UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources
Food is an essential organic substance required for the growth and proper functioning of all living organisms. It provides nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals for the growth, development, and maintenance of large populations present on the Earth. To meet ever ever-increasing demand for food, improvement in food resources is required.
UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Need For Improvement In Food Resources In India
- India is a populous country. Its population is over one billion people and it is still growing. To feed this growing population, we will soon require more than a quarter of a billion tonnes of grain every year.
- This requirement can be fulfilled by farming on more land, but India is already intensively cultivated. So, we do not have a scope of increasing the area of land under cultivation. It is, therefore, necessary to increase our production efficiency for both crops and livestock.
- To meet these requirements, the Green Revolution has contributed to increasing food grain production. The white revolution has led to better availability of milk. Scientific research has also contributed to these revolutions.
- These revolutions mean that our natural resources are being used more intensively. Due to this, there are more chances of causing damage to our natural resources, and environment and disturbing its balance completely.
- We should increase our food production without degrading our environment and disturbing its balance. This can be done by incorporating sustainable practices in agriculture and animal husbandry.
- High yields from farms can be obtained easily by undertaking scientific management practices. It includes mixed farming, intercropping, and integrated farming practices (For Example. a combination of agriculture practices with livestock/ poultry/ fisheries/ bee-keeping).
Types of Crops
- Crops are cultivated By- humans hemps hu their own benefit. The important types of crops ate:
- Cereal crops These plants are cultivated to provide daily energy requirements, For Example. wheat, rice, maize, millet, and Sorghum (provide carbohydrates for energy requirement).
- Pulses These plants are cultivated to fulfill protein requirements, For Example. gram (chana), pea (matar), black gram (urad), green gram (moong), pigeon pea (arhar), lentil (masoor), etc.
- Oilseed crops These plants provide necessary fats and oils, For Example, soybean, groundnut, sesame, castor, mustard, linseed, and sunflower.
- Vegetables, spices, and fruits These plants fulfill the requirement of a variety of vitamins and minerals with small quantities of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, For Example. cabbage, onion, pepper, etc.
- Fodder crops These plants are raised as food for the livestock, For Example. berseem, oats sudan grass, etc.
- Each crop requires different climatic conditions, temperature and photoperiods for their growth and completion of life cycle. Growth of plants and flowering depend on the duration of sunlight. Plants also need sunlight to perform photosynthesis (photoperiods).
Classification of Crops
- Crops are classified on the basis of seasons as follows
- Kharif crops These crops are grown in hot and rainy season from the month of June to October. For e.g. paddy, soybean, pigeon pea, maize, cotton, green gram, groundnut, black gram, etc.
- Rabi crops These crops are grown in dry and winter season from the month of November to April. For Example. wheat, gram, pea, mustard, linseed, barley, etc.
UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Improvement In Crop Yield
The practices involved in farming to increase crop production can be divided into three stages:
The first is the choice of seeds for planting. The second is the nurturing of the crop plants. The third is the protection of the growing and harvested crops from loss.
Accordingly, the major groups of activities for crop yields i an be classified as:
- Crop variety improvement
- Crop production management
- Crop protection management.
Crop Variety Improvement
- The main aim of this practice is to find a variety of crop, which can withstand different situations like high soil salinity, diverse climatic conditions and water availability (drought and flood).
- In order to accept the new varieties of crops, it is necessary that the variety should produce high yields under different conditions found in different areas. For this, farmers should be provided with good quality seeds of a particular variety. The seeds should be of the same variety and germinate under the same conditions.
- Varieties or strains of crops can be selected by breeding for various traits such as disease resistance, response to fertilizers, product quality, and high yields. A new variety developed with all such features is highly acceptable.
Ways for Improvement in Crop Variety
There are two ways to incorporate desirable characteristics into crop varieties. These are:
(1) Hybridisation It is the crossing between genetically dissimilar plants to produce a new type (hybrid) or High Yielding Variety (HYV).
It is further of following types:
- AIntervarietal The cross is made between two plants belonging to different varieties of crops. It is the most common method used in plant breeding.
- Interspecific The cross is made between two plants belonging to different species of same genus.
- Intergeneric The cross is made between plants belonging to different genera.
(2) Genetically modified crops It involves the manipulation of crop plants for increasing their yield, improving quality, sustainability, etc. Genetic manipulation provides desired characteristics in the crop.
