UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings Long Answer Type Questions
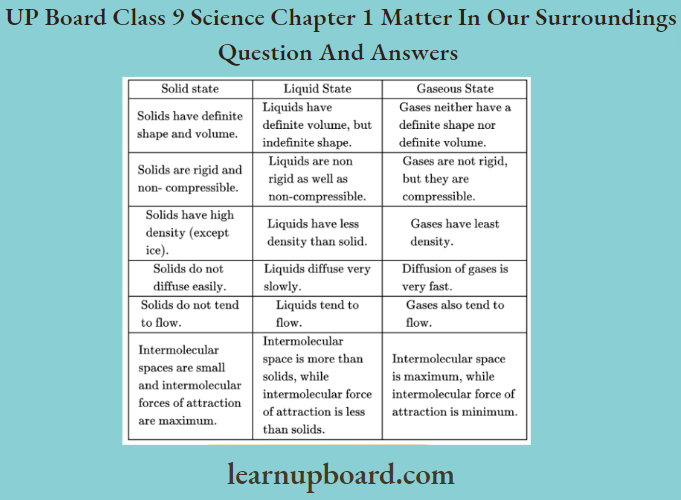
Question 1. What are the differences between solid, liquid and gaseous states?
Answer:
Differences between solid, liquid and gaseous states are as follows
Question 2.
- Explain the term density. Arrange different states of matter in increasing order of density.
- Explain how ice floats on water.
Answer:
- The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. Density depends upon the volume of the substance. Substances with small intermolecular spaces have small volumes and high densities.
- The increasing order of intermolecular spaces between the different states of matter is solid < liquid < gas. Thus, the increasing order for their density would be gas <liquid<solid.
- Ice is a solid, but it has a cage-like structure in which some spaces are present between the particles of water.
- These spaces are trapped by the air particles. These spaces are larger as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water.
- Thus, the volume of ice is greater than that of water. Hence, the density of ice is less than water and it floats on water.
Read and Learn More Class 9 Science Solutions
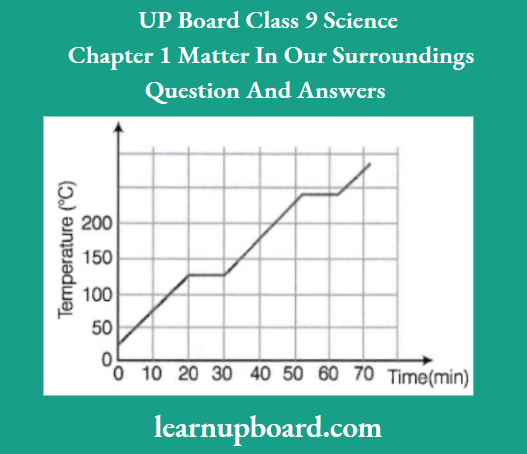
Question 3. Benzoic acid is used as a food preservative. The given graph shows the heating curve for benzoic acid. Study the graph and answer the following questions:
- At what time does benzoic acid begin to
- Melt?
- Boil?
- What is the melting point of benzoic acid?
- What happens to the temperature while benzoic acid melts?
- What is the physical state of benzoic acid during a time interval of 35-45 minutes?
Answer:
- Benzoic acid begins to melt at 20 min.
- Benzoic acid begins to boil at 52 min.
- The melting point of benzoic acid is120°C.
- The temperature remains constant atl20°C until all the benzoic acid has melted.
- The physical state of benzoic acid is liquid during the time interval of 35-45 min.
Question 4.
- What is matter? Write two properties of solids and two properties of liquids.
- Give reasons for the following:
- Ice at 0°C appears colder in the mouth than water at 0°C.
- Doctors advise putting strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person with having high temperature.
Answer:
- Matter is a substance which has mass and occupies space.
- In solids, the force of attraction between particles is strongest and intermolecular space is much less.
- In liquids, the force of attraction is relatively less and intermolecular space is more in comparison to solids.
- As ice absorbs the latent heat of fusion too from the mouth so, it feels colder than the water at the same temperature, i.e. 0°C.
- As the temperature of the patient’s body is high, the water from the wet strips evaporates by absorbing the heat from the body. This lowers the body temperature of the patient. That is why, doctors advised putting strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person suffering from high fever.
Question 5. The temperature-time graph given below shows the heating curve for pure wax.
