UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Chapter In A Nutshell
- Materials can be classified as metals and non-metals.
- Metals differ from non-metals in physical and chemical properties.
- Metals are usually solids except for mercury, which is liquid at room temperature.
- Metals are hard materials except sodium and potassium which are soft metals that can be easily cut by a knife.
- Metals are lustrous, sonorous, malleable arid ductile. They conduct heat and electricity.
- Metals have high melting points except gallium which melts in the hand i.e., at body temperature.
- Non-metals exist in all three states — solid, liquid and gas. They are brittle, non-lustrous, non-sonorous, poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- Metals usually combine with oxygen to form metallic oxides, which are basic. These oxides react with water to form bases.
- Sodium and potassium are the most reactive metals which react readily with oxygen, even at room temperature. That is why they are stored in kerosene oil.
- Copper reacts with atmospheric oxygen and acquires a green coating of a mixture of copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)j) and copper carbonate (CuCOj) on its surface.
- Non-metals combine with oxygen and form non-metallic oxides, which are also known as acidic oxides. These oxides react with water to form acids.
- Phosphorus rapidly bums in the air at room temperature to form phosphorus oxide. It is thus stored in water to avoid its contact with the atmospheric oxygen.
- Metals react with water depending upon their reactivity to form oxides or hydroxides and hydrogen gas. Non-metals do not react with water.
- Some very reactive metals like sodium and potassium react violently with cold water.
- Metals like gold, silver and platinum do rot react even with steam. They are called noble metals.
- Iron reacts with moisture in the air to form iron oxide. Iron oxide is brownish-red in colour and is called rust
- Metals react with acids to form corresponding salts with the evolution of hydrogen gas. Non-metals do not react with acids.
- Most of the metals generally do not react with bases at room temperature. Metals like aluminium and zinc react with strong bases like sodium hydroxide to form complex compounds with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
- Some of the metals in their increasing order of reactivity are Gold, Silver, Copper, Iron, Zinc, Aluminium, Magnesium, Sodium and Potassium.
- A reaction in which a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its solution is called a displacement reaction.
- Metals and non-metals are used in the industries, kitchens, household items, transport, etc.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Important Terms And Definitions
Malleability: The property of metals by the virtue of which they can be hammered or beaten into thin sheets is known as malleability.
Ductility: The property of metals by the virtue of which they can be drawn to thin wires is known as ductility.
Sonorous: The property of metals to produce a ringing sound when struck by an object is known as sonorous.
Metallic lustre: The property of metals by the virtue of which they shine is called metallic lustre. Metalloids: Materials that show the properties cf both metals and non-metals are called metalloids.
Physical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals
Materials are of two types – metals and non-metals. Metals usually exist in the solid state. They are hard, lustrous, sonorous, malleable, ductile and good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals have high; density and high melting points. Examples of metals are Aluminium, gold, silver, copper, sodium, etc.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Non-metals exist in all three states, liquid and gas. They are soft, brittle, non-lustrous, non-sonorous and poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are neither ductile nor malleable. Examples of non-metals are sulphur, oxygen, bromine, carbon, etc.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 1
Aim: To show that metals are malleable while non-metals are non-malleable
Procedure:
