UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Chapter Objectives
- Reproduction is essential for the continuation of a species.
- Gametes are the reproductive cells produced by the sex organs.
- The male reproductive system in animals includes a pair of testes, a pair of sperm ducts, and a penis.
- Testes produce sperm or the male gametes.
- A sperm is a very small, single-celled structure with all the usual cell components. It consists of a head, a middle piece, and a tail.
- The female reproductive system in animals consists of a pair of ovaries, oviducts or fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina.
- Each ovary produces one mature ovum or egg every month and discharges it into the oviduct.
- The uterus is a hollow. muscular, pear-shaped organ in which the embryo develops.
- Asexual and sexual reproduction are the two modes of reproduction in animals.
- In asexual reproduction, a new individual is formed from the cell of a single parent.
- Binary fission and budding are the two methods of asexual reproduction.
- In binary fission, a fully-grown cell divides to produce two new cells. Amoeba reproduces by binary fission.
- In budding new individuals are formed as an outgrowth from a single parent. These extensions are called buds.
- A fully matured bud detaches itself from the parent body and becomes a new individual capable of existing independently.
- Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes. Human beings and other
mammals reproduce sexually. - Fertilisation is the fusion of sperm and ovum to form a fertilised egg or zygote. It is the first step in the process of reproduction.
- When male and female gametes fuse inside the female’s body as in human beings, dogs, cats, etc, the fertilisation is referred to as internal fertilisation.
- External fertilisation occurs when male and female gametes combine outside the female’s body.
- Viviparous animals give birth to young ones. Human beings, dogs, cats, etc., are viviparous animals.
- Oviparous animals lay eggs, which later develop into young ones. Frogs, birds, etc., are examples of oviparous animals
- Metamorphosis is the transformation of a larva into an adult through a series of changes.
- Larva is an animal’s early form having features, different from the adult.
Read and Learn More UP Board Notes for Class 8 Science
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Important Terms and Definitions
Cloning: It is the process of production of an exact copy of an organism.
Foetus: It is that stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified.
In vitro fertilization (IVF): It is a technique in which the egg is fertilised outside the body of the female.
It is used when women are not able to conceive due to blockage of oviducts.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Reproductive Organs
Answers: The male reproductive organs consist of a pair of testes, a pair of sperm ducts and a penis. Testes produce nearly millions of sperm. The male gamete or the sperm is single-celled and has a head, a middle piece and a tail. Ovaries, oviducts or fallopian tubes, a uterus and vagina are the main female reproductive organs. The female gamete or the ovum is produced by the ovaries. When a male gamete fertilises a female gamete, it results in the formation of a zygote.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- The embryo gets embedded in the fallopian tube.
- Sperms are single-celled.
- The male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes, two sperm ducts and a penis.
- The zygote divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells.
- The egg of a human female contains a large amount of yolk.
Answers:
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
2. Multiple Choice Questions.
1. Which of the following is not a male reproductive organ?
- Penis
- Testes
- Sperm ducts
- Fallopian tubes
Answers: 4) Fallopian tubes
2. Which of the following is referred to as the beginning of an individual?
- Sperm
- Male gametes
- Zygote
- Embryo
Answers: 3) Zygote
3. Which of the following statements is true for fertilisation?
- Meeting of an egg and a sperm cell
- Fusion of the male and female gametes
- Results in carrying of inherited characters to the next generation
- All of these
Answers: 4) All of these
4. Which one of the following is known as a sex cell?
- Zygote
- Gamete
- Embryo
- Foetus
Answers: 2) Gamete
3. Fill in the Blanks.
- A male gamete is known as a/an______ and a female gamete is known as a/an
- The stage of a developing embryo at which all body parts become identifiable is known as a______
- A multicellular animal starts its life as a single cell known as a_______
- In human beings, the embryo develops inside the________of the female.
- In human beings, fertilisation takes place in the
Answers:
- Sperm, ovum
- Foetus
- Zygote
- Uterus
- Fallopian tubes
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Short Answer Type Questions
1. Describe the female reproductive system in brief.
Answers:
The female reproductive system in brief
The female reproductive system consists of ovaries, oviducts or fallopian tubes and the uterus. The female gametes called the ova or eggs, are produced by the ovaries. The ovaries discharge one mature, single-celled egg into the oviduct of human females every month.
