UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Concepts
- Types of Synthetic Fibres
- Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
- Plastics
- Plastics and the Environment
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Learning Objectives
- Fibres made by human beings are called synthetic fibres. Rayon, nylon, polyester, acrylic, etc., are examples of synthetic fibres.
- A synthetic fibre is a chain of small units joined together to form a large single unit called a polymer.
- Rayon or artificial silk resembles silk in appearance, texture and shine. It is made from the chemical treatment of wood pulp.
- Rayon can be woven like silk fibres and can be dyed in many different colours. It is used for making saris, dresses, aprons, caps, carpets, etc.
- Nylon is made without using any animal or plant-based raw material. It is made from coal, water and air.
- Nylon fibre is strong, elastic, wrinkle-free, light and absorbs little water. It is the first fully-synthetic fibre. It is lustrous and easy to wash.
- Due to high tensile strength of nylon fibre, it is used for making parachute fabric, ropes for climbing mountains, etc.
- Polyester is made up of units of a chemical called ester a compound which gives fruits their fruity smell.
- Polyester is easy to wash, does not get wrinkled and is suitable for making shirts, dresses, etc. Terylene and PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) are examples of polyester.
- Terylene is used for making fine fabrics and PET is used for making bottles, jars, etc.
- Many fabrics are made by mixing two types of fibres. For example, poly cot is made by mixing polyester and cotton and poly wool is made by mixing polyester and wool.
- Acrylic is another type of synthetic fibre, which is used for making sweaters, shawls and blankets.
- Synthetic fibres are less expensive, available in many different colours, have high tensile strength, durable and easy to maintain.
- On heating, synthetic fibres melt. They do not absorb moisture and can catch fire easily.
- Plastic is also a polymer like synthetic fibres. However, the arrangement of small units is not the same in all types of plastic.
- Plastics which can be bent easily and deforms on heating are known as thermoplastics. Polythene and PVC (polyvinyl chloride) are thermoplastics and are used for making toys, combs, containers, etc.
- Plastics which cannot be softened by heating are called thermosetting plastics. Examples of thermosetting plastics include Bakelite and Melamine.
- Bakelite is a poor conductor of electricity and heat and is used for making electric switches and handles of kitchen utensils.
- Melamine resists fire and can tolerate heat better than other types of plastics, it is used for making tiles, utensils and fabrics that resist fire.
- Plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity and that is why electric wires and electric equipment are covered with plastic.
- Plastics are lightweight, not very expensive, non-reactive and have good strength.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
- Plastic is used in healthcare industry for making syringes, threads that are used for stitching wounds, packaging of medicines, surgical gloves and medical instruments.
- Special plastic cookware is used for cooking or heating food in the microwave ovens.
- Teflon is a special plastic on which water and oil do not stick, it is used as a non-stick coating on cookware.
- Plastic is non-biodegradable, i.e. it cannot be decomposed through natural processes. Some plastics take many years to decompose.
- Animals eating the food wastes swallow polythene bags which choke their respiratory
- system and lead to their death. Polythene bags clog drains too.
- We should avoid the use of polythene bags and should use reusable cloth or jute bags.
We should segregate waste into biodegradable and non-biodegradable ‘Waste before throwing them. We should not throw garbage or wrappers anywhere other than the garbage bins. - We should recycle plastic as much as possible. However, recycled plastic cannot be used for storing food.
- To reduce plastic pollution one should avoid its use as much as possible and use biodegradable plastics.
- We must remember the 4 R principle: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Types Of Synthetic Fibres
- We wear clothes that are made up of different types of fabrics. Fabrics are made of fibres. There are two types of fibres: natural and man-made. Silk, cotton, wool, etc. are natural fibres because they are obtained from natural resources. Fibres made by human beings are called synthetic fibres. Rayon, nylon, polyester, acrylic, etc., are examples of synthetic fibres.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Activity 1
Aim: To test, the strength of different threads or fibres
Procedure:
- Tie a 60 cm long cotton thread to the clamp of a stand.