1. Take a small iron nail, a piece of coal, a piece of thick aluminium wire and a pencil.
2. Hit hard all the materials one by one with a hammer.
3. Note down the observations in the observation table.
Observation:
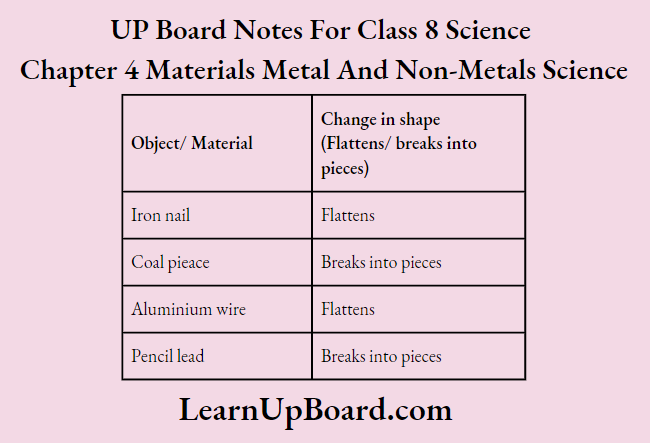
Conclusion: Iron and aluminium are malleable while coal and pencil lead are non-malleable materials. This shows that metals are malleable i.e., they can be beaten into thin sheets. Non-metals are non-malleable.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 2
Aim: To show that metals are good conductors of electricity while non-metals are poor conductors of electricity
Procedure:
1. Make an electric circuit as shown below.
2. Connect the circuits one by one with an iron nail, a piece of sulphur, a piece of coal and a copper wire.
3. Note down your observations in the observation table.
An electric circuit
Observation:
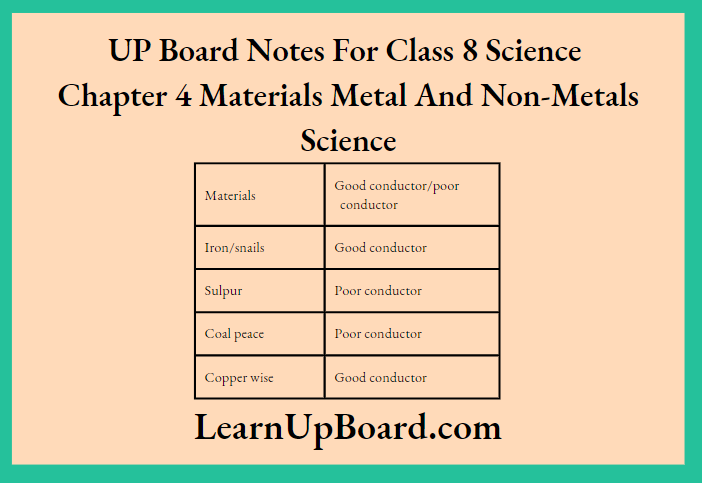
Conclusion: Metals are good conductors of electricity-‘ while non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Objective Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Metal and non-metals have the same physical properties.
2. All non-metals possess lustre.
3. Cooking utensils are made of metals because they/ are good conductors of heat.
4. Mercury is a non-metal found in the solid state.
Answers: 1. False 2. False 3. True 4. False
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Short Answer Type Questions
1. What do you understand by the ductility and malleability of a metal? Give examples of two metals which are both ductile and malleable.
Answer.
Ductility and malleability of a metal
Ductility is the property of metals by which they can be drawn into thin wires. Examples of ductile metals are copper, silver, etc.
Malleability is the property of metals which means that they can be hammered into thin sheets or foils. Examples of malleable metals are gold, silver, etc.
2. Why aluminium and copper are used for making electrical wires?
Answer. Aluminium and copper are metals. They are duct le and good conductors of electricity. Therefore, aluminium and copper are used for making electrical wires.
Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals
Reaction with oxygen – Metals react with oxygen to form metallic oxides which are basic. Non¬metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides which are acidic.
Reaction with water – Metals react with water to form either oxides or hydroxides and hydrogen gas. Most of the non-metals do not react with water.
Reaction with acids and bases – Metals react with acids to form corresponding salts with the evolution of hydrogen gas. Metals usually do riot react with bases. Most of the iron metals do not react with acids; and bases.
A more reactive metal tends to displace a less reactive metal from its solution. Such a reaction; is known as a displacement reaction.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 3
Aim: To show that metallic oxides are basic in nature
Procedure:
1. Take a spoonful of rust and dissolve it in a small amount of water.
2. Shake the mixture well and test the solutior with red and blue litmus papers.
3. Observe the colour change of the Irtmus paaer.
Observation: The solution of rust and water changes the colour of red litmus paper to blue. The colour of blue litmus paper does not change.
