UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Chapter In A Nutshell
- Fuels of different varieties are used for various purposes in homes, industries, automobiles, etc.
- Cowdung, wood, coal, charcoal, petrol, diesel, natural gas, L.P.G., etc., are various types of fuels.
- Some fuels bum with a flame while some fuels do not give flame on burn ng.
- Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance bums in the presence of oxygen to give off heat and light.
- Fuels are combustible substances that may exist as solids, liquids or gases.
- The presence of oxygen is essential for the process of combustion.
- A combustible substance starts burning when it attains its ignition temperature.
- Substances which have very high ignition temperature do not catch fire easily while substances like sodium and phosphorus which have low ignition temperature catch fire when exposed to air.
- The ignition temperature of inflammable substances is very low. They catch fire rapidly and burn with fame.
- Three important requirements essential to initiate a fire are the presence of oxygen, the Presence of a combustible substance arid heat supply to attain the ignition temperature of the combustible substance.
- Fires can be controlled by – cutting off the supply of air bringing down the ignition temperature or removing the combustible substance.
- Water is used to extinguish fire as it cools the combustible substance below its ignition temperature. In addition, the water vapours formed, surround the combustible substance and cut off the air supply. Water works as a fire extinguisher only when things like wood, paper, etc. catch fire.
- The fire caused by to burning of oil or petrol cannot be controlled by water as water is heavier than oil. It settles down below the oil and oil continues to bum.
- Water is not used in case of fires caused by electrical equipment as water is a good conductor of electricity and can thus cause electrocution.
- Sand or carbon dioxide is used to control fires caused by the burning of liquid fuels or electricity.
- Carbon dioxide is stored in cylinders in liquid form under high pressure.
- Combustion can be classified as rapid combustion, spontaneous combustion and explosion.
- The substances which vaporise on burning, give out flames. For example, kerosene oil.
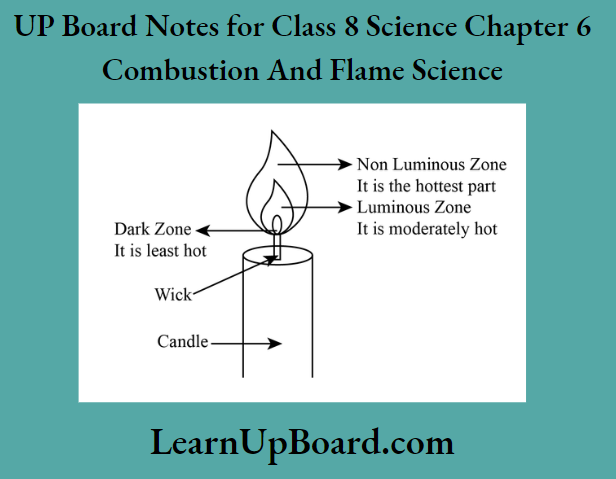
- The flame of a candle is divided into three zones – the innermost zone (dark zone), the middle zone (luminous zone) and the outermost zone (non-luminous zone).
- The non-luminous zone is the hottest part of the flame.
- The luminous zone of flame usually contains unburnt particles of carbon in it
- A good fuel is readily available, cheap, bums easily in air, produces large amounts of heat and does not leave any unwanted substance behind.
- The efficiency of a fuel is determined by its calorific value. The higher the calorific value of a fuel, the better the fuel.
- The unit of calorific value is kilojoules per kg (KJ/kg).
- Burning of fuels causes air pollution, health hazards, global warming, acid rain, etc.
- Global warming results in the melting of polar glaciers which leads to a rise in the sea level. This may cause floods in the coastal areas.
- Nitrogen and sulphur oxides are produced by the burning of fossil fuels. These oxides dissolve in rainwater to produce acid rain.
- Acid rain is harmful to plants, buildings, statues, soil, etc.
- CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is a clean fuel as it causes no air pollution.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Important Terms And Definitions
Combustible substances: The substances which bum easily in the presence of oxygen to give heat; and light are called combustible substances.
Non-combustible substances: The substances which do not bum in the presence of oxygen are called non-combustible substances.
Ignition temperature: The minimum temperature at which a substance catches fire or starts burning; is called its ignition temperature.
Inflammable substances: Substances which have very low ignition temperature and quickly- catch fire are called inflammable substances.
Rapid combustion: The type of combustion in which a substance burns quickly to produce heat and light is known as rapid combustion.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Spontaneous combustion: The type of combustion in which a substance bursts into flames on its own is called spontaneous combustion.
