UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe
- Types of Microorganisms
- Useful Microorganisms
- Harmful Microorganisms
- Nitrogen Fixation
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Chapter In A Nutshell
- A microscope is an instrument used for seeing objects or living organisms that are too small to view with naked eyes or even with a magnifying glass.
- Organisms that cannot be seen with naked eyes are called microorganisms.
- The branch of science which deals with the study of microorganisms is called microbiology.
- Disease causing microorganisms are known as pathogens.
- The diseases that are caused by pathogens and transmitted through air, food, water or direct physical contact are known as communicable or infectious diseases.
- A biological compound which is injected or introduced orally into the body of human beings to develop immunity against pathogens is called a vaccine.
- Antibiotics are compounds which destroy or arrest the gro wth of pathogers.
- There are four major groups of microorganisms: bacteria, fungi, algae and protozoa.
- Viruses are borderline organisms, which are living while inside the body of their host but are non¬living when outside.
- Protozoa are unicellular microorganisms that are found in freshwater sources. They have saprophytic mode of nutrition.
- Bacteria are unicellular organisms.
- In favourable conditions, bacteria reproduce by binary fission.
- Bacteria are used in the preparation of semm and vaccines.
- Bacteria spoil food by producing toxins.
- Methods like dehydration, salting, deep freezing, irradiation, canning, vacuum drying, etc., are used for preserving food.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
- Food preserv ation increases the storage period of food: makes its transportation easy and helps in obtaining off-season food materials.
- Bacteria can cause diseases like tetanus, cholera, pneumonia, typhoid and tuberculosis in human beings: black rot in cabbage; fire blight in pears and anthrax in animals.
- Agae are autotrophic microorganisms that contain chlorophyll. They may be unicellular, multicellular or colonial.
- Fungi are saprophytes that grow vigorously in damp, warm, dark places.
- The process of conversion of sugar into acids, alcohol or gas by the action of yeast is known as fermentation.
- Fermentation is usea in breweries to produce alcoholic beverages on a commercial scale.
- Nitrogen fixation is the process by which atmospheric nitrogen is fixed for the use of plants.
- The continuous circulation of nitrogen througi the living and non-living components of biosphere is known as the nitrogen cycle. Through this process, nitrogen is converted into its various forms.
- Nitrogen cycle includes nitrogen fixation, ammonification, nitrification and denitrification. It maintains the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Important Terms and Definitions
- Food preservation: The process of treating food to retain its nutritive value and prevent spoilage is called food preservation.
- Dehydration: Dehydration is the process of removing water. Canning: Canning is the process of preserving food in sterilised, air-tight cans.
- Ammonification: The process of conversion of proteins into ammonia by the action of bacteria is called ammonification.
- Pasteurisation: Pasteurisation is the process in which milk is heated to a high temperature and then cooled quickly to destroy almost 99% of bacteria.
- Nitrification: Conversion of ammonia into nitrates by the action of bacteria is called nitrification.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Types of Microorganisms
- Microorganisms cannot be seen with naked eyes and are present in almost everywhere. Microorganisms are useful as wells harmful to human beings.
- There are four major groups of microorganisms: bacteria, fungi, algae and protozoa. Bacteria are unicellular organisms. They may be autotrophic, saprophytic or parasitic.
Viruses are borderline organisms. They grow and multiply only inside their host When outside the body of a host, they are non-living and can be crystallised. The viruses which infects bacteria are called bacteriophage virus. Diseases like common cold, influenza, etc. are caused by viruses. Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a disease caused by a virus known as HIV. - Protozoa are unicellular microorganisms. They are found in freshwater sources like lakes, pools, etc., and have saprophytic mode of nutrition, i.e., they feed upon dead or decaying organic matter. They cause diseases like dysentery and malaria.

- Road shaped bacteria
- Bread Mould
- Spirogyra
- Amoeba
- Viruses
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Activity 1
Aim: To observe microorganisms found in the soil
Procedure:
- Put some moist soil in a beaker.
- Add a bit of water to the beaker and stir gently.