Factors of Crop Variety Improvement
Some of the factors for which crop variety improvement is done are as follows
- Higher yield Variety improvement is done to increase the productivity of the crop per acre.
- Improved quality The definition of quality is different for different crops. For e.g. baking quality is important in wheat, protein quality in pulses, oil quality in oilseeds and preserving quality in fruits and vegetables.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance Biotic stresses (diseases, insects and nematodes) and abiotic stresses (drought, salinity, water logging, heat, cold and frost) affect crop production to a great extent. Varieties resistant to such conditions are always preferred as they help to improve crop production.
- Change in maturity duration Short duration or a period between sowing and harvesting makes a crop more economical. It allows the farmers to grow multiple rounds of crops in a year. It also reduces the cost of crop production. Uniform maturity makes the harvesting process easy. It also reduces losses during harvesting.
- Wider adaptability Developing varieties that can grow and adapt to different conditions help in stabilizing crop production. Thus, a single variety can be grown in different regions with different climatic conditions.
- Desirable agronomic characteristics These characteristics depict good growth and higher productivity in plants. Plants showing such characteristics are preferred more than others, e.g. tallness and profuse branching are preferred characters for fodder crops. Dwarfness is desired in cereals
Crop Production Management
- It involves the control of various aspects of crop production for the best yield. It requires skilful dealing with almost all aspects of crop production.
- It is the money or financial condition which allows farmers to take up different forming practices and agricultural technologies. There is a correlation between higher inputs and yields.
- The purchasing capacity of former for inputs decides cropping system and production practices. Thus production practices can be grouped at three levels, ,.e. no cost, low cost and high cost production practices.
Crop production management includes the management of
1. Nutrient Management
- Like animals, plants also require nutrients for their growth and development. Nutrients are the inorganic elements, which are supplied to plants by air, water, and soil. There are sixteen essential nutrients for plants.
- Essential plant nutrients are divided into two categories which are as follows:
(1) Macronutrients These include six nutrients. They are utilized by plants in large quantities, hence, known as macronutrients. They are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulfur.
(2) Micronutrients These include seven nutrients. They are required by plants in smaller quantities. They are iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and chlorine.
- Deficiency of any of these nutrients affects physiological processes in plants including reproduction, growth, and susceptibility to disease. Nutrients can be supplied to the soil m the form of manure and fertilizers. It helps to increase the yield of crops.
- Manures are natural fertilizers. These are the organic sustances formed by the decomposition of animal-excited plant wastes. It supplies small quantities of nutrients to
- Based on the type of biological marching used, manure can be classified as:
(1) Compost and vermicompost The process in which Farm waste materials like livestock excreta (cow dung, etc), vegetable waste, animal refuse, domestic waste, sewage waste, straw, eradicated weeds, etc., are decomposed in pits is known as composting.
- The compost is rich in organic matter and nutrients.
- The preparation of compost by using earthworms to hasten the process of decomposition of plant and animal refuse is called vermicomposting.
(2) Green manure Some plants like sunhemp or guar are grown and mulched by ploughing into the soil before sowing of the crop seeds. These green plants turn into green manure. It helps in increasing nitrogen and phosphorus content in the soil. It also helps to improve hydration, aeration and crumb structure of the soil.
The advantages of manure are as follows:
- Manure enriches soil with nutrients and organic matter (called humus).
- Manure increases soil fertility and decreases the harmful effects of pesticides and insecticides on soil.
- It helps in improving soil structure by increasing the water-holding capacity in sandy soil. In clayey soil, a large quantity of organic matter helps in drainage and avoiding water logging.
- By the use of biological waste material (manure), we can protect the environment from excessive use of fertilisers.
- Manure helps in the recycling of farm waste.
Fertilizers: They are commercially produced plant nutrients. They supply Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (NPK) to the soil.
The advantages of fertilizers are as follows:
- They are easily available, easy to use, and store.
- They help in the higher yields of high-cost farming.
- They are used to ensure good vegetative growth (leaves, branches, and flowers) and give rise to healthy plants.
The disadvantages of fertilizers are as follows:
- They need to be applied carefully in terms of proper dose, time, and looking after the pre and post-application precautions for their complete utilization.
- For example, excessive use of fertilizers can cause water pollution as they get washed away when they arc not absorbed fully by the plants due to excessive irrigation.