Conclusion: Metallic oxides are basic in nature.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 4
Aim: To show that non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature AM Procedure:
1. Take a small amount of sulphur powder in a deflagrating spoon and heat it.
2. As sulphur starts burning introduce the spoon into the gas jar or glass tumbler.
3. Cover the lid and ensure that the gas produced does not escape from the jar.
4. Add a small amount of water it the jar and cover the jar with the lid quickly.
5. Shake the tumbler well and test the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
Observation: When sulphur bums in oxygen, it produces sulphur dioxide. On dissolving this sulphur dioxide in water, sulphurous acid is formed.
so2 +H2O > H2SO,
SJafr.rD’-xde Sjiphjrojt *od
Sulphurous acid changes the colour of blue litmus Daperto red.
Conclusion: Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides. These oxides are acidic in nature. These oxides dissolve in water to form acid.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 5
Aim: To show the reaction of sodium metal with water
Precaution: The size of the sodium metal should be nearly the size of a wheat grain. A pair of tongs must be used to handle the piece of sodium metal.
Procedure:
1. Take a 250 ml beaker or a glass tumbler and fill it half with water.
2. Cut a small piece of sodium metal carefully.
3. Dry the piece of sodium metal and wrap it in a small piece of cotton.
4. Put the wrapped sodium piece into the bea<er containing water and observe carefully.
5. Touch the beaker after the reaction.
6. Test the solution with red arid blue litmus paper
Observation: Sodium metal reacts vigorously with water and catches fire. The beaker becomes hot during the reaction. The solution turns red Irtmus blue.
Conclusion: Metals like sodium are very reactive. They react vigorously with water ana release a large amount of heat.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 6
Aim: To show the reaction of metals and non-metals with acids
Precaution: Use a test tube holder to hold the test tube and keep the mouth of the test tube away from your face.
Procedure:
1. Take samples of metals and non-metals as given in the observation table.
2. Put them in separate test tubes and label them as A, B, C, D, E and F.
3. Add 5 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid in each test tube with a dropper.
4. Observe the reaction in the test tubes.
5. If the reaction does not occur in cold solution, warm the test tube.
6. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test t Jbe.
7. Repeat the activity using dilute sulphuric acid and note the observations in the observation table.
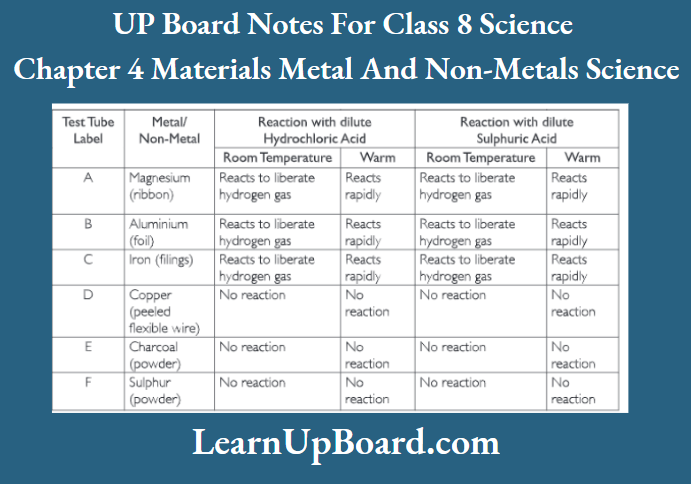
Conclusion: Metals react with acids to liberate hydrogen gas. The rate of this reaction increases as the temperature of the acid increases. Non-metals do not react with acids.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 7
Aim: To show the reaction of metals with strong bases
Precaution: Use a plastic spatula to handle the pellets of sodium hydroxide
Procedure:
1. Dissolve 3-4 pellets of sodium hydroxide in 5 ml of water in a test tube.
2. Drop a piece of aluminium foil into the test tube.
3. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test, tube and observe.
Observation: The burning matchstick extinguishes with a pop sound.