- After the soil particles have settled down at the bottom, take a drop of water from this beaker and observe it under the microscope.
Observation: Tiny organisms are seen in the drop of water.
Conclusion: Microorganisms are found in soil.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Activity 2
Aim: To observe microorganisms found in pond water
Procedure:
- Collect water from a pond.
- Observe a drop of pond water under the microscope.
Observation: Tiny organisms are seen in the dome of water.
Conclusion: Microorganisms are found in the pond water.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Microorganisms are found only in aquatic habitats.
- Microorganisms are tiny organisms which cannot be seen without a microscope.
- A bacterium is a microorganism.
- Microorganisms are not found in soil.
- Pond water may contain many different types of microorganisms.
- Protozoa are unicellular organisms.
Answers:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
2. Fill in the blanks.
- Bacteria are useful as well as_______ to human beings.
- Microorganisms are found in almost all types of__________ .
- Viruses are___________ outside the body of a host.
- Most fungi are__________ .
Answers:
- Harmful
- Habitats
- Non-living
- Saprophytes
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why are viruses placed on the borderline between living and non-living things?
Answer
Viruses do not have cytoplasm or definite nudes. They are living only inside the body of their host Outside the host body, they can be crystallised like salt or sugar. Hence, viruses are placed on the borderline between living and non-living things.
Question 2. What is a bacteriophage?
Answer
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage is a virus, which infects and replicates within a bacteria. Scientists are trying to use them as therapy against multi-antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe the differences in Amoeba and Paramecium in detail.
Answer:
The differences in Amoeba and Paramecium in detail are
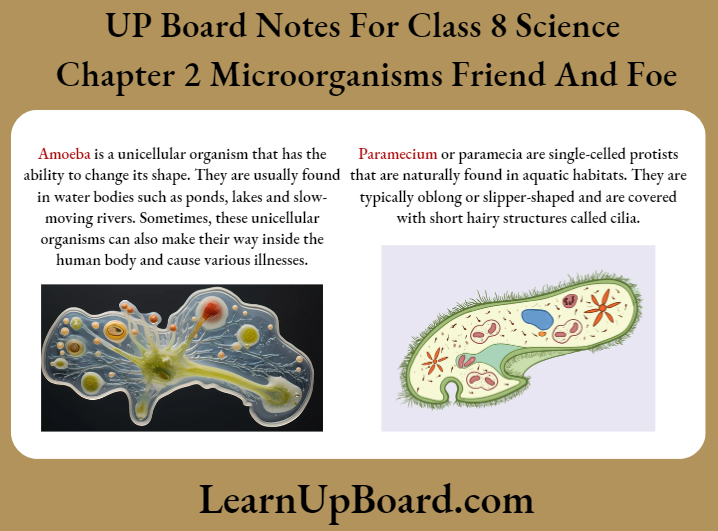
Useful Microorganisms
- Microorganisms are useful to human beings in many different ways. Bacteria and fungi are the main decomposers and help in the recycling of substances in nature. Commercially, bacteria are used for producing vinegar, rotting of flax and jute fibres, curing and ripening of tea leaves, tanning of leather, etc. The action of Lactobacillus bacteria changes milk into curd. In agriculture, bacteria help in the recycling of matter nitrogen cycle, etc. Rhizobium bacteria live in the root nodules of leguminous plants and help in fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Antibiotics such as streptomycin, Chloromycetin, etc. are obtained from bacteria. Many well-known antibiotics like penicillin are obtained from fungi. Fungi decompose dead and decaying parts of plants, animals and their waste products and make the soil fertile. Yeast is used on a large scale in bakeries, the cheese industry’ and for the production of organic acids and alcohol. At home, yeast is used for making food items such as I and dosa. etc. Mushrooms are edible fungi. Algae are used for preparing medicines, food, cosmetics and nitrogen or potassium-rich manure. Protozoa are used for the degradation of waste and sewage and as research materials.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And FoeActivity 3
Aim: To observe the growth of yeast in the dough
Procedure:
- Add some sugar and yeast power to Zi kg four (atta or maida).
