the northern part of the sky.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