Explosion: The type of combustion in which a substance bumps very rapidly with the evolution of tremendous amounts of heat, light and sound energy is called an explosion.
Flame: The gaseous light-emitting part of a fire is called a flame.
Calorific Value: The amount of heat energy released by the complete combustion of I kg of a fuel is: called its calorific value.
Global warming: Global warming is the slow rise in the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Combustion
Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance burns in the presence of oxygen to give off heat and light. The minimum temperature at which a substance catches fire or starts burning is called its ignition temperature.
Inflammable substances like petrol, alcohol, and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) catch fire easily as these substances have very low ignition temperatures. Fires can be controlled by cutting off the air supply, removing the combustible substance, or bringing down the ignition temperature using fire extinguishers.
Combustion can be classified as rapid combustion, spontaneous combustion and explosion.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 1
Aim: To identify combustible and non-combustible substances Procedure:
1. Take the materials given in the observation -.able.
2. Bum each of these materials one by one.
3. Note down the observations in the observation table.
Observation:
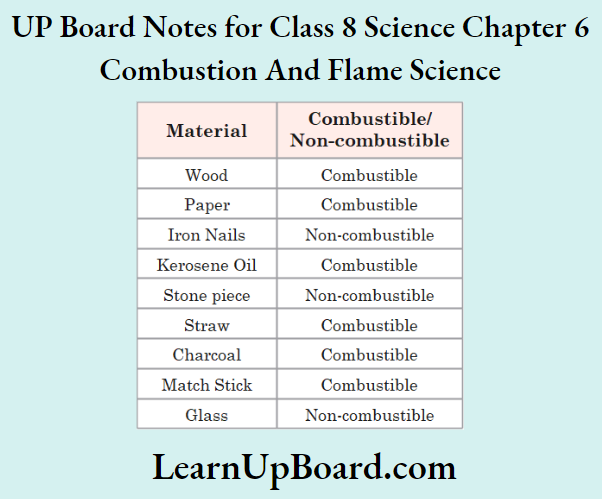
Conclusion: Wood, paper, kerosene oil, straw, charcoal, and matchsticks are combustible substances while iron nails, stone pieces, and glass are non-combustible substances.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 2
Aim: To investigate the conditions necessary for combustion Procedure:
1. Case (a) Fix a candle on a table and put a glass chimney over it
2. Rest the candle on a few wooden blocks such that air can enter the chimney.
3. Observe the flame of the candle.
4. Case (b) – Remove the wooden block and ‘est the chimney on the table.
5. Observe the flame of the candle again.
6. Case (c) – Put a glass plate over the chimney and observe the flame.
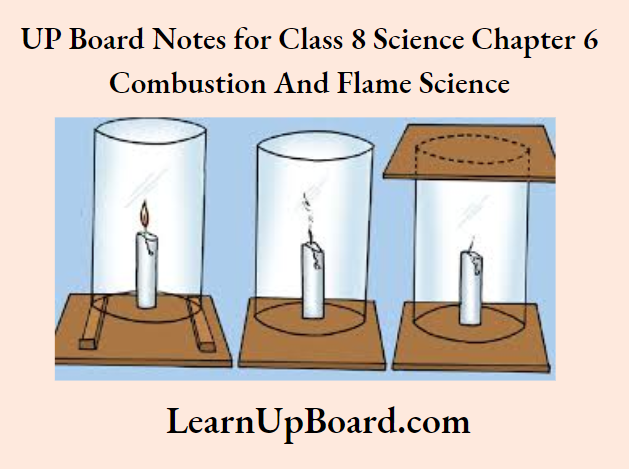
Experiment to show that air is necessary for burning
Observation:
1. The candle burns freely in case (a) when air can enter the chimney from below.
2. The flame of the candle flickers and produces smoke in case (b) when air does not enter the chimney from below.
3. The flame of the candle goes off in case (c) when air is not available.
Conclusion: Air is necessary for the process of combustion to take place
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 3
Aim: To show that combustion takes place in the presence of air
Procedure:
1. Place a piece of burning wood or charcoal on an iron plate or tawa.
2. Cover it with a glass jar or tumbler, or a transparent plastic jar.
3. Observe the burning wood or charcoal.
Observation: The wood or charcoal stops burning after some time.