2. What organs in human beings produce gametes?
Answers:
In human beings, the male gamete or the sperm is produced by a pair of testes and the female gamete or the ovum is produced by a pair of ovaries.
Modes of Reproduction
Answers:
Modes of Reproduction
Animals have two modes of reproduction: sexual and asexual. When male and female gametes combine to form a zygote, it is known as sexual reproduction. The zygote divides repeatedly to form an embryo, which embeds itself in the wall of the uterus and develops into a foetus. The different stages of a frog starting from the egg to the adult are:
Egg → Larva →→ Adult
When organisms are reproduced by a single parent, it is known as asexual reproduction. The two methods of asexual reproduction are budding and binary fission. Hydra reproduces through budding. Single-celled organisms such as Amoeba reproduce asexually through binary fission.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Activity 1
Aim: To observe the colour and size of frog’s eggs
Procedure:
1. Visit a pond during the rainy or spring season.
2. Notice the things floating in it.
Observation: Dull-white, bunches of frog eggs can be seen floating on the surface of the water.
Conclusion:
1. Frogs move to ponds in the rainy or spring season and female frogs lay hundreds of eggs in water.
2. These eggs are dull white, are not covered by a shell and are held together by a layer of jelly which also protects them.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Activity 2
Aim: To observe the eggs of frogs, lizards, butterflies moths, hens crows or any other bird
Procedure:
1. Visit a garden near your home or school.
2. Look for the eggs of frogs, butterflies, lizards and crows.
3. Visit a local shop to look at the eggs of a hen.
4. Observe the eggs and note down the differences among them.
5. Note the size, colour and shape of each type of egg.
6. Make drawings of these eggs in your notebook.
Observation: The eggs of each organism are different in shape and size.
Conclusion:
1. Animals such as hens, frogs, etc., lay eggs outside their bodies. Such animals are called oviparous animals.
2. Animals such as cows, dogs, etc., do not lay eggs but give birth to young ones. Such animals are called viviparous animals.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Activity 3
Aim: To study budding in Hydra
Material Required: Permanent slides of Hydra and a microscope
Procedure:
1. Observe the permanent slides of Hydra under the microscope.
2. Observe them first under the low-power lens and then under the high-power.
3. Look for bulb-like projections from the parent body and count them.
4. Observe the size of different projections or buds.
5. Draw a rough sketch of what you observe.
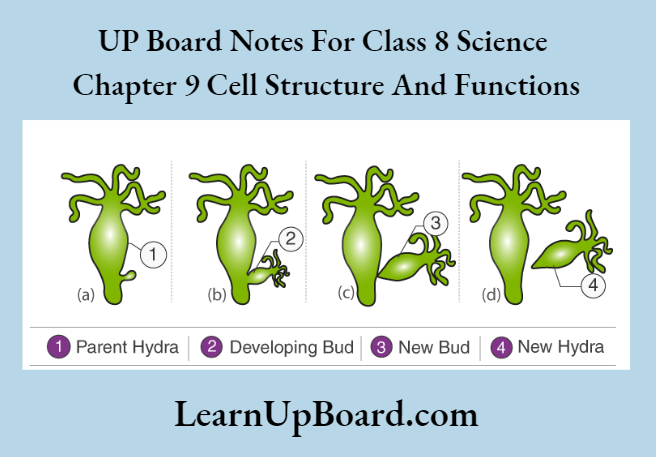
Observation: Each Hydra has one or more than one bud.
A bud is an outgrowth, which develops as cells divide constantly at a particular location.
A fully matured bud detaches itself from the parent body and becomes a new individual capable of existing independently.
Conclusion: Hydra reproduces asexually through budding.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Objective Type Questions
1. State whether the following statements are true or false.
Answers:
- In sexual reproduction, male and female gametes combine to form a zygote.
- All animals reproduce through sexual reproduction.
- Out of the millions of sperm produced, only one of the sperm fuses with the egg.
- Fertilisation occurs inside the body of a cow.
- Amoeba reproduces asexually through budding.
- Cows and dogs are viviparous animals.
Answers:
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
2. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1. Which of the following animals reproduces through budding?
- Rat
- Elephant
- Human beings
- HydraAnswers. 4) Hydra
Question 2. What is the process of formation of an adult frog from the larva called?
- Internal fertilisation
- External fertilisation
- Sexual reproduction
- MetamorphosisAnswers. 4) Metamorphosis
Question 3. What is the stage between the egg and the larva in a butterfly called?