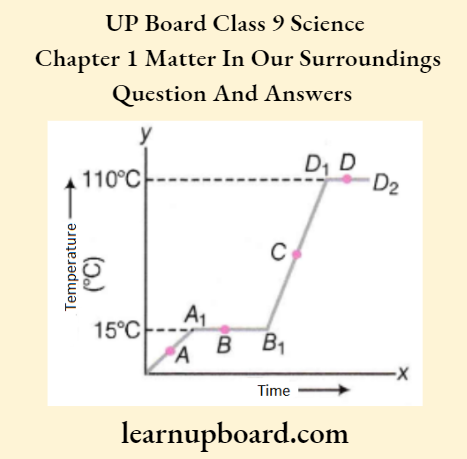
From the graph, answer the following:
- What is the physical state of the substance at points A, B, C, and D?
- What is the melting point of the wax?
- What is its boiling point?
- Which portions of the graph indicate that a change of state is taking place?
- Name the terms used for heat absorbed during the change of states involved in the above processes.
Answer:
- At point A = Solid wax
- At point B=Solid as well as liquid wax (Melting continues)
- At point C=Liquid wax
- At point D = Liquid as well as vapour state (Boiling continues)
- Melting point of wax = 15°C
- Boiling point of wax = 110°C
- Straight lines in the curve parallel to the time-axis (tf-axis) indicate the change of state. These portions are Ax to Bx (solid to liquid) and D1 to D2(liquid to vapour state).
- During melting, at the melting point, the heat absorbed is called latent heat of fusion. During boiling, at boiling point, the heat absorbed is called latent heat of vapourisation.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Which of the following matters? Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer:
- Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter. Matter can exist in three physical states, liquid and gas.
- Chair and almonds are solid states of matter. A cold drink is a liquid state of matter. Air and the smell of perfume are gaseous states of matter.
Question 2. Give reasons for the following observation. The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell of cold food, you have to go close.
Answer:
- Particles of matter are continuously moving. They possess kinetic energy. As the temperature rises, particles move faster.
- The particles of the aroma of hot food mix with the particles of air and reach us several metres away, but to get an aroma or smell of cold food, we have to go close because the particles that carry the smell of cold food move slower as compared to particles that carry the smell of hot sizzling food.
Question 3. A diver can cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer:
This observation shows that the particles of matter have spaces between them.
Question 4. What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Answer:
Characteristics of particles of matter are as follows :
- They are very small in size.
- They move faster in a gaseous state as compared to a solid or liquid state.
- They diffuse faster at higher temperatures.
Question 5. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (Density = Mass/Volume). Arrange the following in the order of increasing density. Air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Answer:
The increasing order of density is : Air < exhaust from chimneys < cotton < water <honey < chalk < iron
Question 6.
- Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
- Comment upon the following.
Rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Answer:
- For differences Refer to the text on the gaseous state and effect of change of temperature on page 4.
- Rigidity The property due to which an object retains its shape and size is known as rigidity. Solids are rigid while liquids and gases are not. Compressibility
The property due to which a substance is reduced to its lower volume when force is applied is called compressibility. Gases are the most compressible while solids and liquids are not.
- Fluidity The property due to which a substance tends to flow is known as fluidity. Gases and liquids can flow, hence they are known as fluids.
- Filling a gas container Particles of a gas move freely in all directions and occupy all the space available to them. Hence, gas fills the container.
- Shape The geometry of an object is called its shape. Solids have a definite shape while gases and liquids do not.
- Kinetic energy The energy of particles of matter due to their movement is called their kinetic energy.
- Gases have maximum kinetic energy among the three states of matter. Kinetic energy increases with the rise in temperature and vice-versa.
Density The mass per unit volume of a substance is called its density.
∴ \(\text { Density }=\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Volume }} \text { or } D=\frac{m}{V}\)
Generally, a substance has a maximum density in its solid state as compared to a liquid or gaseous state. Units of density are kg m-3 or g cm-3.
Question 7. Give reasons.
- A gas fills the vessel in which it is kept.
- A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
- A wooden table should be called a solid.
- We can easily move our hands in the air but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Answer:
- Particles of gas have the least forces of attraction between them hence, they move freely in all directions and occupy all the space available to them. Hence, a gas fills the vessel in which it is kept.
- Due to the high kinetic energy possessed by the gas particles, they randomly move at a high speed within the container.
