UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Objectives
- Cells are the building blocks of all living organisms. Therefore, a cell is the smallest basic structural unit of life.
- The shape and size of a cell depend on its functions.
- The size of a cell is measured in micrometers (um) or microns.
- Most cells are microscopic and can only be seen when enlarged or magnified under a microscope.
- The size of the cell is not related to the size of the organism. An organism with billions of cells begins life as a single cell.
- Organisms made up of only one cell are called unicellular organisms such as Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, bacteria, etc.
- Organisms made up of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms.
- A typical cell consists of three parts namely- cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The cell membrane of plant cells is surrounded by an additional outer thick layer known as their cell wall.
- Cell wall supports and safeguards the plants’ cells against temperature changes, high wind speed, moisture, etc.
- Cytoplasm is a thick, jelly-like substance present inside the cell.
- Different cell organelles present in the cytoplasm are mitochondria, plastids, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, lysosomes, ribosomes, and centrosomes.
- Plastids and vacuoles are present only in plant cells.
- The centrosome is present only in animal cells.
- Non-living substances such as water, sugar, minerals, proteins, lipids, etc. are also present in the cytoplasm.
- The nucleus is the most important part of a cell. It is located within the cytoplasm at the center of the cell.
- The nucleus consists of the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and chromosomes.
- The nuclear membrane is the thin semi-permeable membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
- The nucleolus is a small spherical body present within the nucleus. The main function of nucleolus is to synthesize ribosomes.
- Chromosomes possess genes or the units of heredity of living organisms.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Important Terms And Definitions
Tissue: It is a group of similar cells that perform various specific functions.
Organ: It is a group of similar types of tissues to perform a particular function.
Organelles: These are the smaller components of the cell that perform various functions in the cell.
Gene: These are the carriers of hereditary characters from one generation to another.
Pseudopodia: The false foot present in the amoeba that performs locomotion and helps to trap the food particles called pseudopodia.
Cell inclusions: Non-living constituents of the cell are known as cell inclusions.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
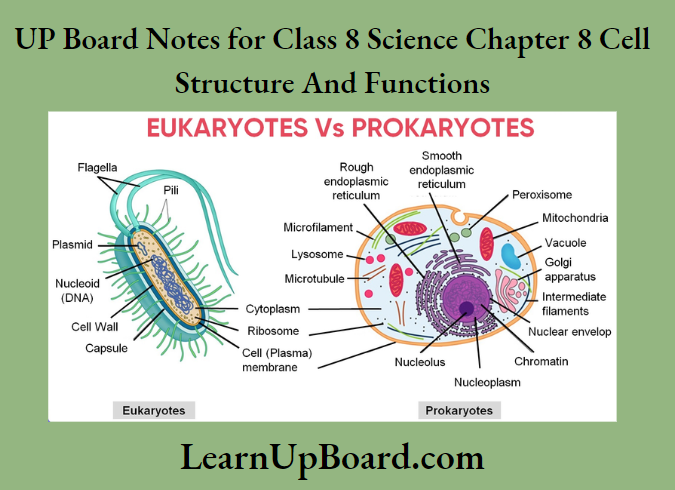
Prokaryotic cells: The cells without well-organized nuclear material are called prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotes: The organisms having prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. For example, bacteria and blue-green algae.
Eukaryotic cells: The cells which have a well-organized nucleus along with the nucleus membrane are called eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotes: The organisms having eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. For example, onion cells, human cheek cells, etc.
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life
- Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of a living organism. Cells are complex living structures. Robert Hooke discovered the cell in 1665.
- Organisms made of a single cell are known as unicellular organisms, for example, Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, etc. Organisms made of several cells are called multicellular organisms.
- Cells can be spherical, spindle, or long branched like in red blood cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells respectively. Generally, cells are microscopic and are not visible to the unaided eye. By using a microscope they can be magnified or enlarged.
- A group of specialized cells together form the tissues. Tissues are in turn grouped to form specified structures called organs.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Organisms made of more than one cell are called multi-cellular organisms.
- Cells are complex non-living structures.
- Most cells can be seen by unaided eyes.
- Cells are the basic structural unit of all living organisms.
- Pseudopodia helps Amoeba in moving and capturing food.