- At the free end of the thread, tie a very small pan so that small weights or marbles can be placed on it
- One by one, add weights or marbles to the pan till the cotton thread breaks.
- Note down the total weight or the total number of marbles that broke the cotton thread.
- Repeat these steps with woollen, silk and nylon threads of the same thickness and length.
- Record your observations.
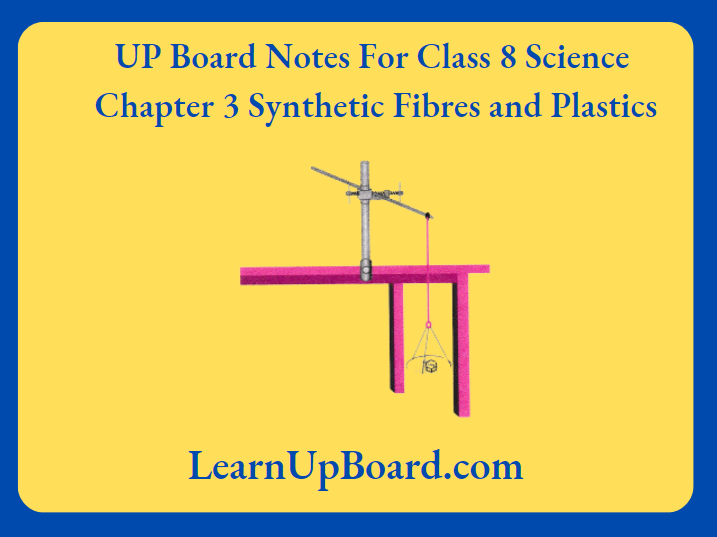
An iron stand with a thread hanging from the clamp
Observation: The weight required to break the threads made out of cotton, wool, silk and nylon fibres varied with the thickness of the threads. However, for the threads having the same thickness and length, nylon required the highest weight or number of marbles to break ft.
Conclusion: Nylon thread requires the highest weight to break. Nylon fibres are stronger than woollen, silk and cotton fibres.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And PlasticsObjective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Nylon is used for manufacturing tyres and high-strength ropes.
- Rayon is a natural fibre.
- Fibres obtained from natural resources such as plants and animals are called natural fibres.
- All synthetic fibres are obtained from plants or animals.
Answers.
- True
- False
- True
- False
2. Fill in the blanks.
- _________stands for Polyethylene terephthalate.
- The process in which a large number of simple molecules combine chemically to form a giant molecule is called_________.
- Rayon is obtained from_______.
Answers.
- PET
- Polymerisation
- Wood pulp
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why is nylon used for making parachute cloth and ropes for mountain climbing?
Answer
Nylon fibres are very strong and have very high tensile strength. Hence, they are used for making parachute cloth and ropes for mountain climbing.
Question 2. Some people do not consider rayon a truly synthetic fibre. Why?
Answer
All synthetic fibres are made from raw materials of petroleum origin called petrochemicals. Rayon, on; the other hand, is made from chemical treatment of wood pulp. Wood is obtained from plants and hence, rayon is not considered to be a truly synthetic fibre.
Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
- Synthetic fibres are strong, light and durable. Fabrics made from synthetic fibres do not absorb water, are wrinkle free and easy to maintain. Fabrics made from synthetic fibres are available in many different colours and usually less expensive. For example, rayon or artificial silk is lustrous, can be woven like silk and much less expensive than silk On heating, synthetic fibres melt and can easily catch fire.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Activity 2
Aim: To observe the amount of water absorbed by cloth Dieces made from natural and synthetic fibres
Procedure:
- Take two cloth pieces of same size, one cotton and the other polyester.
- Put equal amount of water in two mugs of the same size.
- Soak the two cloth pieces into the two mugs.
- Take the cloth pieces out of the mugs after five minutes and spread them in the Sun to dry.
- Compare the amount of water left in the two mugs.
Observation: The mug that had the cotton cloth soaked in it has a lesser amount of water left than the one in which the polyester cloth was soaked.
Conclusion: Synthetic fibres absorb very little water as compared to natural fibres.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Fabrics made from synthetic fibres are usual y wrinkle-resistant.