- Add warm water and knead to make soft dough.
- Leave the dough for two hours and then observe it.
Observation: The dough has risen.
Conclusion: Yeast grows or reproduces rapidly in warm and wet dough releasing carbon dioxide gas. The bubbles of carbon dioxide get trapped inside the dough and hence, it rises. Therefore, the bread made with such dough is very light and spongy.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And FoeActivity 4
Aim: To observe the fermentation of sugar
Procedure:
- Fill a 500 mL beaker about 3/4th with lukewarm water.
- Dissolve 2-3 teaspoons of sugar into it
- Add half a spoon of yeast powder to this water.
- Leave the beaker covered for 4 – 5 hours.
- Smell this water after 4-5 hours.
Observation: The sugar, yeast and water mixture smells like alcohol.
Conclusion: The sugar’ has been converted into alcohol by the action of yeast This process is known as fermentation.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And FoeActivity 5
Aim: To observe conversion of biodegradable waste to manure
Procedure:
- Fill two pots halfway through with soil and able them as A and B.
- Fill the remainder of pot A with plant waste and the remainder of pot B with polythene bags, empty glass bottles and broken plastic toys.
- Cover both the pots with a cloth and leave them undisturbed for 3 – 4 weeks.
- Observe the pots after 3 4 weeks.
Observation: Plant waste in pot A has decomposed and changed into manure. However, polythene bags, glass bottles and plastic toys are unchanged.
Conclusion: Microbes present in the soil decompose plant waste as it is biodegradable but waste like polythene bags cannot be decomposed by microbes.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And FoeObjective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Decomposers help in recycling of materials n nature.
- Milk is converted into curd by the action of algae.
- The process of conversion of sugar into acids, alcohol or gas by the action of yeast is known as fermentation.
- Penicillin is obtained from a virus.
- Rhizobium bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Answers:
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is an antibiotic?
- Lactobacillus
- Yeast
- Renin
- Tetracycline
2. ‘Which of the following is a microorganism?
- Insects
- Bees
- Yeast
- Frog
3. Which of the following is used for obtaining the antibiotic streptomycin?
- Bacteria
- Protozoa
- Yeast
- Algae
4. Which of the following types of fibres are obtained by the action of microorganisms on the stem of plants?
- Jute
- Cotton
- Wool
- Silk
Answers:
- (4) Tetracycline
- (3) Yeast
- (1) Bacteria
- (1) Jute
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are vaccines?
Answer
Vaccines
Vaccines are antigens of mild strains of pathogens of a specific disease. When injected into the bloodstream, they stimulate white blood cells to produce antibodies against the pathogen.
Question 2. How is bread formed?
Answer
Formation Of Bread:
For making bread, a bit of yeast powder and sugar are mixed with wheat flour and the flour is made into dough using warm water. Presence of warmth and sugar stimulates the growth of yeast and as a result, it multiplies rapidly releasing carbon dioxide. Bubbles of carbon dioxide make the dough to rise and hence, the bread baked with this dough is light and spongy.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Harmful Microorganisms
- Besides being useful, microorganisms can cause a lot of harm too. The diseases which are caused by microorganisms and transmitted by air, food, water and d red physical contact are known as communicable or infectious diseases.
- Certain human diseases caused by bacteria are tuberculosis, typhoid, cholera, leprosy, tetanus, and pneumonia.
- Certain human diseases caused by viruses are common cold, influenza, chickenpox, smallpox, poliomyelitis, rabies, measles, AIDS and hepatitis.
- Certain human diseases caused by fungi are, athlete’s foot, ringworm and eczema
- Certain human diseases caused by protozoans a^, malaria and amoebic dysentery
- Certain plant diseases caused by bacteria are, citrus canker and black rot n cabbage and animal diseases
- Bacteria can spoil food by producing toxins in it…Algal bloom, which is the result of eutrophication, eventually leads to depletion of oxygen in water leading to loss of aquatic life forms.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Hepatitis is caused by a virus.