Conclusion: Metals like aluminium react with strong bases to produce hydrogen gas.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Activity 8
Aim: To show that a more reactive metal can replace a less reactive metal from its solution Procedure:
1. Take five 100 ml beakers and label them as A, B, C, D and E
2. Take 50 ml of water in each beaker and dissolve a teaspoonful of:
Beaker A: Copper Sulphate (CuSO^ and Z’rc granules (Zn)
Beaker B: Copper Sulphate (CuSOJ and Iron nail (Fe)
Beaker C: Zinc Sulphate (ZnSOJ and Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker D: Iron Sulphate (FeSOJ and Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker E: Zinc Sulphate (ZnS04) and Iron nail (Fe)
3. Keep the beakers undisturbed for some time and observe the changes in them.
Observation: Beaker A: Zinc replaces copper from the copper sulphate solution and the blue colour of the copper sulphate solution fades. A red powder)’ mass of copper settles at the bottom of the beaker.
Copper Su I phate (C JS04 )+Zi nc (Zn) > Zi nc Sulphate (ZnS04)+Copper (Cu)
CcJou’ets
Beaker B: Iron replaces copper from copper sulphate solution to form iron sulphate. A red powdery mass of copper settles at the bottom of the beaker.
Copper Sulphate (CuS04)+lron(Fe) iron Sulphate (FeS04) + Copper (Cu)
Bu* colour Rfo
Beaker C: No change is observed in the beaker.
Beaker D: No change is observed in the beaker.
Beaker E: No change is observed in the beaker.
Conclusion: A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its solution. Such a reaction is called a displacement reaction.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Non-metals vigorously react with water.
2. Metal oxides are basic:n nature.
3. Phosphorus is a non-metal which is stored in water.
4. Hydrogen gas bums with a pop sound.
Answers: 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. True
2. Fill in the blanks.
1. _______and_____are stored in kerosene oil.
2. Iron reacts with oxygen to form____
3. Metals like gold and platinum do not even react with steam. These metals are called____
metals.
Answers: 1. Sodium, potassium 2. Iron oxide 3. Noble
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why potassium is not stored in the water?
Answer. Potassium is a reactive metal. It reacts violently with water at room temperature and catches fire. Hence, it is not stored in water but kept in the kerosene oil.
2. Why gold ornaments look new even after several years of use?
Answer. Gold is a non-reactive metal. It does not tarnish. It is unaffected by air, water and acids. Thus, gold ornaments look new even after several years of use.
Uses of Metals and Non-Metals
Answer. Metals like aluminium and copper are used to make electrical wires, iron is used to construct buildings and bridges, aluminium, iron and copper are used in utensils, tools and machinery, gold and platinum are used to make jewellery, magnesium is used to make fireworks, etc.
Non-metals like oxygen is essential for respiration in living beings, hydrogen is used as a fuel, diamond is a form of carbon used as a gemstone, iodine is used as an antiseptic, nitrogen is used to preserve food, chlorine is used for water purification, etc.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Objective Type Questions
1. Fill in the blanks.
1. _____is a form of carbon used as a gemstone.
2. Food is wrapped in foils made up of______
3.______ is a non-metal used in the purification of water.
Answers: 1. Diamond 2. Aluminium 3. Chlorine
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Long Answer Type Questions
1. List two uses of metals and non-metals.
Two uses of metals are:
1. Metals like iron are used in the construction of buildings and bridges.
2. Metals like gold and platinum are used for making jewellery.
Two uses of non-metals are:
1. Oxygen is essential for respiration in living beings.
2. Nitrogen is used to preserve food. It is a nutrient required by the plants to grow.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
- Zinc
- Phosphorus
- SulphurAnswers. The material which can be beaten into thin sheets is (1) Zinc
Question 2. Which of the following statements is correct?
- All metals are ductile.
- All non-metals are ductile.
- Generally, metals are ductile.
- Some non-metals are ductile.
Answers. The correct statement is (3) Generally, metals are ductile.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks.