- Continuous use of fertilizers can destroy soil fertility because the organic matter in the soil does not get replenished. Hence, microorganisms in the soil are harmed by the use of fertilizers.
- They provide short-term benefits. Thus, for maintaining soil fertility, short-term benefits of using fertilisers and long-term benefits of using manure must be considered in order to aim optimum yields in crop production.
2. Irrigation Methods
- The process of supplying water to crop plants in fields by means of canals, reservoirs, wells, tubewells, etc., is called irrigation. Agricultural practices in India are rain-dependent.
- The success of a crop mainly depends on timely monsoons and sufficient rainfall during its growing season. Ensuring that water will be supplied to the crops at the right stages and in the required amounts, the expected yields of any crop can be increased.
- Farmers depend on various natural resources like ponds, wells, canals, etc., for the irrigation of their farmlands.
- Some commonly used irrigation systems depending on the type of water resources available for agricultural purposes are as follows:
- Wells: They are constructed wherever groundwater is present for irrigation. They are of two types:
- Dug wells Water is collected from water-bearing strata.
- Tube wells Water can be drawn from deeper strata using pumps.
Canals: They are an elaborate and the extensively used method of receiving water from reservoirs like dams or rivers. The main canal is further divided into other branches that have distributaries to irrigate fields.
River Lift Systems: This method is used in areas, where canal flow is insufficient or irregular due to insufficient reservoir release. Here, water is directly drawn from the rivers for supplementing irrigation in areas close to rivers.
Tanks: These are small storage reservoirs. They catch and store the run-off of smaller catchment areas.
Modern Techniques
- These are fresh initiatives for increasing water availability for agriculture by augmenting groundwater. They include
- Rainwater harvesting Rainwater is collected into the ground by digging tunnels, etc. This water percolates into the soil, thus maintaining the water table.
- Watershed development Small check-dams are built to increase groundwater levels. The purpose of check-dams is to stop the rainwater from flowing away and also to reduce soil erosion.
Cropping Patterns: It involves raising crops so as to obtain maximum benefit from the same piece of land. It reduces the risk of crop failure, disease, etc. For this purpose, crops can be grown in different ways. Some of them are:
Mixed Cropping: In this practice, two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same piece of land. For Example Wheat + Gram, Wheat + Mustard, Groundnut -(-Sunflower, etc. Some advantages of mixed cropping are:
- Improves soil fertility.
- The risk of total crop failure due to uncertain monsoon is reduced.
- Gives some insurance against the failure of one of the crops.
Intercropping
- In this, two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. A few rows of one crop alternate with a few rows of another crop. The crops are selected be on the basis of their nutrient requirements.
- Two crops must have different nutrient requirements from each other. For example. Soybean + Maize, Finger millet (bajra) 4-Cowpea (lobia), etc.
Some advantages of intercropping are:
- It ensures maximum utilization of supplied nutrients and better returns.
- It prevents the spread of pests and diseases to all the plants of one crop in a field.
- Both crops give better returns in it.
Crop Rotation
- In this type of practice, different crops are grown on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession. The crop combination depends upon the duration of the crops.
- One crop is grown on a field and after its harvest, a second crop is grown on the same field. This can also follow a third crop. The crop to be chosen after one harvest depends upon the availability of moisture and irrigation facilities.
Crop Protection Management
- In fields, crops have to be protected from weeds, insects, pests, and diseases. Crop protection management includes methods to reduce such kinds of infestation.
- If not controlled in time, they can cause heavy damage to the crops in a way that most of the crops are lost.
Various threats to crops include:
1. Weeds
These are the unwanted plants in the cultivated field. They compete with the crops for food, space, and light.
Weeds take up nutrients and reduce the growth of the crop. Therefore, they should be removed during the early stages of crop growth in order to obtain a good harvest.
Examples of weeds are:
- Xanthium (gokhroo), Parthenium (gajar ghas), Cyperinus rotundus (motha), Amaranthus, Chenopodium, wild oat, etc. The following are the methods to control weeds:
- Mechanical methods Uprooting, weeding with harrow or hand, ploughing, burning, and flooding.
- preventive methods of Proper seedbed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping, and crop rotation.
2. Insect Pests
- They affect the health of the crop and reduce its yield. Inseam pests attack the plants in the following ways:
- They cut the root, stem, and leaf, For Example. locusts.