Due to this random movement, the particles hit each other as well as the walls of the container. The force by which these particles strike the container exerts pressure on its walls. - A wooden table has a definite shape and volume. It is very rigid and cannot be compressed. Wood has all the characteristics of a solid. Hence, a wooden table should be called a solid.
- Particles of air are very far apart from each other due to negligible forces of attraction between them. Therefore, our hands get sufficient space to move in the air. We also displace the air particles without much effort.
- But in a solid block of wood, particles are closely packed with the least space between them due to strong intermolecular forces of attraction. So, there is no possibility of moving hands through a block of wood.
Question 8. Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer:
- The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. As the volume of a substance increases, its density decreases.
- Though ice is solid, it has a cage-like structure in which some spaces are present between the particles of water (these spaces are left when water solidifies). These spaces are trapped by the air particles.
- In fact, these spaces are larger as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water. Thus, the volume of ice is greater than that of water.
- Hence, the density of ice is less than that of water. A substance with a lower density than water can float on water. Thus, ice floats on Water.
Question 9. Convert the following temperatures to Celsius scale.
- 300 K
- 573 K
Answer:
For converting Kelvin to Celsius, the formula is
K-273 = °C
- 300K-273 =27°C
- 573 K – 273 = 300°C
Question 10. What is the physical state of water at
- 250°C?
- 100°C?
Answer:
- Water vapour or steam.
- Liquid water as well as water vapour, as steam and water, co-exist atl00°C.
Question 11. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer:
- During the change of state, the temperature remains constant because the heat provided is utilised for breaking the attraction forces between the particles of the substance.
- This happens at the melting point (or boiling point) of the substance and the heat used is called the latent heat of fusion (or vapourisation). During condensation or solidification, the vice-versa happens.
Question 12. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer:
Applying high pressure and reducing temperature, helps to liquefy atmospheric (or any other) gases. Because under these conditions, the particles come closer, kinetic energy decreases and the gas is liquefied.
Question 13. Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer:
- On a hot dry day, the temperature is high and the humidity is low. The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in temperature and a decrease in humidity. A desert cooler functions on the principle of evaporation.
- The water takes heat from the hot desert cooler and evaporates. The evaporation of water cools the pads and the circulating water. As a result, the incoming air also gets cooled down.
Question 14. How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Answer:
- Earthen pots contain tiny pores. During summer, when water is poured into an earthen pot, some of the water seeps through pores to the outer surface.
- The water molecules on evaporation escape from the tiny pores of the earthen pot. The heat required for evaporation is taken from the earthen pot and the water in it.
- This results in a lowering of the heat content of the remaining water and the water becomes cool.
Question 15. Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone petrol or perfume on it?
Answer:
Acetone or petrol are volatile liquids which evaporate readily. When these liquids are kept on the palm, their particles gain energy from the palm or surroundings and evaporate, thus causing the palm to cool.
Question 16. Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Answer:
A saucer or plate has more surface area in comparison to a cup. Therefore, the evaporation of tea occurs more in the saucer rather than cup and more cooling is observed in a saucer.
Question 17. What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Answer:
Type of clothes should we wear in summer
We should wear cotton clothes in summer because cotton is a good absorber of water and helps in absorbing the sweat and exposing it to the atmosphere for easy evaporation thereby, causing a cooling sensation.
Question 18. Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer:
When ice melts, it absorbs the energy equal to the latent heat of fusion from the surroundings so, it causes cooling more effectively than the water at the same temperature (because water does not absorb energy from the surroundings).
Question 19. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer:
Steam causes more severe burns than boiling water. The reason is that it releases the extra amount of heat (latent heat) which it has already taken during vapourisation (when the steam was formed from water).
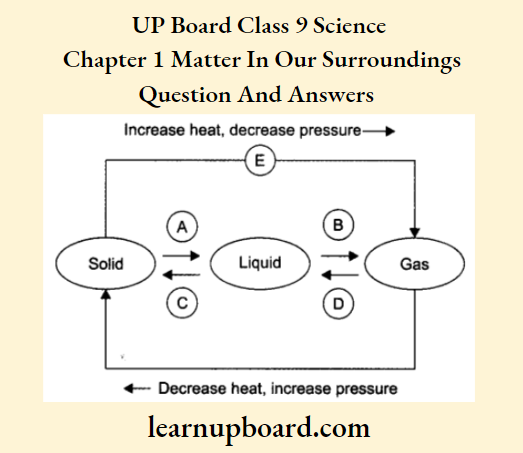
Question 20. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
Answer:
A = Melting or fusion, here the solid changes into a liquid.