- Synthetic fibres melt on heating.
- Fabrics made from natural fibres are less expensive as compared to the ones made from synthetic fibres.
- Synthetic fabrics are not durable.
Answers
- True
- True
- False
- False
2. Fill in the blanks.
- fibres can be dyed into many different colours.
- Clothes made from synthetic fabrics are durable and easy to.
- Synthetic fibres do not absorb
- We should not wear clothes made Tom synthetic fibres while working near.
- Wool is but its synthetic counterpart, acrylic, is cheap.
Answers.
- Synthetic
- Maintain
- Water
- Fire
- Expensive
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Plastics
Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a polymer However, the arrangement of other small units is not same in all types of plastic. In some plastics, the arrangement is linear and in others it is cross-linked. Plastics can be melted and moulded into desired shapes. They can be recycled, coloured into different colours, rolled; into sheets and drawn into wires. Polythene is an example of plastic.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Thermoplastics become hard on heating.
- Plastics are lightweight and durable.
- Teflon does not let oil and water stick to it.
- Plastics have no use in the medical industry.
- The arrangement of small units in some plastics is linear, while in others it is cross-linked.
Answers.
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
2. Fill in the blanks.
- The clothes of firefighters are made fire resistant by using____________.
- Polythene bags are made out of____________.
- Bakelite and melamine are examples of_____________ plastics.
- _______________coating is used in non-stick cookware.
Answers.
- Melamine
- Plastic
- Thermosetting
- Teflon
3. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. Which of the following describes plastics?
- Strong and corrosion resistant
- Weak and prone to corrosion
- None of these
- Good conductor of heat and electricity
2. Which of the following is true about PVC?
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Thermoplastic
- Bends easily
- All of these
3. Which of the following are the characteristics of plastics?
- Can be moulded easily into various shapes
- Are good conductors of heat
- None of these
- Are Delicate
4. Which of the following applies to melamine?
- Thermoplastic
- Fire resistant
- Bends easily
- Weak
5. Which of the following is the most commonly used form of plastic?
- PVC
- Bakelite
- Melamine
- Polythene
Answers.
- (1) Strong and corrosion resistant
- (4) All of these
- (1) Can be moulded easily into various shapes
- (2) Fire resistant
- (4) Polythene
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. List a few uses of polythene.
Answer
Few uses of polythene
Polythene sheets are used as packaging material. Polythene containers and pipes are used for storing and transporting water, oil and other materials. Polythene is also used as a water-proofing material.
Question 2. What is bakelite? Why is it used to make handles of utensils and most electrical fittings such as electrical switches, sockets, etc.?
Answer
Bakelite
Bakelite is a thermosetting plastic. It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. Therefore, it is used for making handles of utensils and most electrical fittings.
Plastics and the Environment
- Disposal of plastic is a major problem. Plastic is non-biodegradable, i.e., it cannot be decomposed through; natural processes. Some plastics take many years to decompose. Plastics are not environmentally friendly. It does not get completely burnt and releases poisonous gases on burning, which pollutes the environment ;
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Plastic is non-biodegradable.
- To dispose of plastic, we should bum it
- Polythene bags choke animals when they accidentally ingest them.
- To reduce pollution, we must remember the principle to reduce, reuse, recycle and recover.
- Candy wrappers can be thrown on the side of the roads.
- It is best to use recycled Plastic containers for storing food.
- To reduce plastic pollution, we should avoid the use of non-biodegradable plastic.
Answers.
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
2. Match the items in column A with those in column B.
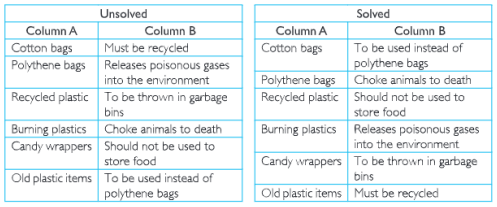
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer
some fibres are called synthetic
Some fibres are called synthetic because they are made by human beings. The raw materials used for preparing synthetic fibres are petrochemicals.
Question 2. Mark the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because:
- It has a silk-like appearance.