- They suck the cell sap from various parts of the plant, For Example. aphids.
- They bore into stems and fruits, For Example. shoot borer larvae. Pests can be controlled in many ways such as:
Use of resistant varieties.
- Summer plowing In this method, fields are
- plowed deep during summers to destroy weeds and pests.
3. Crop Diseases
- Diseases in plants are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These pathogens are present in and transmitted through the soil, water, and air.
- Crop diseases can be controlled by the use of pesticides like herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. They are sprayed on crop plants in limited amounts. Excessive use of these chemicals is harmful to many species of plants and animals. It also causes environmental pollution.
Storage of Grains
- During the storage of grains, high losses can occur in agricultural produce.
- Factors responsible for such losses can be categorized as:
- Biotic factors These include rodents, fungi, insects, mites, and bacteria.
- Abiotic factors These include inappropriate moisture and temperature conditions in the place of storage.
- The effects of these factors on grains are as follows:
- Degradation in quality.
- Poor germinative capacity.
- Discoloration of the produce.
- Loss in weight.
- All these lead to poor marketability and heavy economic losses. Some of the preventive and control measures during storage are:
- The proper storage of grains can be done by proper treatment and systematic management of warehouses.
- Strict cleaning of the produce before storage.
- Proper drying of the produce in sunlight and then in shade.
- Fumigation should be done to kill pests. In fumigation, the insect pests are exposed to fumes of chemicals.
UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the scientific management of livestock. It can be defined as the science of rearing, feeding, breeding, disease control, and utilization of animals. Animal-based farming includes cattle, goat, sheep, poultry, and fish farming.
Need of Animal Husbandry
It is required to meet the increasing demands of animal-based goods like milk, meat, eggs, leather, etc., according to the size of the population and the living standards of the people.
It sets guidelines for proper management and a systematic approach to animal rearing.
Cattle Farming: In India, cattle husbandry is done for two purposes; milk and draught labor for agricultural work (such as tilling, irrigation, and caning).
Cattle in India belong to two different species:
- Bos indices (cows)
- Bos bubalis (buffaloes).
On the basis of the work done by cattle, they can be divided into two categories:
- Milch animals These are milk-producing females or dairy animals.
- Draught animals These are used to do labor work on farms.
Breeds of Cattle
- Indigenous or local breeds are selected because of their high resistance to disease, For Example. Redsindhi and Sahiwal.
- Exotic or foreign breeds They are selected because of their long lactation period, For Example. Jersey and Brown Swiss.
These two breeds can be cross-bred to get both the desirable qualities in animals.
Lactation Period: It is the period of milk production after the birth of a calf. Milk production largely depends on the duration of the lactation period. We can increase the milk production by increasing the lactation period.
Farm Management for Cattle
- Efficient farm management is essential for humane farming, better health of animals, and production of clean milk. Various measures for farm management are as follows:
- Proper cleaning and shelter facilities are required for cattle.
- Regular brushing of animals should be done to remove dirt and loose hair.
- The cattle should be sheltered in well-ventilated roofed sheds in order to protect them from rain, heat, and cold.
- The floor of the catde shed should be sloping so as to keep it dry and facilitate cleaning.
Food Requirements of Cattles
Food is required for dairy catdes for following two purposes:
- For maintenance, Food is required to support the animal to live a healthy life.
- For producing milk The type of food is required during the lactadon period.
Different types of animal feeds are:
- Roughage This is largely fibrous and contain low nutrients. For example. green fodder, silage, hay and legumes. ‘
- Concentrates These are low in fibre. They contain relatively high levels of proteins and other nutrients. For example. cereals like gram and bajra.
Apart from the above mentioned products, some feed additives containing micronutrients promote the health and milk output of dairy animals. It should also be noted that catde should be given balan^d rations with all the nutrients in proportionate amounts.
Diseases in Cattles
Like other animals, catdes also suffer from a number of diseases. These besides causing death, also reduce milk production.
The parasites of catde can be of following types:
- External parasites They live on the skin and cause skin diseases, For Example. lice, mites, etc.
- Internal parasites They include worms that affect stomach and intestine and flukes that damage the liver.
Cattles also get infectious iliseascs from various bacteria and v,ms. As preventive measure, vaccinations are given to farm animals against many viral and bacterial diseases.