B = Evaporation or vapourisation, here the liquid changes into a gas.
C = Condensation or liquefication, here the gas changes into liquid.
D = Freezing or solidification, here the liquid changes into a solid.
E Sublimation, here solid directly changes into a gas without coming into a liquid state.
F-Sublimation, here gas changes into a solid without coming in a liquid state.
Question 21. Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale.
- 293 K
- 470 K
Answer:
- 293 K- 273 =20°C
- 470K-273 = 197°C
Question 22. Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
- 25°C
- 373°C
Answer:
- 23°C + 273 =298 K
- 373°C + 273 = 646 K
Question 23. Give a reason for the following observations:
- Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
- We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer:
- Naphthalene being a sublimable substance converts directly from a solid to a gaseous state by taking heat from the surroundings through the process, called sublimation.
- The naphthalene balls keep on forming naphthalene vapours which slowly disappear into the air. Hence, no residue is left after some time.
- The smell or aroma of perfume reaches several metres away due to the fast diffusion of the gaseous particles of perfume through air.
Question 24. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles-water, sugar, and oxygen.
Answer: Oxygen (gas) < Water (liquid) < Sugar (solid).
Question 25. What is the physical state of water at
- 25°C?
- 0°C?
- 100° C?
Answer:
- Liquid state
- Solid or liquid state (transition state)
- Liquid or gaseous state
Question 26. Give two reasons to justify.
- Water at room temperature is a liquid.
- An iron almirah is solid at room temperature.
Answer:
- Water is liquid at room temperature as
- It tends to flow.
- It takes the shape of the vessel in which it is filled, but its volume does not change.
- An iron almirah is solid at room temperature because
- It has a definite shape and volume.
- It is hard and rigid.
Question 27. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a gas. Justify the given statement by giving two reasons.
Answer:
The two reasons to justify that carbon dioxide is a gas are:
- Carbon dioxide does not have a fixed volume. It can be compressed by applying pressure.
- Carbon dioxide does not have a fixed shape. It can take the shape of the container in which it is filled.
Question 28. Give one similarity and one dissimilarity between a liquid and a gas.
Answer:
Similarity Both liquids and gases are fluids and take the shape of the container in which they are placed.
Dissimilarity A gas can be compressed easily whereas a liquid cannot. A small quantity of gas can fill an entire given container. Also large quantity of a gas can be contained in a small space. A given amount of a liquid has a fixed volume at a given temperature.
Question 29. How melting point of a substance indicate the strength of its forces of attraction?
Answer:
More stronger the force of attraction, the more energy is required to break these forces. Hence, the substance which has a higher melting point indicates that its particles are tightly held.
Question 30. The melting points of two solids X and Y are 300 K and 400 K, respectively. Which has more intermolecular forces?
Answer:
The melting point of a solid is an indication of the strength of intermolecular forces between the particles of the solid. It shows that the strength of forces would be maximum in Y and minimum in X.
Question 31. Interconversion of states of matter occurs at constant temperatures. Explain.
Answer:
During the interconversion of state from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas, the temperature remains constant till all the solid has melted or all the liquid has vapourised. The heat energy is used up to overcome the forces of attraction.
Question 32. It is not proper to regard the gaseous state of ammonia as vapours. Explain.
Answer:
The gaseous state of a substance can be regarded as vapours only in case, if it is a liquid or solid at room temperature. Since ammonia is a gas at room temperature, its gaseous state cannot be regarded as vapours.
Question 33.
- The conversion of solid to vapours is called sublimation. Name the term used to denote the conversion of vapours to solids,
- The conversion of a solid state to a liquid state is called fusion. What is meant by the latent heat of fusion?
Answer:
- It is also known as sublimation.
- The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure and at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion.
Question 34. Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment.
Answer:
- The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C, but steam gives out more energy (due to latent heat of vapourisation) in comparison to boiling water.
- It is because, when water changes into steam, it absorbs the latent heat of vapourisation, but when steam condenses to form water, an equal amount of latent heat is given out without changing the temperature.
Question 35. Which phenomenon occurs during the following changes?
- Formation of clouds
- Drying of wet clothes
- Wax melts in the sun
- The size of naphthalene balls decreases
Answer:
- Condensation
- Evaporation
- Fusion
- Sublimation
Question 36. How will you change water from a gaseous state to a liquid state? Suggest a simple activity.