- Pulses should be stored in wet containers.
- Bacteria spoil food by producing toxins in it.
- Malaria is caused by protozoa.
- Rust and smuts in plants are caused by fungi.
- Dehydration helps in preserving food.
- The bacteria which do not require oxygen for their growth are called anaerobic bacteria.
- Sodium benzoate is a chemical preservative.
- Refrigeration is storing at a high temperature.
- Salt is used as a preservative in jams.
- The foot and mouth disease is a human disease.
- Lactobacillus is a harmful bacterium.
- Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria
- Chickenpox and smallpox are caused by fungi.
- Typhoid is a communicable disease.
Answers:
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
2. Fill in the blanks.
- Pathogens are the m microorganisms that cause__________
- Pasteurisation means heating milk to a high ‘.emperature and then immediately_______it.
- The most commonly used chemical food preservative is__________.
- Diphtheria is caused by_________.
- Polio, AIDS and measles are caused by_______________.
- Large algae that grow in oceans are called___________.
Answers
- Diseases
- Cooling
- Sodium benzoate
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Seaweeds
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Multiple Choice Questions.
1. ‘Which of the following microorganisms causes malaria?
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Bacteria
- Fungi
2. Which of the following microbes causes leprosy?
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Bacteria
- Fungi
3. ‘Which of the following methods is used for preserving pickles?
- Pasteurisation
- Sterilisation
- Salting
- None of these
4. Which of the following is not used as a chemical preservative for food?
- Vinegar
- Ammonia
- Sodium benzoate
- Sodium bisulphate
5. Which of the following is the best method for preserving milk?
- Pasteurisation
- Sterilisation
- Refrigeration
- Salting
6. Papad is preserved by which of the follow ng methods?
- Chemical preservation
- Salting
- Refrigeration
- Dehydration
7. Which of the following microorganisms causes food poisoning?
- Staphylococcus
- Penicillium
- Lactobacillus
- None of these
8. Which of the following microorganisms causes citrus canker in plants?
- Algae
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- None of these
Answers
- (b) Protozoa
- (c) Bacteria
- (c) Salting
- (b) Ammonia
- (a) Pasteurisation
- (d) Dehydration
- (a) Staphylococcus
- (c) Bacteria
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And FoeShort Answer Type Questions
1. What are some of the methods that can help in preserving food?
Some of the methods that can help in preserving food are
Action of bacteria spoils food. Heating food at a very high temperature kills bacteria or storing food at a very-’ low temperature such as in a refrigerator prevents spoilage of food. Chemical preservatives such as sodium benzoate, excess of salt or sugar as in pickles and jams respectively, dehydration as in papad and canning food items are other ways that can prevent spoiling of food.
2. Name a few chemical preservatives.
Few chemical preservatives
Few chemical preservatives are vinegar, sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite.
3. Suggest some methods to prevent the growth of moulds.
Mould or fungi grow in warm and wet conditions. Hence, their growth can be prevented by:
- Keeping the temperature low
- Making use of clean and closed containers for storing food items
- Keeping 0 lings dry
4. How can we stop the spread of communicable diseases?
Communicable diseases are transmitted by air, food, water and direct physical contact Spread of communicable diseases can be stopped by putting the infected person in quarantine, vaccinating against disease-causing microbes, taking full course of antibiotics prescribed by the physician, keeping our body and surroundings clean and always eating and drinking clean food and drinks.