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
2. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. Which one of the following is a unicellular organism?
- Elephant
- Rat
- Humans
- ParameciumAnswers. (4)Paramecium
2. In which one of the following organisms is aispseudopodia found?
- Paramecium
- Amoeba
- Bacteria
- None of these
Answers. (2)Amoeba
3. Who discovered cells?
- Theodor Schwann
- Albert Einstein
- Robert Hooke
- Matthis jakkob
Answers: (3)c)Robert Hooke
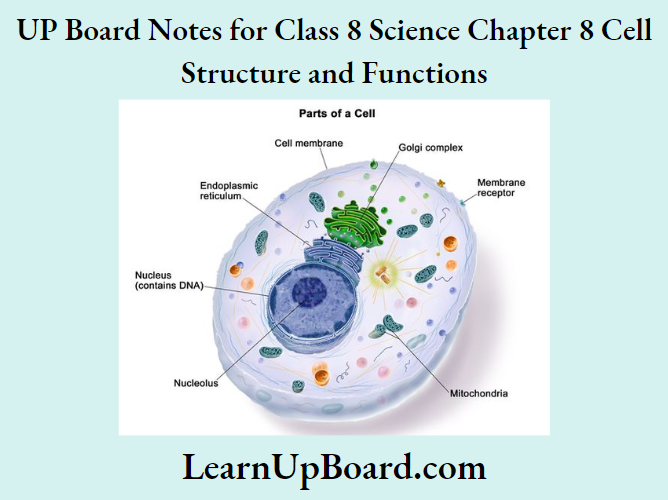
Parts of the Cell
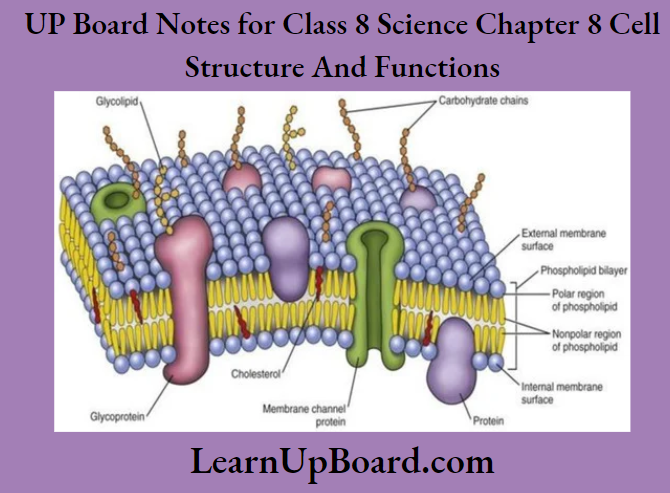
The basic structure of all cells comprises three main parts: the cell membrane or plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane is a thin, delicate layer that protects the cells, gives them a definite shape, and separates one cell from the other. It surrounds the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Cytoplasm is a thick, jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It contains different cell organelles and other nonliving substances.
The nucleus controls all the activities of the cell and regulates its growth. A thin membrane called the nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. A small round-shaped body called na nucleolus is present within the nucleus. Thread-like structures called chromosomes are also present in the nucleolus, which carry genes.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Activity 3
Aim: To observe the basic components of the cells.
Procedure:
- Peel off the dry pink covering of the onion bulb using forceps or your hand.
- Separate the thin layers of onion peel from inside the onion bulb using forceps.
- Cut the separated onion peel into smaller pieces with the help of forceps.
- Put a drop of water on the glass slide and place the onion peel.
- Put a drop of methylene blue solution on the onion peel and cover with overslip.
- Place the slide under the microscope and observe it.
Observation:
Several cells can be seen lying side-by-side bound by the cell membrane and an additional layer called the cell wall. A spherical-shaped nucleus is present in the center of each cell.
Conclusion:
The basic components of all cells are the cell membrane, nucleus , and cytoplasm. The cell wall is an additional layer present in plant cells.