Answer:
- Water can be changed from a gaseous state to a liquid state by passing the water vapour through a water condenser as used in the case of simple distillation.
- Activity Take ice-cold water in a glass. Observe the outer surface of the glass. You find small droplets of water on it.
- These water droplets are formed as a result of condensation of water vapour present in the air to form liquid water.
Question 37. How do changes in temperature and humidity affect the rate of evaporation?
Answer:
- The rate of evaporation increases by increasing the temperature of the liquid. When the temperature of a liquid is increased by heating, more particles of the liquid get enough kinetic energy to go into a vapour state. This increases the rate of evaporation.
- When the humidity of the air is low, then the rate of evaporation is high and water evaporates rapidly. When the humidity of air is high then the rate of evaporation is low and water evaporates very slowly.
Question 38. Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion. Comment.
Answer:
Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion
- Diffusion is the process in which molecules of a substance move from the place of (their) higher concentration to the place of (their) lower concentration.
- But during osmosis, the water (or solvent) molecules move from (their) lower concentration to the place of their higher concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Thus, osmosis is termed a special kind of diffusion.
Question 39. Why does honey diffuse in water at a slower rate than ink?
Answer:
The density of honey is greater than that of ink, thus, honey takes a longer time to spread and hence, honey diffuses at a slower rate than ink.
Question 40. The table below shows the melting and boiling points of four pure substances. Which substance is a liquid at room temperature and would rapidly evaporate if left exposed to the air?
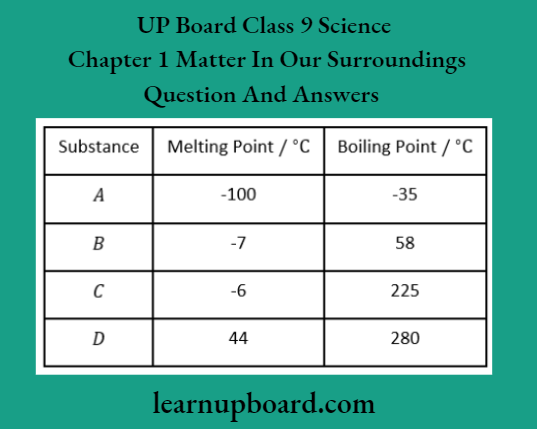
Question 41.
- A sponge can be compressed, yet it is solid. Explain.
- Name the state of matter that has minimum space between particles.
Answer:
- A sponge has minute holes, in which air is trapped, when we press it, the air is expelled out and we can compress it. Hence, a sponge can be compressed, instead of being a solid.
- Solid state has minimum space between their particles.
Question 42. The cover plate is removed from the gas jars shown in the diagram. After several days, the colour of the gas is the same in both jars. Why does this happen? Explain.
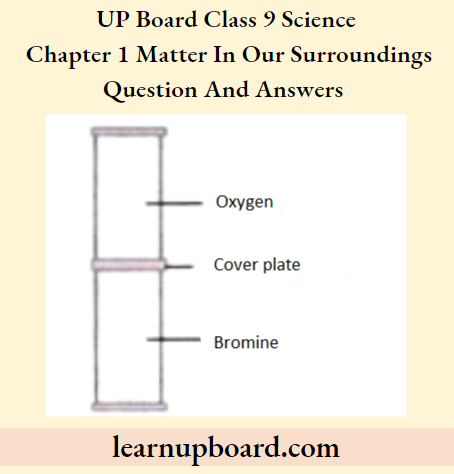
Answer:
- Diffusion has occurred in the jars. Bromine molecules move from a region where they are of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, i.e. they move in the above gas jar.
- Oxygen molecules move from a region where they are of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, i.e. they move to the below gas jar.
- Diffusion continues until both gas jars have a uniform distribution of bromine and oxygen molecules.
Question 43. Classify the following into osmosis/ diffusion.
- Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water.
- Spreading of virus on sneezing.
- Earthworms die on coming in contact with common salt.
- Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
- Preserving pickles in salt.
- Spreading of smell of cake being baked throughout the house.
- Aquatic animals use oxygen dissolved in water during respiration.
Answer:
Osmosis
1. Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water.
3. Earthworms dying on coming in contact with common salt.
4. Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
5. Preserve pickles in salt.
Diffusion
2. Spreading of virus on sneezing.
6. Spreading of the smell of cake being baked throughout the house.
7. Aquatic animals use oxygen dissolved in water during respiration.
Question 44.
