UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Abstract
- The force that opposes the relative motion between two objects in contact with each other is called friction.
- Air is a mixture of gases. About 78% of this mixture is nitrogen and 21% is oxygen. Rest 1% is formed by the gases like carbon dioxide, argon, methane, ozone and water vapour.
- Any undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air is called air pollution.
- Vehicles produce harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide, which pollute the air.
- Smog is a thick fog-like layer in the atmosphere formed especially during winter. It causes breathing problems such as asthma, cough and wheezing in children.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in refrigerators, air conditioners and aerosol sprays cause depletion of the ozone layer. The ozone layer protects us from the harmful ultraviolet rays of the Sun.
- The Supreme Court of India has ordered industries to switch to cleaner fuels like CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas).
- Contamination of water by harmful substances such as sewage, toxic chemicals, silt, etc., is known as water pollution.
- An ambitious plan called the Ganga Action Plan was launched in 1985 to save River Ganga from water pollution.
- It is important to conserve water because it is a precious natural resource. Hence, we should follow the scheme of reduce, reuse and recycle.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Important Terms And Definitions
Pollutants: Substances which cause pollution are called pollutants.
Greenhouse effect: The trapping of Sun’s radiation by the Earth’s atmosphere due to the increasing level of gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and water vapour in the atmosphere is called greenhouse effect. These gases are called greenhouse gases.
Global warming: The increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere due to the increasing levels of greenhouse gases is known as global warming.
Potable water: Water which is purified and fit for drinking is known as potable water.
Chemical contamination: Discharge of harmful chemicals into rivers and streams causing pollution of water is known as chemical contamination.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Eutrophication: Gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen and other plant nutrients due to excessive fertiliser runoff into an aquatic ecosystem such as a lake is known as Eutrophication.
Air Pollution: Causes, Effects and Ways to Control it
Air is essential for the survival of all living things. The combustion of fuels in automobiles, trucks and jet planes is the major source of air pollution. Air pollution can be reduced to a great extent by using clean fuels like CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and unleaded petrol.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Activity 1
Aim: To compare the quality of air in a park and a busy road; a residential area and an industrial area; a busy traffic intersection at different times of the day for example early morning, afternoon and evening; and a village and a town
Procedure:
- Visit the places listed above and notice the quality of air at these places.
- Note down your observations.
Observations:
- A park is full of fresh air, whereas a busy road is much polluted because of fumes, smoke, dust and sound.
- A residential area is polluted but compared to an industrial area its pollution level is negligible.
- Early in the morning, the traffic intersection is relatively free from any pollutants. However, in the afternoon, it becomes much polluted due to vehicular smoke. In the evening, the air at a traffic intersection becomes extremely polluted.
- A village is usually not polluted, whereas the air in a town is polluted.
Conclusion: Air quality varies from place to place. It gets affected by the presence of undesirable substances such as vehicular emissions. The contamination of air by unwanted substances that have a harmful effect on both the living and the non-living objects is known as air pollution.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Activity 3
Aim: To prepare a list of air pollutants, their sources and effects
Observation:

Conclusion:
- 1Excessive amount of carbon dioxide in the air leads to respiratory problems.
- Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. Excessive amount of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere results in trapping more than required amount of Sun’s radiation and leads to a rise in the average temperature of the atmosphere. This is called the greenhouse effect and it leads to global warming.
- Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas. Inhaling it can prove to be fatal.
- CFCs damage the protective ozone layer of the atmosphere.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Air pollution is caused by natural sources only.
- The quality of air in villages is generally better than in big cities.
- Particulate matter consists of tiny particles suspended in air.
- Deforestation leads to a decrease in the amount of CO₂ in the air.
- Carbon dioxide is the main gas responsible for greenhouse effect.
Answers:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. greenhouse effect leads to which of the following?
- Melting of glaciers
- Decrease in the Earth’s average temperature
- Depletion of the ozone layer
- Forest fire
Answers: 1) Melting of glaciers
Question 2. Which of the following gases mixes with blood and prevents it from carrying oxygen?
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Carbon monoxide
- Carbon dioxide
Answers: 3)Carbon monoxide
Question 3. Which of these damages the ozone layer?
- Methane
- Chlorofluorocarbons
- Carbon monoxide
- Oxygen
Answers: 2) Chlorofluorocarbons
Question 4. Which of these may be caused because of air pollution?
- Bronchitis
- Asthma
- Irritation in eyes
- All of these
Answers: 4) All of these
3. Fill in the blanks.
- Deforestation results in______amount of CO₂ in the air.
- In the context of air pollution, SPM stands for_______
- ______ diseases are caused by air pollution.
- _____ is produced from incomplete burning of fuels such as petrol and diesel.
- The rain that becomes unusually acidic due to the presence of acidic gases is called_______
Answers:
- Increased
- Suspended Particulate Matter
- Respiratory
- Carbon monoxide
- Acid rain
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Short Answer Type Questions
A. How does carbon monoxide act on human beings?
Answers: Carbon monoxide combines with the haemoglobin in the blood and cuts off the supply of oxygen to the cells. This results in headache, drowsiness, coma and even death.