- It is obtained from wood pulp.
- Its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Answer.
2. It is obtained from wood pulp.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
- Synthetic fibres are also called ________or___________fibres.
- Synthetic fibres are synthesised from a raw material called____________.
- Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a____________.
Answers.
- Man-made, artificial
- Petrochemicals
- Polymer
Question 4. Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer
Parachutes, ropes used for mountain climbing and tents are made of nylon and this indicates that nylon fibres are very strong.
Question 5. Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer
Plastic containers are favoured for storing food because:
- Plastic does not react with food, air or water.
- Plastic is strong and lightweight.
- Plastic containers come in many different sizes, shapes and colours.
Question 6. Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
The difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics
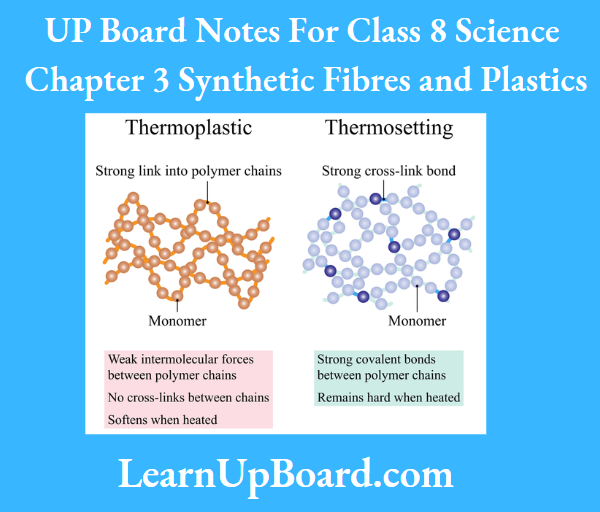
Question 7. Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
(a) Saucepan handles (b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
Answer.
(a) Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics because thermosetting plastic is a bad conductor of heat and does not deform on heating.
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards are made of thermosetting plastic because thermosetting plastic is a bad conductor of electricity and hence, reduces the risk of an electric shock
Question 8. Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled and ‘cannot be recycled. Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches?
Answer
Can be recycled: Plastic toys, carry bags, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, plastic chairs
Cannot be recycled: Telephone instruments, cooker handles, plastic coverings on electric wires, electrical switches
Question 9. Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer
Rana should buy cotton shirts because cotton has pores that let the air in and out. On the other hand, synthetic fabrics are very tightly woven and hence, they do not allow air to pass in and out. Cotton clothes soak sweat and give a dr/ feeling, while synthetic clothes have little water-absorbing properties.
Question 10. Give examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
Answer
Plastics do not react with air and water and hence, they do not corrode. Plastics do not decompose when left in the open for a long. For example, water is kept in plastic bottles, and pickles and food items are stored in plastic containers because the bottles or the containers do not corrode.
Question 11. Should the handle and bristles of a toothbrush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Answer
No. different mater also should be used for making handles and bristles of a toothbrush because bristles help in cleaning the teeth and the handle is just to support them. Bristles must be soft, and delicate and should be designed to clean teeth well, while the handle should be hard and rigid.
Question 12. ‘Avoid plastics as far as possible. Comment on this advice.
Answer:
Avoid plastics as far as possible.
Plastics are not environmentally friendly. They release poisonous gases on bum ng. They are non-biodegradable and hence, pollute soil, water and air. Animals choke on swallowing polythene bags and die. Polythene bags also clog the drains. Therefore, the use of plastic should be avoided as far as possible.
Question 13. Match the materials in column A with their characteristics given in column B.
Answer:

Question 14. ‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping in the conservation of forests. Comment.
Answer
Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping in the conservation of forests
Natural fibres are obtained from natural resources, i.e., plants and animals. On the other hand, synthetic fibres are made from petrochemicals and not from forests or plants. Thus, for manufacturing synthetic fibres we do not need to cut trees or use products obtained from animals.
Question 15. Describe an activity to show that thermoplastics are poor conductors of electricity.