- Explain the interconversion of three states of matter in terms of the force of attraction and kinetic energy of the molecules.
- Arrange the three states of matter in the increasing order of rate of diffusion and particle motion.
Answer:
- During the interconversion of a solid into a liquid and liquid into a gas at an increasing temperature, the kinetic energy of the molecules increases and the force of attraction among molecules decreases and vice-versa.
- Rate of diffusion, Solid < liquid < gas
- Particles motion, Solid < liquid < gas.
Question 45. How do you differentiate between solids, liquids and gases based on their melting and boiling points?
Answer:
Solids have melting and boiling points above room temperature. Liquids have a melting point below room temperature and a boiling point above room temperature. Gases have both melting and boiling points below room temperature.
Question 46.
- Dry ice is compressed under high pressure. What happens to it when the pressure is released?
- Define
- Melting point
- Fusion.
Answer:
- On releasing the pressure, dry ice sublimes to a vapour state without undergoing a liquid state.
- Melting point The definite temperature at which a solid starts melting is called the melting point of that solid, for example., the melting point of ice is 0°C or 273.16 K.
- Fusion The process of conversion of a solid into liquid state on heating is called fusion or melting.
Question 47. What is dry ice? How is it formed?
Answer:
Dry ice
- Dry ice is solid carbon dioxide which sublimes to form carbon dioxide gas without going into a liquid state. The term dry is used to denote sublimation.
- On sublimation, vapours of carbon dioxide create a foggy dense appearance denoted by the term ice. Hence, solid carbon dioxide is also termed dry ice.
- Dry ice is formed when gaseous carbon dioxide is compressed and stored under high pressure. On decreasing pressure to 1 atm, it again changes to the gaseous form without coming into a liquid state.
Question 48. Draw a well-labelled diagram showing the sublimation of ammonium chloride.
Answer:
Take some ammonium chloride in a China dish and place the China dish on a tripod stand. Cover the China dish with an inverted glass funnel.

- Sublimation of ammonium chloride Put a loose cotton plug in the upper open end of the funnel to prevent the ammonium chloride vapour from escaping into the atmosphere.
- The China dish is heated by using a burner. On heating, ammonium chloride changes into white vapours.
- These vapours rise up and get converted into solid ammonium chloride on coming in contact with the cold, inner walls of the funnel.
Question 49. From the graph given below:
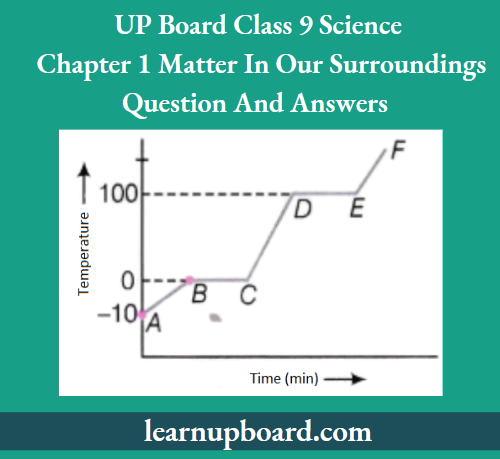
- Which region contains only solids?
- Which region contains all liquids?
- Which region shows latent heat of vapourisation?
Answer:
- AB is the region that contains only solids.
- The CD is the region that contains all liquids.
- DE is the region that shows latent heat of vapourisation.
Question 50. Comment on the following statements:
- Evaporation produces cooling.
- The rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with an increase in humidity.
- Sponge though compressible is a solid.
Answer:
- Evaporation of liquid produces cooling because liquid takes away the heat from the surroundings, thereby producing a cooling effect.
- If humidity is high, then air is already saturated with water vapour, i.e. it has a lot of water vapour. Therefore, it will not take more water vapour easily. Hence, the rate of evaporation decreases.
- The sponge has minute holes in which air is trapped. The material is also not so rigid. On pressing this, air is expelled out, which is why, it can be compressed, but it is solid as it has a definite shape and volume and does not change its shape unless compressed.
Question 51.
- How will you show that the process of evaporation depends on the nature of the liquid?
- Why a drop of Dettol is evenly distributed in a bucket of water without the need to stir?
Answer:
- Take 10 mL of ether (a low boiling point liquid with a boiling point of 34°C) in a test tube and 10 mL of water (boiling point 100°C) in another test tube. Keep both the test tubes near the window for some time. It is observed that ether evaporates in a shorter time. Thus, the lower the boiling point of the liquid, the higher is its rate of evaporation.