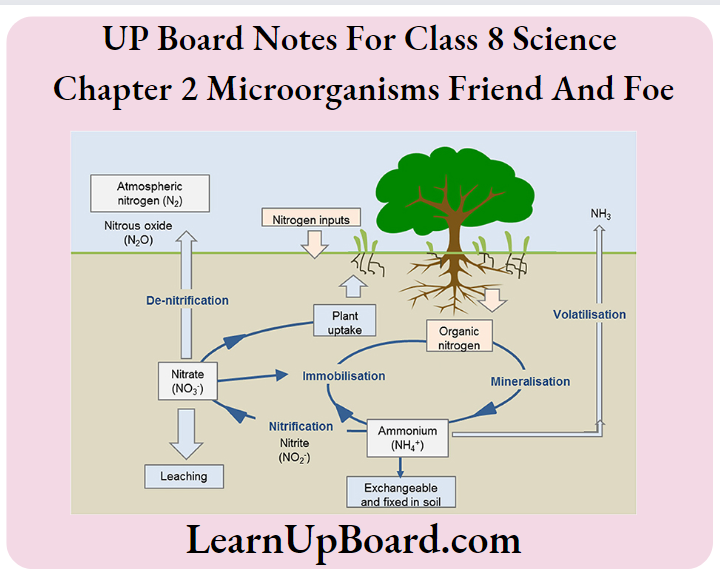
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Nitrogen Fixation
- The continuous circulation of nitrogen through the living and non-living components of biosphere is; known as nitrogen cycle. Through this process, nitrogen is converted into its various forms. The nitrogen cycle; includes nitrogen fixation, ammonification. nitrification and denitrification. It maintains the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Rhizobium bacteria live in the root nodules of leguminous plants and blue-green algae fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into nitrogenous compounds.
- Lightening too converts! atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds. Parts of nitrogenous compounds in the soil are; converted directly into atmospheric nitrogen and the remaining is taken up by the plants. Plants convert; nitrogenous compounds to proteins. These proteins are eaten by animals and returned to soil either as I waste product of excretion or after death through decomposition by microbes.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Blue-green algae and Rhizobium bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- Ammonification is the process of conversion of ammonia into proteins.
Answers:
- True
- False
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Long Answer Type Questions
1. Make a flowchart to show the nitrogen cycle.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Exercise
1. Fill in the blanks:
- Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a__________.
- Blue-green algae fix __________directly from the air to enhance the fertility of the soil.
- Alcohol is produced with the help of____________.
- Cholera is caused by_____________.
Answers:
- Microscope
- Nitrogen
- Yeast
- Bacteria
2. Tick the correct answer
1. Yeast is used in the production of
- Sugar
- Alcohol
- Hydrochloric Acid
- Oxygen
2. The following is an antibiotic:
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Streptomycin
- Alcohol
- Yeast
3. Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is:
- Female Anopheles mosquito
- Cockroach
- Housefly
- Butterfly
4. The most common carrier of communicable diseases is:
- Ant
- Housefly
- Dragonfly
- Spider
5. The break or idli dough rises because of:
- Heat
- Grinding
- Growth of yeast cells
- Kneading
6. The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called:
- Nitrogen fixation
- Moulding
- Fermentation
- Infection
Answers.
- (2) Alcohol
- (2) Streptomycin
- (1) Female anopheles mosquito
- (2) Housefly
- (3) Growth cf yeast cells
- (3) Fermentation
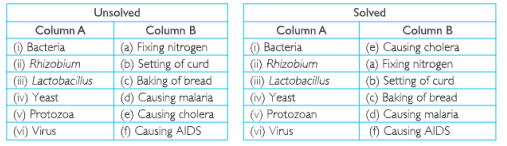
3. Match the Organisms in column A with their action in column B
 4. Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
4. Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
No, microorganisms cannot be seen with the naked eye because they are too small. We can see them under a microscope.
5. What are the major groups of microorganisms?
The major groups of micro-organisms are bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae and viruses.
6. Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Rhizobium bacteria and blue-green alga can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
7. Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
The beneficial aspects of microorganisms are as follows:
- Microorganisms are decomposers and they help in the recycling of substances.
- Blue-green algae and Rhizobium bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds and increase the fertility of the soil.
- Lactobacillus helps in the formation of milk products like curd and cheese.
- Yeast helps in the formation of alcohol and bakery products like bread and cakes.
- Products like idli and dosa are prepared by the action of fungi.
- Medicines such as penicillin are made from fungi.
- Mushrooms are edible fungi.
- Algal cell extract such as agar is used for preparing medicines, food and cosmetics.