Answer:
Take a few items made of thermoplastics such as a piece of PVC pipe and a toy. Now set up the circuit as shown in the given illustration and one by one insert the thermoplastic item between terminals A and B. If the bulb starts glowing, then the item is a good conductor of electricity. Otherwise, it is a bad conductor of electricity. You would find that the bulb would not glow with any of the items made of thermoplastics. This indicates that thermoplastics are bad conductors of electricity.
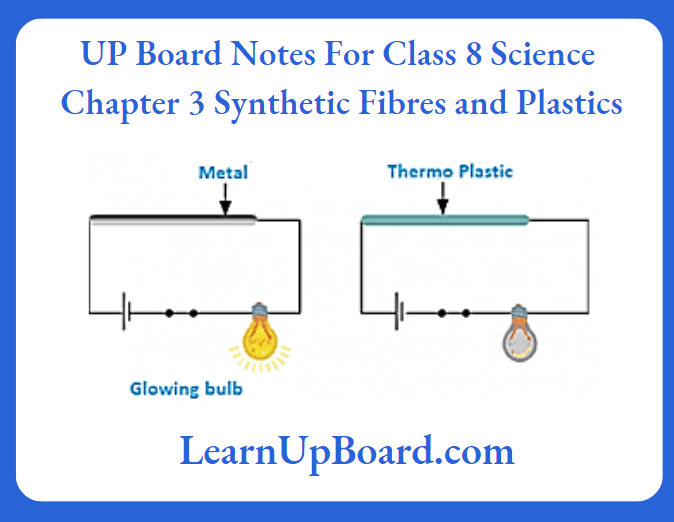
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Hots Corner
Question 1. On Diwali, we are told not to burst crackers while wearing synthetic clothes. Why?
Answer
Synthetic clothes melt on heating and stick to the skin of the person wearing them. This can result in really bad bums and hence, it is advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working near the fire.
Question 2. Plastics are very useful as well as less expensive than other materials. Which characteristics of plastics make them harmful to the environment?
Answer
Plastics are non-reactive. They do not get corroded by air or water. Hence, they do not biodegrade; and this is the property which makes them harmful to the environment.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Practice Exercise Objective Type Questions
1. Fill in the blanks.
- ____________is used for making sweaters, shawls and blankets.
- Synthetic fibres are strong but light in______________.
- Thermoplastics become ______________on heating.
Answers
- Acrylic
- Weight
- Deformed
2. Circle the odd one out.
- Nylon, rayon, polyester, silk, acrylic
- Terrycot, poly cot, nylon, poly-wool, terry wool
- Handles of cookware, firefighter clothes, car paint, melamine tray, water bottle
Answers
- Silk
- Nylon
- Water bottle
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Polycot is made by mixing polyester and wool.
- Bakelite is a bad conductor of heat and electricity.
- Plastics are weak and non-resistant to corrosion.
Answers
- False
- True
- False
4. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. Which of the following is used for making electrical switches?
- Teflon
- Polythene
- Bakelite
- PVC
2. ‘Which of the following types of plastic would you use to ma<e baby toys?
- Bakelite
- Melamine
- Teflon
- Thermoplastic
3. ‘What do you call a large unit which is made up of many smaller units of the same type?
- Polymer
- Compound
- Element
- None of these
4. ‘Which of the following can be made with thermosetting plastics?
- Combs
- Bottles
- Buckets
- All of these
5. Why are electrical wires covered with a plastic covering?
- Plastic is durable
- Plastic is a bad conductor of electricity
- Plastic is light-weight
- Plastic is not very expensive
Answers
- (3) Bakelite
- (4) Thermoplastic
- (1) Polymer
- (4) All of these
- (2) Plastic is a bad conductor of electricity
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is polyester?
Answer
Polyester Fabric
Polyester is made up of units of a chemical called ester-a compound which gives fruits their fruity smell Polyester is easy to wash and does not get wrinkled. Terylene and PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) are examples of polyesters.
Question 2. Why does hot water deform water bottles?
Answer
Water bottles are usually made of thermoplastics, which deform on heating. Hence, hot water deforms water bottles.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