- Phosphorus is a very____ non-metal
- Metals are_____conductors of heat and
- Iron is_____reactive than copper.
- Metals react with acids to produce_______gas.
Answers: (1) Reactive (1) Good, electricity (3) More (4) Hydrogen
Question 4. Mark if the statement is true and ‘P if it is false.
- (Generally, non-metals react with acids.
- Sodium is a very reactive metal.
- Copper displaces zinc from the zinc sulphate solution.
- Coal can be drawn into wires.
Answers: (1) F (2) T (3) F (4) F
Question 5. Some properties are listed in the following Table. Distinguish between metals and non-metals based on these properties.
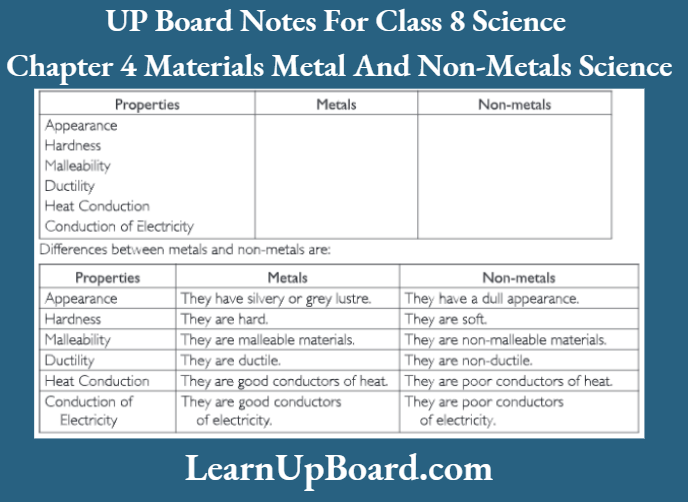
Question 6. Give reasons for the following.
- Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
- Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
- Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
- (Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answers.
- Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items because aluminium is malleable and less reactive to air and water.
- Immersion rods used for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances because metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Only a more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its solution. Copper is a less reactive metal than zinc. Therefore, copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
- Sodium and potassium are very reactive metals. They react vigorously with water to form oxides or hydroxides. Therefore, they are stored in kerosene oil.
Question 7. Can you store lemon pickles in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer. No, lemon pickles cannot be stored in an aluminium utensil because lemon contains citric acid which reacts with aluminium to produce a salt of aluminium and hydrogen gas. This will spoil the food and make it unfit for eating.
Question 8. Match the substances given in Column A with their
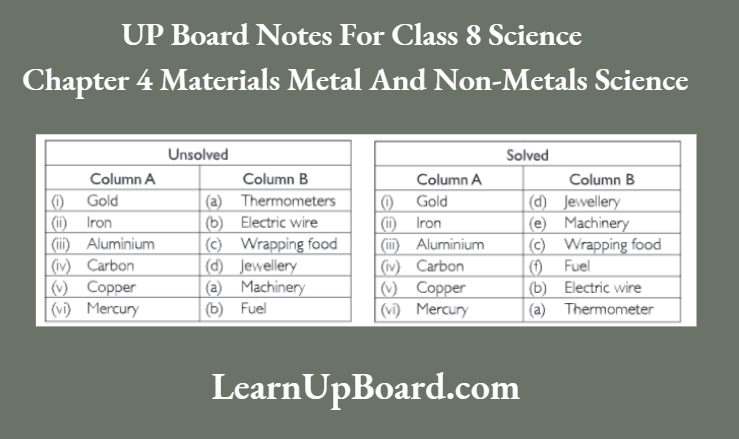
Question 9. What happens when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate.
(b) Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution? Write word equations of the reactions involved.
Answers.
- When sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate, copper reacts with the acid and produces copper sulphate and hydrogen gas.
Copper + Sulphuric Acid » Copper Sulphate + Hydrogen Gas - Iron is a more reactive metal than copper. When iron nails are placed in the copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper and forms iron sulphate. This reaction fades the blue colour of the copper sulphate solution and a brown deposit of copper is seen at the bottom of the beaker.