- Pupa
- Adult
- Caterpillar
- None of these answers. 1) Pupa
Question 4. By which stage are the parts of an embryo identifiable?
- Adult
- Larva
- Pupa
- FoetusAnswers. 4)Foetus
Question 5. What term is given to an organism that has both the male and the female sex organs?
- Unisexual
- Multisexual
- Hermaphrodite
- Asexual
Answers: 3) Hermaphrodite
C. Fill in the blanks.
- Amoeba reproduces asexually through____
- Budding is a form of______reproduction.
- External fertilisation occurs in_______
- Gametes are produced in_____reproduction
Answer: 1. Binary fission 2. Asexual
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is binary fission?
Answers:
Binary fission
It is a method of asexual reproduction and is common in single-celled organisms such as Amoeba. In this method, a fully grown parent cell divides itself to produce two daughter cells. Each daughter cell gives rise to a new individual.
2. What is the difference between unisexual organisms and hermaphrodites?
Answers:
The difference between unisexual organisms and hermaphrodites
Unisexual organisms are those in which male and female gametes are produced by separate individuals Hermaphrodites are organisms in which the same individual produces both the male and female gametes.
3. How are chicks born?
Answers:
Internal fertilisation takes place in hens but they do not give birth to young ones. The zygote moves down the oviducts and protective layers are formed around it. One of these protective layers is the hard shell. The hen lays the eggs once this hard shell is formed and sits on them to provide them with warmth. In three weeks, the embryo within this shell develops into a chick. Once the chick is fully developed it breaks open the eggshell and comes out.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
Answers:
The importance of reproduction in organisms
Reproduction is an important biological process because it ensures the existence and continuity of a species. It also helps in the transmission of heredity from one generation to another.
Question 2. Describe the process of fertilisation in human beings.
Answers:
The process of fertilisation in human beings
The first step in the process of reproduction in human beings is the fusion of a sperm and an ovum or egg. Millions of sperm are released into the female’s body out of which only one of the sperm may fuse with the egg. Such fusion of the egg and the sperm is called fertilisation. During fertilisation, the nucleus of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus. The zygote thus formed is the beginning of a new individual.
Question 3. Choose the most appropriate answer.
1. Internal fertilisation occurs
- in the female body
- outside the female body
- in the male body
- outside the male body
Answer: (1) in the female body
2. A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of
- Fertilisation
- Metamorphosis
- Embedding
- Budding
Answer: (2) Metamorphosis
3. The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
- None
- One
- Two
- Four
Answer: (2) One
Question 4. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
Answers:
- Oviparous animals give birth to young ones.
- Each sperm is a single cell.
- External fertilisation takes place in frogs.
- A new human individual develops from a cell called a gamete.
- An egg laid after fertilisation is made up of a single cell.
- Amoeba reproduces by budding.
- Fertilisation is necessary even in asexual reproduction.
- Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction.
- A zygote is formed as a result of fertilisation.
- An embryo is made up of a single cell.
Answers:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- Budding
- Four
- True
- False
Question 5. Give two differences between a zygote and a foetus. It is unicellular.
Zygote
It is formed by the fusion of the male and female gametes.
Foetus
It is formed by the repeated divisions of the zygote. It is multicellular.
Question 6. Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Answers:
Asexual reproduction:
The type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction.
Following are the two methods of asexual reproduction in animals:
- Binary fission: Binary fission involves almost an equal division of the parent cell into two daughter cells, each of which grows into a new individual. This method of reproduction occurs regularly among protozoa like Amoeba, Paramecium, etc.
- (Budding: Budding is the form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual arises from a bud. The bud develops on the parent body, gets detached and grows into a separate individual, for example as in Hydra.
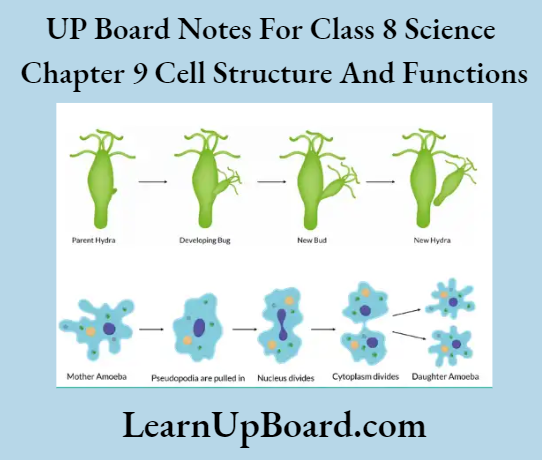
Question 7. In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
The embryo gets embedded in the walls of the uterus.