Poultry Farming
It involves rearing of domestic fowl for the production of eggs and chicken meat. Therefore, improved poultry breeds are developed and Firmed to produce layers for eggs and broilers for meat.
For the improvement of poultry breeds, cross-breeding is done successfully between Indian or indigenous (For Example. Aseel) and foreign or exotic (For Example. Leghorn) breeds.
These cross-breeding programs focus to develop desirable traits like:
- Quality and quantity (number) of chicles.
- Dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production.
- Summer adaptation capacity/tolerance to high temperature.
- Low maintenance requirements.
- Reduction in the size of egg-laying bird with the ability to utilise more fibrous and cheaper diets. This diet is formulated using agricultural byproducts.
Egg and Broiler Production
- Broiler chickens are fed with vitamin-rich supplementary feed for good growth rate and better feed efficiency.
- Care is taken to avoid mortality and to maintain feathering and carcass quality. They are produced as broilers and sent to market for meat purposes.
- Broilers and egg layers have different housing, nutritional and environmental requirements.
- The diet of broilers is rich in protein with adequate fat. In the poultiy feed, the level ofvitamin-A and K is kept high.
Maintenance of the Shelter
The following practices are required for the maintenance of shelter:
- Proper cleaning and sanitation of the shelter.
- Maintenance of temperature and hygiene in the shelter.
- Proper ventilation.
- Prevention and control of diseases and pests.
- Poultry Diseases and Their Prevention
- Poultry fowl suffer from various diseases caused by virus, bacteria, fungi and parasites.
- They also suffer from nutritional deficiency diseases.
- These diseases can be prevented by:
- Providing nutritional diet to poultry birds.
- Proper cleaning and sanitation of shelter.
- Vaccination of poultry birds can prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases. Loss of poultry during an outbreak of disease can also be reduced by proper vaccination.
- Spraying of disinfectants at regular intervals in the shelter.
Marine fishes of high economic value that are formed in seawater are:
- Finned fishes Mullets, bhetki and pearl spots.
- Shell fishes Prawns, mussels, oysters and seaweeds. Oysters are also cultivated for the pearls they produce.
Meld of fishes can be increased by locating large schools of fish in the open sea with the use of satellites and echosounders.
Inland Fisheries
- It includes fishery in freshwater and brackish water. Freshwater resources include canals, ponds, reservoirs and rivers. Brackish water resources are those where seawater and freshwater mix together, For Example. estuaries and lagoons. These are also important fish reservoirs.
- The yield of capture fishing is not high in such inland water bodies. Thus, most fish production from these resources is done through aquaculture.
- Sometimes fish culture is done in combination with rice crops. In this, paddy crop gets ample of water and fishes get food.
Composite Fish Culture (Polyculture)
Fish production by cultivating a single species (monoculture) gives a low yield and demands higher cost. In composite fish culture, a combination of 5 or 6 fish species is cultivated in a single pond having different food habits. Due to this, they do not compete for food with each other. Thus, it helps in more intensive fish farming.
Advantages of Composite Fish Culture
- Both local and imported fish species are used.
- Due to different food habits all the food in pond is consumed by the fishes.
- The fish yield from pond is high as their is no competition for food. For example. Catla is surface feeder, Rohu feeds in the middle-zone of the pond, Mrigal and common carps are bottom feeders, grass carp feeds on weeds in the pond.
Disadvantages of Composite Fish Culture
Many of the fishes breed only during monsoon. Thus, one of the major problem of fish farming is the lack of availability of good quality seed. To overcome this problem, fishes are breed in ponds using hormonal stimulation. It ensures the supply of pure fish seed in desired quantities.
Bee-Keeping
Honey is being widely used for various purposes. Thus, its production has become an agricultural enterprise these days. It is scientifically known as apiculture.
It is the method of rearing, care and management of honeybees for obtaining bee products like honey, bee wax (used in medicinal preprations) etc. For commercial honey production, apiaries or bee farms are established.
Advantages of Bee-Keeping
- Requires low investment.
- Provides varied products like honey (for eating or making other products), wax (used in medicinal and cosmetic preparations), bee venom, etc.
- Acts as an additional source of income for farmers. (hi) Helps in increasing crop yield by better pollination.