Iron + Copper Sulphate > Iron Sulphate + Copper
Question 10. Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
(a) How will she find the nature of the gas?
(b) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answers.
- Saloni can find the nature of the gas by adding few drops of water in the test tube and testing the solution with a red and a blue litmus paper. The blue litmus paper will turn red while the red litmus paper will show no change. This shows that the gas is acidic in nature.
- ‘When a charcoal is burnt, it reacts with oxygen to form an acidic oxide called carbon dioxide.
Charcoal + Oxygen –» Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide released on burning charcoal reacts with water to form carbonic acid.
Carbon Dioxide + Wa: er –»Carbonic Acid
Question 11. One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight?
Answers. Jewellers usually use a strong acidic solution to polish the gold jewellery. When the gold is dipped in the acidic solution, it reacts with the acid. A small amount of the gold dissolves in the acid from the outer layer of the jewellery. Thus, there is a slight loss in the weight of the jeweller)
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Hots corner
1. based on the reactions given below, indicate the most reactive metal and the least reactive metal out of zinc, copper and iron.
Copper Sulphate + Iron⇒ Iron Sulphate + Copper
Iron Sulphate + Zinc ⇒ Zinc Sulphate + Iron
Answers. In the first reaction, iron displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution, therefore, iron is more reactive than copper. In the second reaction, zinc displaces iron from iron sulphate solution, therefore, zinc is more reactive than iron. Therefore, zinc is the most reactive metal and copper is the least reactive metal.
2. Why is graphite not used for making electrical wires?
Answers. Graphite is a form of a carbon which is a non-metal. It is brittle and non-ductile. It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. Therefore, it can not be used for making electrical wires.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Practice Exercises
Objective Type Questions
1. Fill in the blanks.
1. Metals exist in _____state.
2. ______foils are used to decorate sweets.
3. Metals produce a ringing sound when struck by something. This shows that metals are_____
4. _______is a non-metal used in the pencil lead.
5. Non-metallic oxides are_______ in nature.
Answers: 1. Solid 2. Silver 3. Sonorous 4. Graphite 5. Acidic
2. Answer the following questions in one word.
1. Name a metal that can be cut by using a knife.
2. Name a metal which melts at body temperature.
3. Name a metal which is liquid at room temperature.
4. Name a metal which does not react with water, air or acid.
5. Name a non-metal used for making antiseptics.
6. Name a non-metal which is found in the gaseous state.
Answers: 1. Sodium 2. Gallium 3. Mercury 4. Gold 5. Iodine 6. Oxygen
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why phosphorus is stored in water?
Answers. Phosphorus reacts rapidly with oxygen present n air and catches f re. It is, therefore, stored in water to avoid its contact with the atmospheric oxygen.
2. What is the difference in the reaction of oxygen with metals and non-metals? Write their word equation.
Answers.
The difference in the reaction of oxygen with metals and non-metals
Metals react with oxygen to form metallic oxides which are basic in nature. These oxides dissolve in water to form bases.
Metals + Oxygen > Metallic Oxide
Non-Metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides which are acidic in nature. These oxides dissolve in water to form acids.
Non-metals + Oxygen » Non-Metalic Oxide
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metal And Non-Metals Science Long Answer Type Questions
1. Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame and forms a white powdered ash. This ash is dissolved in water and tested with a red and blue litmus paper.
Answer the following questions:
- What is the white ash formed after burning the magnesium ribbon?
- Write the word equation of the reaction that takes place when magnesium ribbon is burnt.
- What happens when the white ash is dissolved in water? Give the word equation.
- (Give one use of magnesium.
Answers.
- The white ash formed after burning the magnesium ribbon is magnesium oxide.
- Magnesium + Oxygen » Magnesium Oxide
- When the white ash is dissolved in water, magnesium hydroxide is formed.
Magnesium Oxide + Water > Magnesium Hydroxide - Magnesium is used in fireworks.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