- A drop of Dettol is diffused in water and can be distributed throughout the water since there is enough space between the particles of water.
Question 52. Look at the following figures and suggest in which of the vessels A, B, C or D, the rate of evaporation will be the highest. Explain.
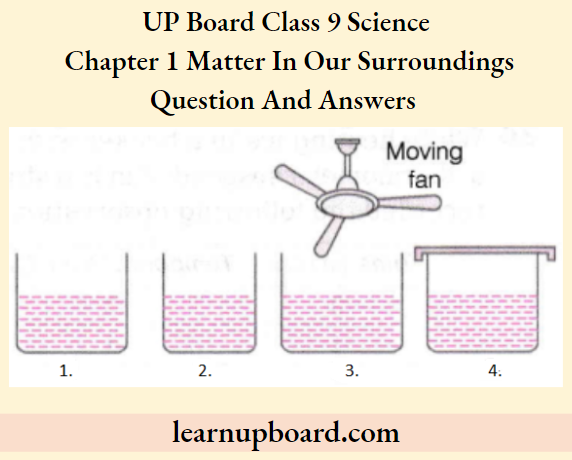
Answer:
- The rate of evaporation will be highest in vessel C as the surface area exposed for evaporation is larger than B ( smaller size).
- The moving fan increases the wind speed which also increases the rate of evaporation. Although A and D are also equal in size to C, A is at a greater distance from the fan and D is covered with a lid.
Question 53.
- Which factors determine the state of a substance?
- Convert 30°C into Kelvin.
- Water droplets are observed on the outer surface of a glass tumbler containing ice-cold water. Give reason.
Answer:
- Temperature and pressure determine the state of a substance.
- 30°C = 273 + 30 = 303 K
- Water droplets are observed on the glass tumbler because water vapours present in the air get condensed on the cold surface of the glass which appears as water droplets.
Question 54. It is a hot summer day. Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes, respectively. Who do you think would be more comfortable and why?
Answer:
- Priyanshi would be more comfortable. The reason is that cotton absorbs sweat from the body and provides a larger surface area for evaporation which causes more cooling effect.
- Nylon being a bad absorber of water does not absorb sweat. Thus, the sweat does not evaporate from the body and Ali would feel uncomfortable.
Question 55. Tarun got an invitation to attend a party. On coming to the place, he found that both his shirt and pants were wet. What step he would take to dry them quickly?
Answer:
Tarun can take the following steps to dry his clothes quickly:
- By spreading them in the air under the sun so that the water may evaporate (increasing the surface area).
- By spreading them under a fan in a room (increasing the wind speed).
- By ironing the clothes (increasing the temperature).
Question 56. While heating ice in a beaker with a thermometer suspended in it, a student recorded the following observations.
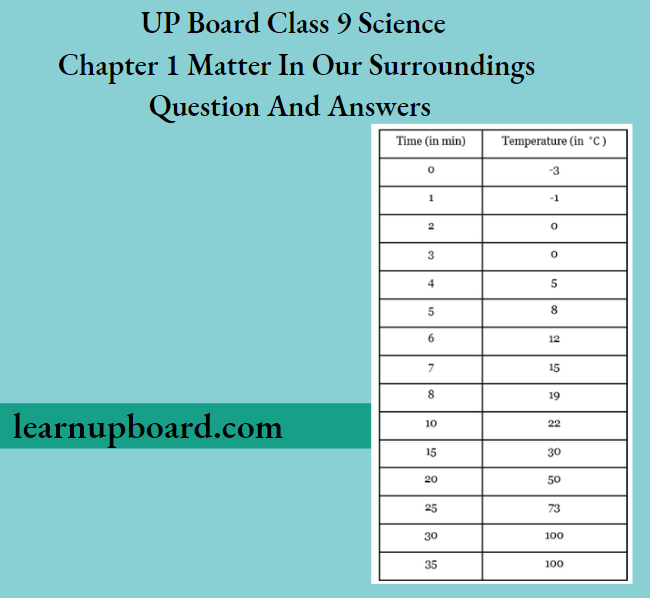
Based on the above observations, answer the following questions:
- State the change (s) observed between 2-3 min and name the process involved.
- Between 30-35 min, the temperature remains constant. State the reason for this. Name the heat involved in the process and define it.