8. What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is the drastic change that takes place during the development of an animal from the larval to the adult stage.
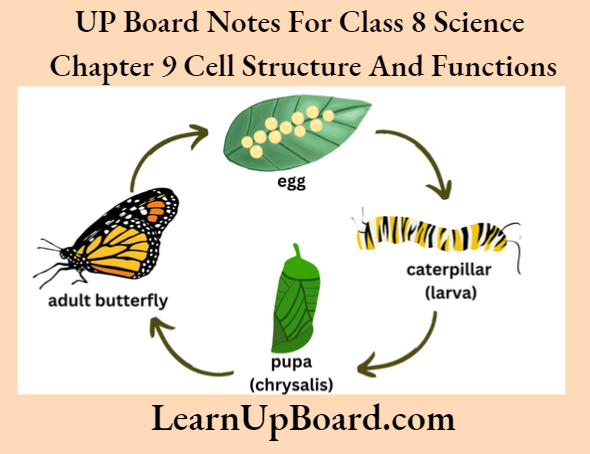
The above figure shows three stages in the development of a frog. egg, tadpole or larva and the adult frog.
The tadpole or larva is different from its adult form. Tadpole has gills for respiration because it lives in water. During metamorphosis, the body of the tadpole changes to become an adult frog. For example, the gills are replaced by the lungs. Another animal in which metamorphosis takes
place is the silkworm.
Question 9. Differentiate between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.

Question 10. Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below.
Across:
- The process of fusion of gametes.
- The type of fertilisation in hens.
- The term is used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of Hydra.
- Eggs are produced here.
Down:
- Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
- Another term for the fertilised egg.
- These animals lay eggs.
- A type of fission in Amoeba.
Across:
- Fertilisation
- Internal
- Buds
- Ovary
Down:
- Testis
- Zygote
- Oviparous
- Binary
External Fertilisation
The fusion of male and female gametes takes
place outside the female body.
Both the males and females discharge their
gametes in water.
Development of embryo occurs outside the
female body.
A few examples are frogs, fish, starfish, etc.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Hots corner
A. Why do aquatic animals like frogs and fish that undergo external fertilisation produce a large number of sperm and eggs?
Answers: The eggs and sperm of aquatic animals get exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. There are other animals present in water, which feed upon these eggs. All these factors reduce the chances of fertilisation of the eggs. Thus, the production of a large number of eggs and sperm is necessary to ensure the fertilisation of at least a few of them.
UP Board Notes For Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction In Animals Objective Type Questions
1. Circle the odd one out.
- Ovary, Oviducts, Uterus, Testes
- Testes, Sperm ducts, Penis, Vagina
- Fertilisation, Embryo development, Metamorphosis, Budding
Answers: 1. Testes 2. Vagina 3. Budding
2. Give one word for the following.
- The process by which a tadpole develops into an adult frog
- The animals that lay eggs
- Mode of reproduction in which both parents are needed
- The cell formed due to the fusion of male and female gametes
- Animals which lay eggs
Answers:
- Metamorphosis
- Oviparous
- Sexual
- Zygote
- Oviparous
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- Viviparous animals give birth to young ones.
- Foetus is another name for the unfertilised egg.
- The first mammal to be cloned was a cow.
- Reproductive cells produced by the male sex organs are called ova.
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
- False
Reproduction In Animals Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is a zygote?
Answers:
Zygote
Zygote is formed from the fusion of the male and the female gametes. It is the first cell of the organism and hence, is also referred to as the beginning of an individual.
2. Sometimes identical twins are born to human beings. What do you think is the reason behind this?
Answers:
At times, the fertilised egg or the zygote splits into two and each of these develops into two individuals. The two resulting offspring are identical twins.
3. Why do several animals like dogs, cats, etc., always produce so many young ones at a time?
Answers:
In animals like dogs, cats, etc., instead of one egg several eggs are fertilised. Each fertilised egg develops into a zygote. Hence, many young ones are produced at a time.
Also Read
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: Structure and Functions
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