Cells observed in an onion peel
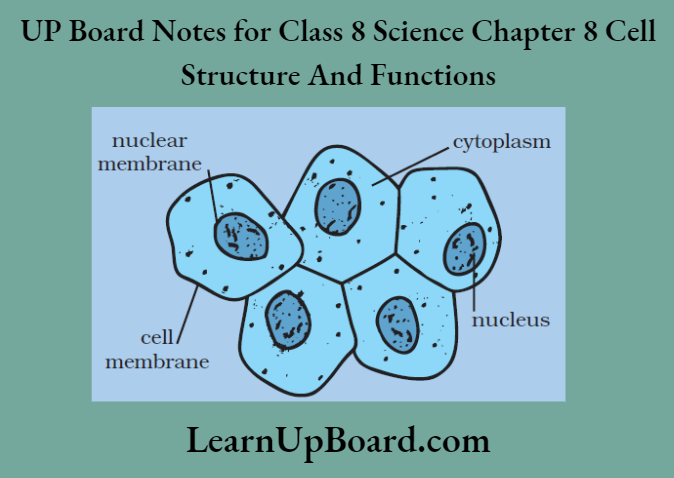
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Activity 4
Aim: To study the human cheek cells
Procedure:
- Break the tip of a clean toothpick or matchstick and use it to scratch the inside of your cheek gently.
- Put a drop of water on the glass slide and place the scraping on it.
- Add a drop of iodine or a few drops of methylene blue solution to it.
- Place the slide under the microscope and observe it.
Observation:
The cells do not have any definite shape and are enclosed within a thin cell membrane. The cell wall is not seen around the cells.
Conclusion:
The basic components of all cells are the cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm. The cell wall is not present in animal cells.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The nucleus is located in the center of the cell.
- Cytoplasm separates the cells from their surroundings.
- Animal cells have cell walls
- The nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
- True
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following cell organelles is present within the nucleus?
- Lysosomes
- Ribosomes
- Chromosomes
- Centrosome
Answers. 3) Chromosomes
2. Which of the following cell organelle is referred to as the ‘powerhouse of the cells?
- Mitochondria
- Protoplasm
- Plastids
- Ribosomes
Answers. 1) Mitochondria
3. Where does protein synthesis take place in a cell?
- Golgi bodies
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Vacuoles
- Ribosomes
Answers. 2) Endoplasmic Reticulum
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why is the plasma membrane also called an electively permeable membrane?
A plasma membrane allows only certain substances such as water and minerals to flow in and out of the cell hence, it is also called a selectively permeable membrane.
2. What is the function of genes?
Function of genes
Genes transfer hereditary features from parents to their offspring.
Comparison of Plant and Animal Cell
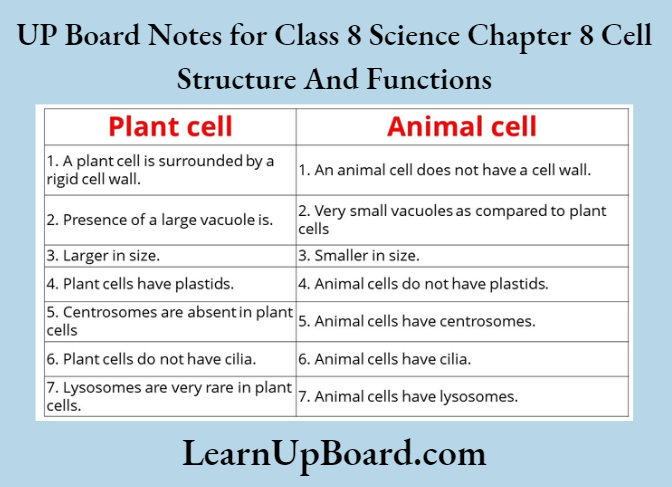
Cell organelles present in animal cells are the same as those in plant cells; however, some cell organelles are present only in plant cells. In plant cells, the cell membrane is surrounded by an additional outer thick layer known as the cell wall which gives rigidity and shape to these cells. Plant cells contain some colored cell organelles, these are called plastids. Plastids that contain green colored pigment chlorophyll are called chloroplasts. Cells also contain certain blank-looking structures in the cytoplasm. These structures are called vacuoles. Vacuoles are large and common in plant cells and much smaller in animal cells.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Objective Type Questions
1. Fill in the blanks.
- Chlorophyll present in leaves is essential for______
- Colored pigments present in the cells of the leaves are called_______
Answers: 1. Photosynthesis 2. Plastids
. 2State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The membrane of an animal cell is surrounded by an additional layer.