Conclusion: Air is necessary for the process of combustion to take place.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 4
Aim: To show that a substance starts burning at its ignition temperature
Procedure:
1. Make two paper cups from paper.
2. Pour about 50 ml of water in one of the cups.
3. Carefully, heat both the cups separately with a candle and observe them.
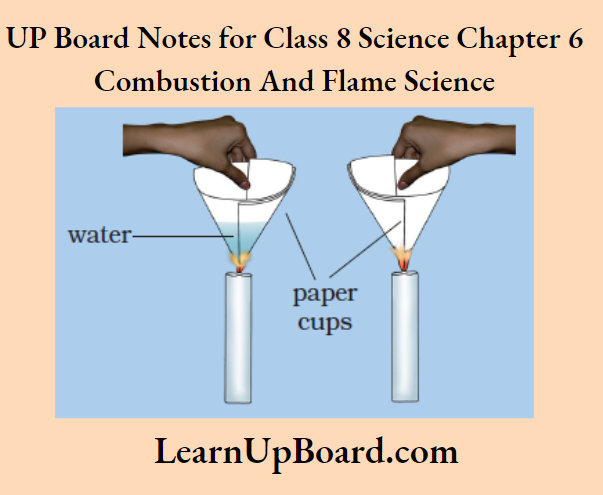
heating paper cups
Observation:
1. The temperature of the empty paper cup reaches its ignition temperature and starts burning.
2. The heat supplied to the paper cup filled with water is transferred to water by conduction. Thus, in the presence of water, the ignition temperature of paper is not reached and it does not burn.
Conclusion: A substance catches fire at its ignition temperature.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Objective-Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Substances which burn easily are called non-combustible substances.
2. Water can be used to extinguish fires caused by to burning of { kerosene oil.
3. A good fuel should be safe to handle.
4 All fuels have the same ignition temperature.
Answers: 1. False 2. False 3. True 4. False
B. Answer the following in one word.
1. Name a gas which is a supporter of combustion.
2. Give an example of an inflammable substance.
3. Which type of combustion produces a tremendous amount of heat, light and sound energy?
Answers: 1. Oxygen 2. Kerosene oil 3. explosion
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Long Answer Type Questions
A. What are the different types of combustion? Give an example of each.
Answers.
Different types of combustion
The different types of combustion are rapid combustion, spontaneous combustion and explosion. Example of rapid combustion – When a burning matchstick is brought near a gas burner, the gas starts burning immediately with the evolution of heat and light
Example of spontaneous combustion – Sodium and phosphorus bums spontaneously when exposed to air. Example of an explosion – When crackers are ignited, heat, sound and light energy are produced.
Flame
Answers.
Flame
The substances which vaporise during burning, give out flames. For example, when we bum a candle wick, the wax around it melts and vaporises upward through the wick. These vapours bum in the air and; produce a flame.
The flame of a candle is divided into three zones – the innermost zone (dark zone), the middle; zone (luminous zone) and the outermost zone (non-luminous zone). No combustion takes place! the innermost zone of the flame while complete combustion takes place in the outermost zone of the flame.
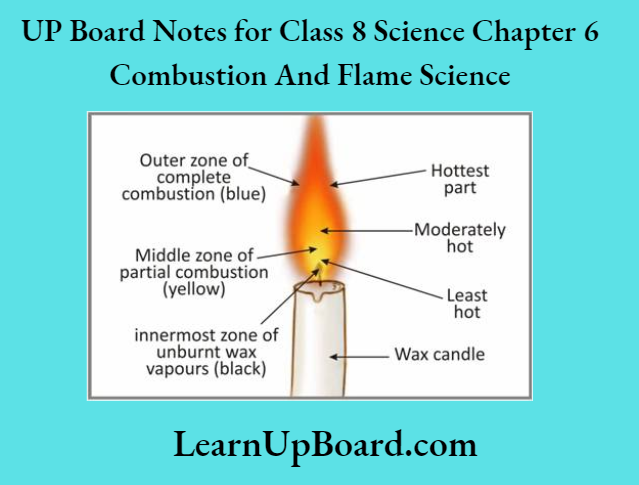
different zones of a candle flame
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 5(1)
Aim: To show that substances that vaporise during burning, give flame Procedure:
1. Light a candle.
2. Hold a glass tube with a pair of tongs and introduce its one end in the dark zone of a non-flickering candle flame.
3. Bring a burning matchstick near the other end of the glass tube.

Observation: The molten wax of the candle rises through the wick and vaporises which gives a flame near the other end of the glass tube.
Conclusion: Substances that vaporise during burning, give flame.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 5(2)
Aim: To show that unbumt carbon particles are present in the luminous zone of the flame Procedure:
1. Light a candle.
2. Hold a clean glass plate or a glass slide into *. he luminous zone of the flame for 10 minutes.
3. Remove the glass plate and observe it.

Observation: A blackish ring is formed on the glass plate or slide.