- Kelp, a brown alga, is a rich source of iodine and potassium.
- Many types of seaweed are used as food in China and Japan.
8. Write a short paragraph on the harms caused by microorganisms.
Besides being useful, microorganisms are responsible for causing a large variety of diseases in plants, animals and human beings. They spoil food by breaking down food molecules and making new products called amines, which are generally smelly. This changes the chemical composition, texture and physical appearance of the food. Such food, if consumed, leads to many diseases including food poisoning. In plants, they cause diseases like wheat rust and citrus canker. In animals, they cause diseases like foot and mouth disease and anthrax. They spoil articles like clothes, leather, etc.
9. What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Antibiotics as chemicals that inhibit the growth of microorganisms without harming the host Precautions to be taken while taking antibiotics are:
- Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor.
- One must finish the entire course prescribed by the doctor.
- Antibiotics, however, are not effective against colds and flu as these diseases are caused by viruses.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Hots Corner
A. Your mother makes curd at home. The curd sets faster in summers than in winters. Why?
Curd, as we know, is formed by the action of Lactobacillus bacteria on milk. Bacteria, including Lactobacillus, can grow and multiply faster during summer as the temperature in summer is appropriate for their growth. Hence, curd sets faster in summers than in winters.
B. Why packets of chips are filled with nitrogen gas rather than with oxygen?
Nitrogen inhibits the growth of aerobic bacteria and the chips stay fresh and are not spoilt by the action of bacteria. Thus, packets of chips are filled with nitrogen gas rather than oxygen.
C. Sameer bought fruit chat from a vendor. Next day he fell ill. What do you think is the reason for his illness?
Fruit chat vendors keep cut fruits in the open for long hours. This invites action of bacteria and they grow and multiply on these fruits. Hence, the toxins produced in the fruits are consumed along with fruit chat and they might be responsible for causing the illness.
D. Dough gets spoilt faster than dry flour. What is the reason behind it?
The dough contains moisture, which is essential for the growth of microorganisms. Dry flour does not have any moisture. Hence, dough gets spoilt faster than dry flour.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Practice Exercise Objective Type Questions
1. Fill in the blanks.
- A bacterium which infects a virus is known as a.
- Disease-causing microorganisms are called.
- Milk is preserved by the process of.
Answers:
- Bacteriophage
- Pathogens
- Pasteurisation
2. Circle the odd one out.
- Bacteria, fungi, houseflies, algae, protozoa
- Chickenpox, pneumonia, smallpox, polio, rabies
- Nitrogen fixation, ammonification, nitrification, fermentation, denitrification
Answers:
- Housefly
- Pneumonia
- Fermentation
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Spoilage of food by bacterial action can be prevented by dehydration, salting or adding preservatives.
- No other organisms besides bacteria are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Answers:
- True
- False
4. Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following are used in making body items?
- Mushroom
- Seaweed
- Yeast powder
- All of these
2 Which of the following are autotrophic?
- Protozoa
- Algae
- Fungi
- Virus
3. Which of the following helps in the nitrogen cycle?
- Rhizobium bacteria
- Blue-green algae
- Lightening
- All of these
4. Which of the following is a disease caused in plants by pathogens?
- Foot and mouth disease
- Rabies
- Citrus canker
- Tuberculosis
5. Which of the following is a communicable disease?
- Typhoid
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Asthma
Answers:
- (d) All of these
- (b) Algae
- (d) All of these
- (c) Citrus canker
- (a) Typhoid
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend And Foe Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is AIDS?
ALDS:
AIDS stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome and is caused by the HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) virus. In this disease, there is severe loss of the body’s immunity and the body j becomes highly susceptible to diseases.
2. What is food preservation?
Food preservation
The process of treating food to retain its nutritive value and prevent its spoilage is called food preservation. Dehydration, salting, deep freezing, irradiation, canning, vacuum drying, etc., are some of the methods used for preserving food. Food preservation increases the storage period of food; makes its transportation easy and helps in obtaining off-sensor food materials.
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