- Vacuoles are more prominent in plant cells.
Answers: I. False 2. True
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Short Answer Type Questions
1. What are the differences between cell walls and cell membranes
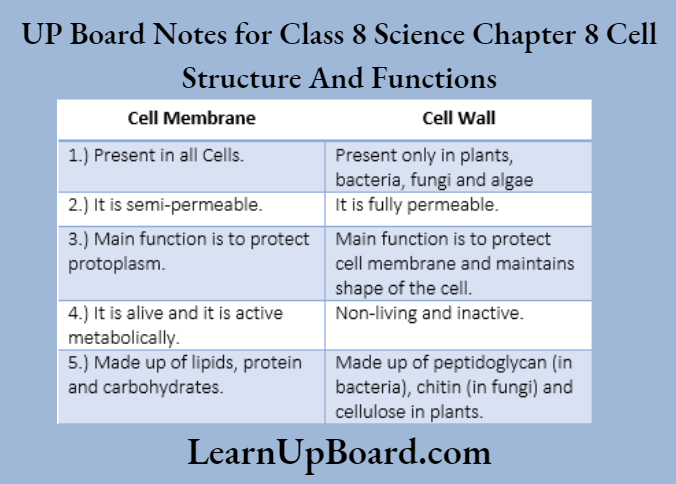
Differences between cell wall and cell membrane are:
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Textbook exercises
2. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
- (Unicellular organisms have one-celled body.
- Muscle cells are branched.
- The basic living unit of an organism is an organ.
- Amoeba has an irregular shape.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
2. Sketch the human nerve cell. What functions do nerve cells perform?
The nerve cells receive and transfer messages as well as control and coordinate the functioning of different parts of the body.
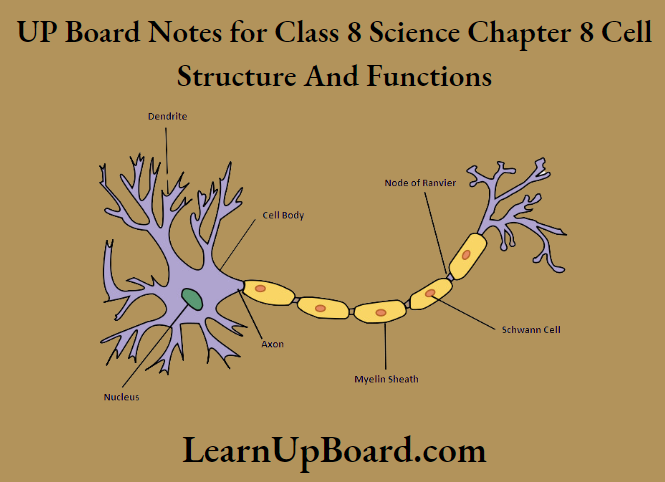
A human nerve cell
3. Write short notes on the following.
(a) Cytoplasm (b) Nucleus of a cell
(a) Cytoplasm is a thick, jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various cell organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, etc. are present in the cytoplasm. It also contains non-living substances such as water, sugar, minerals, lipids, proteins, etc.
(b) The nucleus controls all the activities of the cell and regulates its growth. A thin membrane called the nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. A small round-shaped body called a nuclear Eolus is present within the nucleus. Thread-like structures called chromosomes are also present in the nucleolus, which carries genies or the hereditary unit of living organisms.
4. Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Cytoplasm present between the cell membrane and the nucleus contains the various cell organelles.
5. Make sketches of plant and animal cells. State three differences between them.
6. State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
7. Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genes and help in the inheritance i.e. transfer of characteristics from the parents to the offspring.
8. ‘Cells are the basic structural unit of living organisms. Explain.
As bricks are put together to construct a building, similarly, the body of a living organism is formed of cells. All the basic life functions of an organism occur in the cell. A group of cells forms a tissue that performs a specific function. Different tissues combine to form an organ and different organs together form organ systems which in turn form an organism. Hence, cells are referred to as the basic structural unit of life.
9. Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells. Chloroplasts are green-colored plastids. They are green in color due to the presence of chlorophyll in them. Chlorophyll is vital for photosynthesis as it traps solar energy and uses it to produce food for the plant.
10. Complete the crossword with the help of the clues given below:
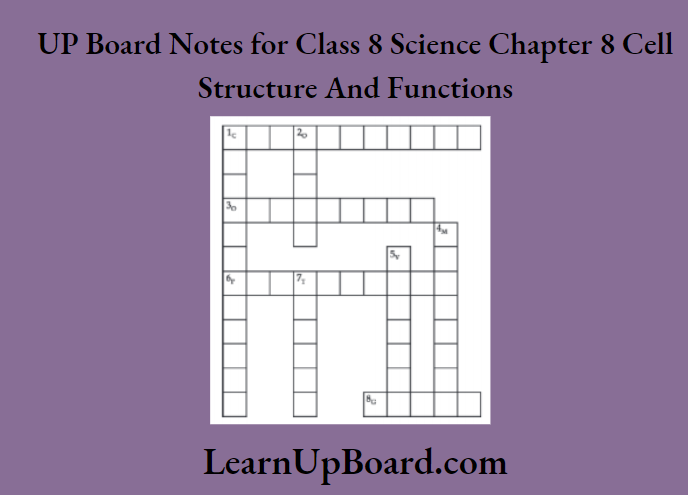
Across:
- This is necessary for photosynthesis.
- Term for the component present in the cytoplasm.
- The living substance in the cell.
- units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down:
- Green plastids.
- Formed by a collection of tissues.
- It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
- Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
- A group of cells.
Across:
- Chlorophy
- Organelles
- Protoplasm
- Genes
Down:
- Chloroplasts
- Organ
- Membrane
- Vacuole
- Tissue
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Hotscorner
A. If you are given two slides, one with an animal cell and the other with a plant cell, how will you differentiate between the animal and the plant cell?
When two slides are observed under a microscope, the cell which shows a well-defined cell wall is a plant cell and the one which does not have a defined cell wall is an animal cell.
The cells with a large number of vacuoles and chloroplasts are plant cells and the cells that lack chloroplast and have a less number of vacuoles are animal cells.
B. Do rats and elephants have nerve cells of different sizes? Give reasons for your answer.
Nerve cells in both rats and elephants are long and branched as they both perform the function of receiving and transmitting messages. This is because the size of a cell depends upon its function and not on the size of the body of the living organism.
UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Functions Practice exercise Objective Type Questions
1. Give one word for the following.
- The living part of the cytoplasm.
- The thread-like structures within the nucleus.
- The most important part of a cell.
- The site of protein synthesis.
- The measurement unit of the size of the cell.
Answers:
- Protoplasm
- Chromosomes
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes
- Micron
2Fill in the blanks.
- The powerhouse of the cell is______
- ______are referred to as the suicidal bags of cells.
- _______synthesize, store, and secrete enzymes and proteins.
- Organisms made of more than one cell are called______
Answer:
- Mitochondria
- Lysosomes
- Golgi bodies
- Multicellular
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The size of the cell is not related to the size of the organism.
- Amoeba do not have a definite shape as pseudopodia keep appearing and disappearing.
- Cells are visible to the naked human eye.
- Lysosomes help in protein synthesis.
- Plastids are present in both animal and plant cells.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
4. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. Which of the following selectively permeable membranes is present around the cells?
- Nuclear membrane
- Cell membrane
- Nucleosome
- Cell wall
Answers. 2) Cell membrane
2. Which of the following cell organelle is also called the control center of the cell?
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
Answer. 2) Nucleus
3. Which of the following are referred to as the ‘kitchen of the cell’?
- Ribosomes
- Centrosome
- Leucoplasts
- chloroplasts
Answer. 4) chloroplasts
4. Which of the following are colorless plastids?
- Chloroplasts
- Leucoplasts
- Chloroplast
- None of these
Answer. 2) Leucoplasts
5. Which of the following is a multicellular organism?
- bacteria
- Amoeba
- Euglena
- Fungi
Answer. 4) Fungi
6. Which of the following organelles is not found in an animal cell?
- Lysosomes
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Chloroplasts
Answer: 4) Chioroplats
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