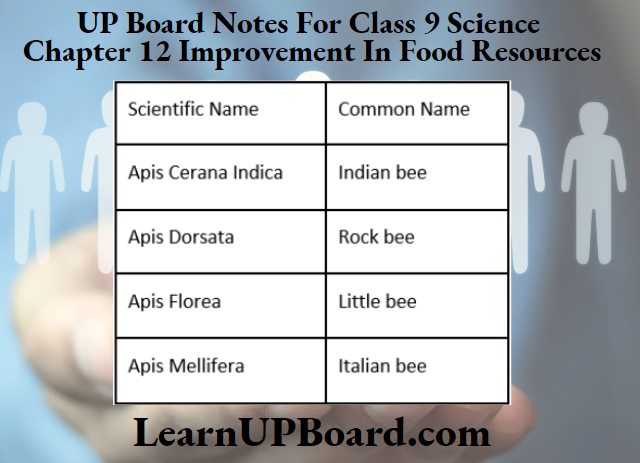
- Out of the above mentioned species, A. mellifera has been brought in the country in order to increase the yield of honey. This is the main variety used for the commercial honey production.
Advantages of Italian Bees
- They have high honey collection capacity.
- They sting somewhat less.
- They can stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed well.
Honey
- It is the major product that is obtained from apiculture.
- Value of honey It depends on pasturage or flowers available to bees for nectar and pollen collection.
- Taste of honey It depends on adequate quantity of pasturage and kind of flowers available.
UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Question And Answers
Question 1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables?
Answer:
Cereals (wheat, rice, maize, etc) are the sources of carbohydrates, which provide energy. Pulses (pea, gram and soybean, etc.) are the source of proteins. Vegetables and fruits provide us vitamins and minerals in addition to small amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Question 2. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop production?
Answer:
Factors which affect crop production are as follows:
- Biotic factors that cause loss of grains are rodents, pests, insects, etc.
- Abiotic factors include drought, salinity, water logging, heat, cold and frost.
Both biotic and abiotic factors cause stresses on crop and affect crop production in the following ways:
- Poor seed germination
- Infestation of insects
- Low yield
- Discolouration of leaves
Question 3. What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements?
Answer:
Desirable agronomic characteristics in crop plants help to give higher productivity. For example:
- Tallness and profused branching are desirable characters for fodder crops.
- Dwarfness is desired in cereals, so that less nutrients are consumed by these crops.
Question 4. What are macronutrients and why are they called macronutrients?
Answer:
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are essential nutrients required for growth, functioning and survival of plants. They are so called because they are required in large amounts by plants. They are six in number, i.e.
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- sulphur
Question 5. How do plants get nutrients?
Answer:
The nutrients to the plants are supplied by soil, which are absorbed by roots of plants. Some nutrients are provided by air and water too.
Question 6. Compare the use of manure and fertilisers in maintaining soil fertility.
Answer:
Effects of the use of manure in maintaining soil fertility are as follows:
- Manures provide a lot of organic matter (humus) to the soil. Humus helps to restore water retention capacity of sandy soil and drainage in clayey soil.
- These are the sources of soil organisms like soil friendly bacteria.
Effects of fertilisers on soil quality are:
- Use of excess fertilisers leads to dryness of soil and the rate of soil erosion increases.
- Due to continuous use of fertilisers, the organic matter decreases. It reduces porosity of the soil and the plant roots do not get sufficient oxygen.
Question 7. Which of the following conditions will give the most benefits? Why?
- Farmers use high quality seeds, do not adopt irrigation or use fertilisers.
- Farmers use ordinary seeds, adopt irrigation and use fertilisers.
- Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilisers and use crop protection measures.
Answer:
Condition will give most benefits because
good quality seeds will give good yield.
irrigation methods will overcome drought and flood situation.
fertilisers fulfil the nutrient requirement of the soil, providing high yield.
crop protection method protects the plants from weeds, pests and pathogens.
Question 8. Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops?
Answer:
Preventive measures and biological control methods should be preferred for protecting crops because :
- they are simple.
- they are economical as they involve less financial investment.
- they minimise pollution and are ecologically safe.
- they minimise the adverse effects on soil fertility.
- they are harmless to other living organisms.
- they are target specific.
Question 9. What factors may be responsible for losses of grain during storage?
Answer:
The major factors responsible for losses of grain during storage are:
- Biotic factors They include attack from insects, rodents, fungi, mites and bacteria.