Answer:
- Between 2-3 min, ice is converted into water and this process is called fusion.
- Between 30-35 min, heat is used for converting water (liquid) to vapour (gas), so the temperature during this period remains constant. It is due to the latent heat of vapourisation.
- Latent heat of vapourisation The amount of energy required to change 1 kg of water to its vapours at its boiling point is known as the latent heat of vapourisation.
Question 57.
What temperature on the Kelvin scale is equal to 50°C?
Describe an activity to show that the rate of evaporation increases with surface area.
Answer:
- 50+273= 323 K
- Activity Take a small amount of water in three containers which have different surface areas. Keep them in sunlight for 2 h. Measure the volume of water left in all three containers. O
- Observation The amount of water left will be the least in a container having the largest surface area among them. Conclusion The Greater the surface area, more will be the rate of evaporation.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. A substance has no mass. Can we consider it a matter?
Answer: No, because matter has a definite mass.
Question 2. A given substance X has definite volume, but no definite shape and can diffuse easily. What is the physical state of a substance X?
Answer:
The physical state of a substance X is liquid because liquids do not have definite shapes, but have a definite volume and can diffuse easily.
Question 3. Rubber band changes its shape. Is it solid?
Answer:
Rubber band changes their shape under force and regain their shape after removing the force. Thus, it is a solid.
Question 4. Why do liquids take up the shape of the container in which they are kept?
Answer:
Forces of attraction are not very strong in liquids which is necessary to maintain their shape. Therefore, they acquire the shape of the container in which they are kept.
Question 5. Why do liquids have a mostly lower density than solids?
Answer:
Liquids have fewer forces of attraction (between their particles), hence less mass and more volume as compared to solids, thus they have less density than solids.
Question 6. What would be the effect of
- Temperature and
- The density of liquids on the rate of diffusion of liquids?
Answer:
- On increasing temperature, the rate of diffusion of liquids increases.
- The rate of diffusion is higher for a liquid having a lower density.
Question 7. Name the properties of gases that help aquatic plants and animals to survive in water.
Answer:
Diffusion, as oxygen diffuses in water, which aquatic plants and animals take in.
Question 8. Why a gas cylinder cannot be half-filled?
Answer:
Particles of gas move randomly at a very high speed and occupy all the space available to them at a very fast speed. Therefore, the gas cylinder cannot be half-filled according to the volume.
Question 9. Why do gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container than solids?
Answer:
In gases, the particles move randomly at high speed and they collide with each other and also with the walls of the container. Thus, they exert more pressure on the walls of the container than solids.
Question 10. Which characteristic of a gas is used in supplying oxygen cylinders to hospitals?
Answer:
Gases are highly compressible and can be liquefied. Due to these properties, gases are used in supplying oxygen cylinders to hospitals.
Question 11. What is the full form of CNG? Mention its one property which makes it so important.
Answer:
The full form of CNG is Compressed Natural Gas. It is a clean fuel which does not create pollution on combustion.
Question 12. Mention two ways to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer:
The two ways to liquefy atmospheric gases are:
- Increasing pressure
- Decreasing temperature
Question 13. At what temperature, do ice (solid) and water (liquid) co-exist together?
Answer:
At 0°C or 273 K (melting point of ice or freezing point of water), both ice (solid) and water (liquid) can co-exist.
Question 14. Why is boiling called a bulk phenomenon?
Answer:
Since, boiling starts from the bulk, i.e. inside the liquid, therefore it is a bulk phenomenon.
Question 15. Why does the temperature remain constant during sublimation?
Answer:
During the process of sublimation, heat given to the system is used to evaporate solid into vapour at constant temperature. B and C both are liquids at room temperature. However, B’s boiling point is quite close to the room temperature and it is therefore volatile.
Question 16. On suffering from fever which will lower your body temperature more, ice or ice cold water? Why?
Answer:
Ice will lower the body temperature more than ice-cold water because the latent heat of the fusion of ice is quite high (335 J/kg). Ice is, therefore, expected to absorb more heat energy from the body and will lower the body temperature more than ice-cold water.
Question 17. Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations.
Answer:
Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns.
When ice melts, it absorbs the energy equal to the latent heat of fusion from the surroundings, therefore, causing a cooling effect. But steam releases the extra heat (equal to the latent heat of vapourisation) which it has absorbed when water is converted into steam. So, steam produces severe burns.