B. List ways to minimise air pollution caused by the use of petrol and diesel.
Answers:
Ways to minimise air pollution caused by the use of petrol and diesel are:
- Supplying sufficient air so that partially burned carbon particles and carbon monoxide are almost absent.
- Using platinum as a catalyst assists complete oxidation of carbon particles and harmful gases.
Water Pollution: Causes, Effects, Ways to Control it
Answers:
Water Pollution
Contamination of water bodies by unwanted substances is called water pollution. Waste materials like chemicals, drugs and paints from different industries are discharged into nearby water bodies.
We Can Control Water Pollution In the Following Ways
Boiling the water kills the disease-causing microorganisms that are present in it. We must learn ways to control water pollution and conserve water, which is a precious natural resource.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Activity 5
Aim: To compare the smell, acidity and colour of different water samples
Procedure:
- Collect samples of water from a tap, pond, river, well and lake.
- Pour each sample into separate glass containers.
- Compare these samples for smell, acidity and colour.
Observation:

Conclusion: Water gets polluted when substances such as sewage, toxic chemicals, salts, etc. get mixed with IT.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Activity 7
Aim: To construct a water filter with simple, everyday materials
Procedure:
- Take a plastic bottle and cut it into two halves from the middle. Use the upper half as a funnel by putting it upside down in the lower half.
- Make layers in the lower portion of the bottle with paper napkins or a fine cloth followed by cotton, sand and then gravel.
- Now, pour dirty water through the filter and observe the filtered water.
Observations: The filtered water was clean and free from odour.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Clean water may not always be safe for drinking.
- Boiling water kills most of the germs present in it.
- Disease-causing microorganisms present in water bodies are good for human beings.
- Oil spills have a positive effect on aquatic life.
- Eutrophication reduces the level of oxygen in water bodies.
Answers:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
B. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1. Which of these is a waterborne disease?
- Cancer
- Measles
- Typhoid
- Cataract
Answers: 3) Typhoid
Question 2. Which of the following is most harmful to aquatic animals?
- Heavy metal ions
- Sodium ions
- Potassium ions
- Chloride ions
Answers: 1) Heavy metal ions
Question 3. Water containing high salt concentration can be purified by which
- Boiling
- UV irradiation
- Filtration
- Reverse osmosis
Answers: 4) Reverse osmosis
Question 4._______ is a common chemical method to purify water.
- Boiling
- Filtering
- Chlorination
- All of these
Answers: 3) Chlorination
C. Fill in the blanks.
- The Ganga Action Plan was launched in______.
- Substances that pollute water are called_____.
- Excessive quantities of fertilisers that run off into water bodies act as______for algae.
Answers:
- 1985
- Water pollutants
- Nutrients
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Short Answer Type Questions
A. Define the term ‘chlorination’.
Answers:
Chlorination Of Water:
Chlorination is a commonly used chemical method for purifying water. It is done by adding chlorine tablets or bleaching powder to the polluted water.
B. How can water pollution be controlled?
Answers:
Water pollution can be controlled by:
- Making sure that industries treat polluted water before it is discharged into rivers and lakes
- Minimising fertiliser run-off into water bodies
- Making sure that domestic sewage is not released into water bodies without being treated first
C. Hot water can also be a pollutant. Explain how?
Answers:
Hot water is discharged into rivers by power plants and industries. As a result the temperature of the water body increases. This adversely affects aquatic plants and animals and disrupts the natural ecosystems that exist in the water bodies..
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Textbook Exercises
Question 1. What are the different ways in which water gets contaminated?
Answers:
Different ways in which water gets contaminated are as follows
Water gets contaminated in various ways, such as by sewage, silt, washing, bathing or other household activities. Additionally, toxic chemicals from industries, garbage and dead bodies of animals and human beings, run-off fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, etc., also contaminate water.
Question 2. At an individual level, how can you help reduce air pollution?
Answers:
At an individual level, the following steps can be taken to reduce air pollution:
- Reduce the use of automobiles; use unleaded petrol or diesel in the automobiles
- Plant trees or vegetation around residential areas
- Use public transport or carpools
- Enforce laws to make sure that industrial and vehicular emissions are treated before being released into the air
Question 3. Clear, transparent water is always fit for drinking. Comment.
Answers:
Clear, transparent water is always fit for drinking.
This statement is incorrect. Clear, transparent water may appear clean but it may not necessarily be safe or fit for drinking. There may be dissolved impurities and disease-causing microorganisms present in the clear water.
Question 4. You are a member of the municipal body of your town. Make a list of the measures that would help your town to ensure the supply of clean water to all its residents.
Answers:
To obtain clean water:
- Industrial waste must be properly treated before being released into water resources.
- Sewage must be treated by physical and chemical methods before it is dumped into water bodies.
- Use of fertilisers should be minimised to reduce its run-off into water bodies.
- Dumping of wastes into water bodies, washing clothes or giving baths to animals on the banks of rivers and disposal of household sewage into water bodies without treating it first should be stopped.
Question 5. Explain the difference between pure air and polluted air.