- Abiotic factors They include inappropriate moisture and temperature in the place or storage.
Question 10. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Answer:
Cross breeding is a method commonly used for improving cattle breeds. It is the process in which indigenous varieties of cattle are crossed with exotic breeds to get a cross-breed which is of desired qualities.
Question 11. Discuss the implications of the following statement: “It is interesting to note that poultry is India’s most efficient converter of low fibre foodstuff (which is unfit for human consumption) into highly nutritious animal protein food”.
Answer:
- Poultry birds are efficient converters of agricultural byproducts and fibrous wastes into high quality meat. As, the waste which is unfit for human consumption can be formulated into cheaper diets for poultry Birds.
- Also, they help in providing eggs, feather and nutrient rich manure. So, the mentioned statement is implicit for poultry birds.
Question 12. What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming?
Answer:
The common management practices include:
- Keeping the shelter well-designed, ventilated and hygienic.
- The animals and birds are given healthy feed with balanced nutrition.
- Both animals and birds must be protected from various diseases. Regular check-up should be done.
Question 13. What are the differences between broilers and layers and in their management?
Answer:
The differences between broilers and layers
- A broiler is a poultry bird specially kept for obtaining meat. Layer is a poultry bird that gives eggs. There is a difference in their housing, nutrition and environmental requirements.
- The daily food requirement of broilers is somewhat different from those of layers. Broilers require protein rich food with adequate fat and high amount of vitamin-A and K. Layers require feed with vitamins, minerals and micronutrients and enough space and proper lighting.
Question 14. How are fish obtained?
Answer:
Fishes are obtained either by capturing them from their natural resources or by culturing them by fish farming.
Question 15. What are the advantages of composite fish culture?
Answer:
Advantages of composite fish culture are as follows:
- Fishes selected for this culture differ in their feeding habits and thus, avoid competition for food between them.
- All these species together use all the food in the pond without competing with each other.
- This increases the fish yield from the pond.
Question 16. What are the desirable characters of bee varieties suitable for honey production?
Answer:
The desirable characters of bee for honey production are as follows:
- The bee should have good honey collection capacity.
- They should be stingless and breed very well.
- They should be able to stay in a beehive for long periods.
Question 17. What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Answer:
Pasturage includes the plants and trees found around an apiary. From them, nectar and pollen are collected by bees to form honey.
Pasturage plays an important role in determining the quantity and quality of honey.
- The quality of honey depends upon the pasturage.
- Kinds of flowers determine the taste of honey.
UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Exercises
Question 1. Explain any one method of crop production, which ensures high yield.
Answer:
Intercropping is a method of crop production, which ensures high yield. During this, two or more crops having different nutrient requirements are grown simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern.
Question 2. Why are manures and fertilisers used in fields?
Answer:
Manures and fertilisers are used to improve soil fertility and increase crop productivity. They replenish deficient nutrients in the soil.
Question 3. What are the advantages of intercropping and crop rotation?
Answer:
Advantages of intercropping are:
- Crops selected in this method differ in their nutrient requirements. This ensures maximum utilisation of the supplied nutrients.
- It prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop in a field. Advantages of crop rotation are:
- It makes the soil fertile and increases the yield from a single field.
- It reduces the use of fertilisers. For example. use of nitrogenous fertilisers is not required as leguminous plants that are grown in crop rotation help in biological nitrogen-fixation.
- It helps in the replenishment of soil fertility
Question 4. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
Answer:
Genetic manipulation
- Genetic manipulation is the incorporation of desirable characters into an organism by hybridisation, mutation, DNA recombination, etc.
- By genetic manipulation, improved varieties of seeds can be obtained having desirable characters like high yield, disease resistance and better adaptability.
Question 5. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
Answer:
Animal husbandry involves the scientific management of the farm animals. Its benefits to farmers are:
- Improvement of the breeds having good desirable characters.
- Better yield in quantity and quality.
- Reduction of input cost.
Question 6. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
Answer:
The main benefits of cattle farming are as follows:
- We get milk from cattle. Various milk products can be manufactured with this milk.
- Cattle can be employed for labour work in agricultural fields for tilling, irrigation and carting.
Question 7. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping?
Answer:
Cross-breeding is the most important practice to increase the production and that too of desired characteristics.