Conclusion: Unbumt carbon particles are present in the luminous zone of the flame.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Activity 5(3)
Aim: To show that the non-luminous zone is the hottest part of the flame. Procedure:
1. Light a candle.
2. Hold a clean thin long copper wire inside the flame for some time.
3. Observe the copper wire just outside the flame.

Observation: The copper wire just outside the flame becomes red-hot
Conclusion: The non-luminous zone is the hottest part of the flame.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Objective-Type Questions
A. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Kerosene oil vaporises while burning.
- A substance which does not vaporise during burning gives flame.
- Camphor bums with a flame.
Answers: 1. True 2. False 3. True
B. Fill in the blanks.
- _____ zone is the hottest part of the flame.
- The innermost zone of a flame is also known as______zone.
- ____ zone of the flame contains unbumt carbon particles.
Answers: 1. Non-luminous 2. Dark 3. Luminous
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why middle zone of a flame is yellowish in colour?
Answers. Partial combustion of the combustible substance takes place in the middle zone of a flame due to an insufficient supply of oxygen in this region. The middle zone consists of unburnt carbon particles which become red hot and impart a yellow colour to the flame.
Fuels
Answers.
Fuels
Fuels are the substances which burn to produce heat and light energy. The efficiency of a fuel is determined by its calorific value. The higher the calorific value of a fuel, the better the fuel. Hydrogen has the highest calorific value.
Burning of carbon-containing fuels like wood, coal, etc. releases unburnt carbon particles into the environment Incomplete combustion of carbon-containing *fuels like petrol, kerosene, etc. produces carbon monoxide. Burning of coal in factories and power plants produces gases like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. Carbon-containing fuels also release carbon dioxide which is a greenhouse gas and causes global warming.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Objective-Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
Acid rain is harmful to plants, buildings, statues, soil, etc.
- CNG produces a high amount of pollutants.
- A good fuel should have low calorific value.
Answers: 1. True 2. False 3. False
2. Fill in the blanks.
- Fuels burn to produce_____and energy.
- Incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels produces______ gas.
- _____ results in the melting of polar glaciers.
Answers: 1. Heat, light 2. Carbon monoxide 3. Global warming
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Long Answer Type Questions
1. List the harmful effects of burning carbon-containing fuels.
Answers.
The harmful effects of burning carbon-containing fuels
Some of the harmful effects of burning carbon-containing fuels are:
1. Burning of fuels like wood, coal, etc. releases unburnt carbon particles which cause respiratory problems such as asthma and bronchitis.
2 Incomplete combustion of fuels like petrol, kerosene, etc. produces carbon monoxide which is a highly poisonous gas. If a person is exposed to carbon monoxide for a long time, it may prove fatal and he may even die.
3. Burning of coal in factories and power plants produces gases like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen d oxide which dissolve in rainwater to form acid rain.
4. Carbon-containing fuels also release carbon dioxide which can trap heat. This increases the temperature of the atmosphere and causes global warming.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Textbook Exercises
Question 1. List the conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answers.
The three important requirements for combustion to take place are:
- The presence of a supporter of combustion live, oxygen
- Presence of a combustible substance
- Heat supply to attain the ignition temperature of the combustible substance
Question 2. Fill in the blanks:
- Burning of wood and coal causes_______ of air.
- A liquid fuel, used in homes is______.
- Fuel must be heated to its______ ______ before it starts burning
- The fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by——
Answers:
- Pollution
- Kerosene oil before it starts burning
- Ignition temperature
- (Water
Question 3. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answers. CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is a clean gaseous fuel. It has a high calorific value. It burns completely in the air and does not produce any harmful gases. It does not leave any residue after burning. So, pollution is reduced by the use of CNG in automobiles in our cities. of air.
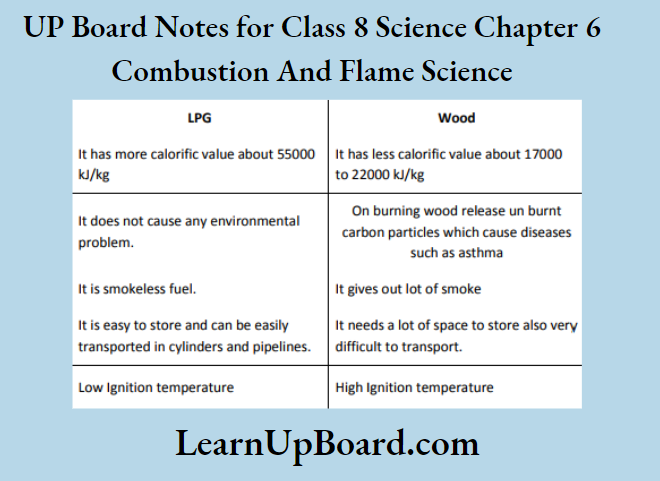
Question 4. Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Question 5. Give reasons:
1)Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment
2)LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
3)Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not
Answers.