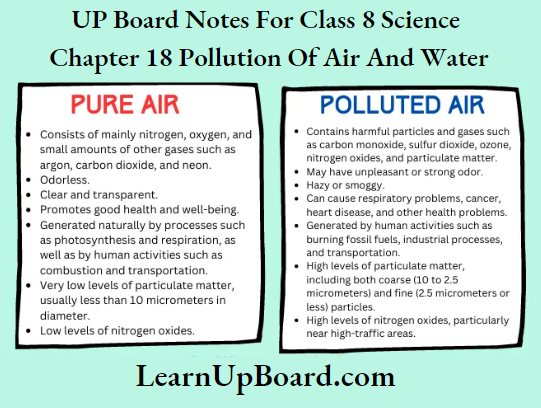
Question 6. Explain the circumstances leading to acid rain. How does acid rain affect us?
Answers:
The circumstances leading to acid rain
Some pollutants like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, etc. react with the water vapour present in the atmosphere to form sulphuric and nitric acids respectively. The acid mixes in the rainwater and thus makes it acidic. Acid rain destroys crops, wild plants, steel rail tracks, monuments, and electrical equipment. It irritates the eyes, nose and throat and adversely affects water bodies.
Question 7. Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
- Carbon dioxide
- Sulphur dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrogen
Answer: 4) Nitrogen
Question 8. Describe the ‘Greenhouse Effect’ in your own words.
Answers:
‘Greenhouse Effect’
The heating of the Earth’s atmosphere due to trapped infrared radiations of the Sun is called the greenhouse effect. There are four gases which can trap infrared radiations: carbon dioxide (CO₂), ozone (03) and methane (CH₂).
Question 9. Prepare a brief speech on global warming. You have to deliver the speech in your class.
Answers:
Global warming
When the Sun’s rays reach the Earth’s surface, some of them are reflected back and the rest are absorbed by greenhouse gases, which include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane and ozone. The absorbed energy maintains the temperature of the Earth. Increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is leading to global warming, which is the increase in the average temperature of Earth. The increase in temperature is leading to melting of polar ice caps and an increase in the water level in the sea. This poses a danger for the people living in coastal areas.
Question 10. Describe the threat to the beauty of the Taj Mahal.
Answers:
Taj Mahal is made up of white marble. The whiteness of the marble used in the monument is at threat owing to air pollution. Industrial establishments around the Taj Mahal emit many harmful gases such as sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, etc. These gases react with the water vapour present in the atmosphere to form sulphuric and nitric acids. These acids come down as acid rain and corrode the marble of the monument.
Question 11. Why does the increased level of nutrients in water affect the survival of aquatic organisms?
Answers:
Excessive quantities of chemicals like nitrates and phosphates present in the fertilisers act as nutrients for algae to flourish. When these algae die, decomposers such as bacteria use the oxygen present in the water to decompose the algae. Thus, there is a reduction in the oxygen level of the water, which adversely affects the survival of aquatic organisms.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Hots corner
1. Carbon dioxide is used by plants. Then why is it considered a pollutant?
Answers:
Carbon dioxide is a natural component of the atmosphere and also a by-product of the process of respiration. However, excessive amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is very harmful as it is a greenhouse gas and traps the infrared radiations of the Sun. This raises the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere and thus excessive amount of carbon dioxide is considered a pollutant.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Practice exercise Objective Type Questions
1. Give one word for the following.
- IA gas which protects the Earth from the harmful ultraviolet radiations of the Sun.
- Commonly used chemical method for purifying water
- Substances which contaminate air and water
- Purified water that is suitable for drinking
Answers:
- Ozone
- Chlorination
- Pollutants
- Potable water
2. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Sewage is a major source of water pollution.
- Greenhouse effect leads to depletion of the ozone layer.
Answers:
- True
- False
3. Circle the odd one out.
- Unleaded petrol, LPG, CNG, CFC
- Dust storms, Automobile exhausts, Volcanic eruptions, Pollen floating in air
Answers:
- CFC
- Automobile exhausts
4. Fill in the blanks.
- A combination of smoke and fog is called_____
- Unpolluted air contains 78%______and 21%______
- The stratosphere layer of the atmosphere protects us from_______
Answers:
- Smog
- Nitrogen, oxygen
- Ultraviolet radiations.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is the ozone hole? What could be its possible effect?
Answers:
Ozone hole
Ozone hole refers to the region in the ozone layer of the atmosphere where the ozone gas is either absent or present in very low concentrations. This region cannot absorb the harmful ultraviolet radiations of the Sun. The UV rays are the leading cause of skin cancer, cataract and damage to the immune system.
2. Why sewage water is called polluted water?
Answers:
Sewage water contains human urine and faeces, wastewater from the kitchen, bathing, washing of clothes and industrial wastes. This water is totally unfit for drinking, washing and for other purposes. It emits a foul smell and contains microorganisms that spread diseases. Hence, sewage water is called polluted water.
3. How can air pollution be controlled?
Answers:
We can control air pollution by:
- Minimising the use of aerosols
- Using compressed natural gas (CNG) as fuel
- Stopping deforestation and planting more trees
- Putting a ban on the use of CFCs
- Using clean fuels or alternative sources of energy in vehicles and factories
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