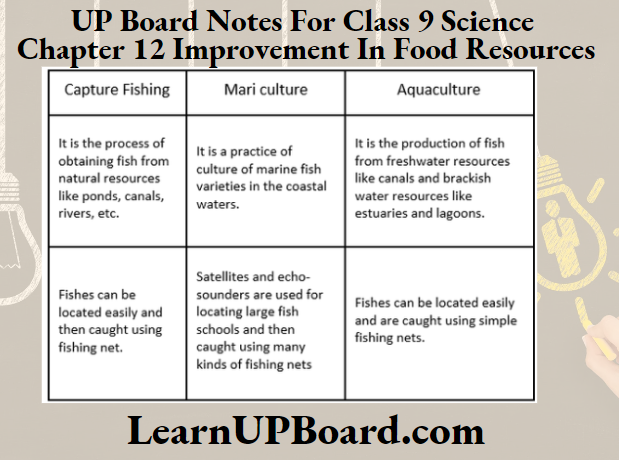
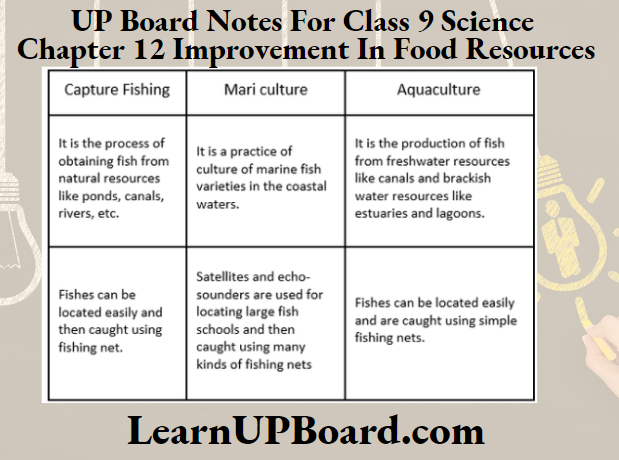
Question 8. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture?
Answer:
Differences between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture are as follows:
UP Board Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Summary
- Improvement in food resources is essential to obtain higher yield to fulfil the need of food for continuously increasing population.
- The green revolution has contributed in increasing the food grain production, while the white revolution has led to better availability of milk.
- High yields from farm can be obtained by undertaking scientific management practices like mixed cropping, intercropping and integrated farming practices.
- Improvement in crop yield are practices involved in farming to increase crop production. In includes crop variety improvement, crop production management and crop protection management.
- Crop variety improvement is a practice to find an improved variety of crop, which can withstand different situations like soil quality, different weather conditions, water availability (drought and flood) and can ultimately give good yield.
- Hybridisation and genetic manipulations are the two ways to incorporate desirable characteristics into crop varieties. Factors for which crop variety improvement is done are higher yield, improved quality, resistance against biotic and abiotic factors, change in maturity duration, wider adaptability and desirable agronomic characteristics.
- Crop production management involves the control of various aspects of crop production for the best yield. It includes nutrient management, irrigation and cropping patterns
- Nutrient management includes adopting various methods to increase the nutrient level in the soil. This is done by adding manures and fertilisers in the field.
- Irrigation is the process of supplying water to crop plants in fields by means of canals, reservoirs, wells and tube wells. Cropping patterns involve raising crops so as to obtain maximum benefit from the same piece of land, reducing the risk of crop failure, disease, etc. It can be done by mixed cropping, intercropping and crop rotation.
- Crop protection management involves the protection of crops from weeds, insects, pests and disease causing organisms. It includes methods to reduce such kinds of infestation. If not controlled in time, they can cause heavy damage to crops.
- Grains are affected by biotic and abiotic factors. Thus, proper measures should be adopted for their storage, For Example. fumigation. Animal husbandry is the scientific management of livestock.
- It is animal based farming of cattle, goat, sheep, poultry and fish.
- 1 Cattle farming is done for milk and drought labour by cattles. Poultry farming is the method of rearing fowls for the production of meat and egg. It aims to improve poultry breeds.
- Fish production refers to capturing and culturing of fishes as a suppliment of animal protein for humans. It is a cheep source of animal protein for our food.
- Bee keeping is scientifically known as apiculture. It is rearing, care and management of honeybees for obtaining honey, wax, etc. For commercial honey production, apiaries or bee farms are established.