(1) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment because water is a good conductor of electricity. Thus, it can cause electrocution.
(2) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood because it is a cleaner fuel than wood. It neither produces smoke nor does it leave any residue after burning. It has a high calorific value. While wood produces a lot of smoke on burning and leaves behind ashes on burning. Wood has a low calorific value.
(3) When paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe is brought near a flame, it does not bum because the heat given to the paper gets transferred to the aluminium pipe and the ignition temperature of the paper is not attained.
Question 6. Different Zones of a Candle Flame
different zones of a candle flame
Question 7. Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answers. The unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed in kilojoules per kilogram (KJ/kg).
Question 8. Explain how C02 can control fires.
Answers.
Co2 can control fires in Following ways
Carbon dioxide is heavier than oxygen and covers the combustible substance like a blanket Thus, carbon dioxide cuts off the contact between the combustible substance and air. This extinguishes the fire.
Question 9. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answers. Green leaves have a lot of moisture in them which increases their ignition temperature. The dr)’ leaves do not contain moisture arid thus, their ignition temperature is low. Therefore, a heap of green leaves do not bum easily but the dr)’ leaves catch fire easily.
Question 10. Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answers. Goldsmiths usually use the outermost layer.e., the non-luminous zone of the flame for melting gold and silver because it is the hottest part of the flame.
Question 11. In an experiment, 4.5 kg of fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 KJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answers. Mass of the fuel = 4.5 <g Heat produced = 180,000 KJ
We know the calorific value = Heat produced by burning I kg of the fuel
Therefore, Calorific value = _ 4Q(000 kl/kg
4.5 kg
Question 12. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answers. Yes, the process of rusting can be called combustion.
Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen and gives off heat and light Rusting of iron is also a chemical process in which iron reacts with oxygen at a very slow rate and gives off heat. So, rusting can be termed as a slow combustion process.
Question 13. Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answers. Ramesh’s beaker will get heated in a shorter time because the outermost part of the flame is the hottest.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Hots Corner
1. Why a person should not run when his clothes are on fire?
Answers. A person, whose clothes are on fire, should not run because running provides more oxygen to the flames. As oxygen is a supporter of combustion, this will increase the fire and cause more burns to the person.
2. Why is a matchstick lighted by rubbing it on the rough surface provided on the side of the matchbox?
Answers. When we rub a match stick on the rough surface of the matchbox, it produces heat due to friction. This heat raises the temperature of the chemical present on the matchstick head to its ignition temperature. Therefore, the chemical substance catches fire and the matchstick starts burning.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Practice Exercises
1. Encircle the correct option in the following sentences:
1. Hydrogen/LPG has the highest calorific value.
2. Not much air is available in the innermost zone/middle zone of a candle flame.
3. The higher/Lower the calorific value of a fuel, the better the fuel.
4. A good fuel should be cheap/expensive.
5. The outermost zone of a candle flame is the coolest/hottest
Answers: 1. Hydrogen 2. Middle zone 3. Higher 4. Cheap 5. Hottest
2. Fill in the blanks.
1. Materials such as glass, metals, ceramics, etc., are known as
2. The outermost zone of a flame is known as
3. A clean fuel does not produce
4. The gaseous light-emitting part of a fire is called
Answers: 1. Non-combustible while burning. 2. Non-luminous zone 3. Smoke materials. 4. Flame
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion And Flame Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why water cannot be used to put off fires caused by oil?
Answers. Water cannot be used to put off fires caused by the oil because:
A)oil is lighter than water and keeps floating on it. Thus, the fire keeps on burning.
Question 2. Why is it dangerous to burn coal in a closed room? It is dangerous to burn coal in a closed room because:
Answers.
1) Burning of coal releases unburnt carbon particles into the environment. These are very fine particles that can cause respiratory problems such as asthma and bronchitis.
2) Incomplete combustion of coal produces carbon monoxide which is a highly poisonous gas. If a person is exposed to carbon monoxide for a long time, it may prove fatal and he may even die.
Question 3. How is a flame produced when a candle wick is burnt?
Answers. When a candle wick is burnt, the wax around it melts and vaporises. The vaporised molten wax moves upward through the wick. These vapours burn in the air and produce a flame.
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
