UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. The white revolution in India has made us self-sufficient in a product. Name it.
Answer:
Milk.
Question 2. Identify two crops from the following, which provide us with carbohydrates for energy requirements. Black gram, wheat, lentil, and rice.
Answer:
Wheat and rice.
Question 3. Name the type of nutrient that we get from mustard seeds and linseed.
Answer:
Mustard seeds and linseed provide us with fats.
Question 4. Select the one that is not a source of starch among the following: Rice, wheat, sunflower seeds, and potato tuber.
Answer:
Sunflower seeds.
Question 5. List two desirable traits for fodder crops.
Answer:
Two desirable traits for fodder crops
Tall plants
Profuse branching.
Question 6. State one importance of photoperiod in agriculture.
Answer:
Photoperiod is important for the growth and flowering of plants.
Question 7. Name two proteins containing rabi crops.
Answer:
Gram and peas.
Question 8. Improved varieties can be produced in both animals and plants. How?
Answer:
Hybridization and genetic modification are two processes used for the production of new and improved species.
Read and Learn More Class 9 Science Solutions
Question 9. What is the advantage of selecting seeds for crops with wider adaptability for agriculture?
Answer:
It helps in stabilising crop production under different environmental conditions.
Question 10. From where do the plants acquire nutrients like nitrogen and hydrogen?
Answer:
The plants acquire nutrients like nitrogen from soil and hydrogen from water.
Question 11. Name the organism used in vermicomposting.
Answer:
Earthworms.
Question 12. Arrange these statements in the correct sequence of preparation of green manure.
- Green plants are decomposed in soil.
- Green plants are cultivated for preparing manure or crop plant parts are used.
- Plants are ploughed and mixed into soil, (iv) After decomposition, it becomes green manure.
Answer:
The correct sequence is (2) → (3) → (1) → (4)
Question 13. Name two plants, which are used as biopesticides in organic farming.
Answer:
Neem leaves and turmeric are used as biopesticides because they can keep pests away from crops.
Question 14. Write an example of intercropping.
Answer:
Example of Intercropping Plants
Soybean + maize is an example of intercropping.
Both crops differ in their nutrient requirements, ensuring maximum utilization of nutrients from the field.
Question 15. Mention any two abiotic factors that affect crop production.
Answer:
Drought and waterlogging.
Question 16. What are exotic breeds in terms of cattle?
Answer:
Exotic breeds in terms of cattle
- Exotic breeds are not native to that place, For Example. Brown
- Swiss and Jersey Swiss are the exotic breeds of cows in India.
Question 17. Milk production in cattles is mainly dependent upon a factor. What is it?
Answer:
Milk production in catdes is mainly dependent upon the lactation period.
Question 18. Which type of food is required by dairy animals?
Answer:
Dairy animals require two types of food:
- Roughage – Largely fibrous
- Concentrates – Low in fibre and contain relatively high levels of proteins and other nutrients.
Question 19. White leghorn is an exotic breed of an animal. Name the animal.
Answer:
It is popular exotic breed of hen that produces long, white eggs and requires less amount of feed.
Question 20. Name the two vitamins, which are added in the poultry feed.
Aswer:
Vitamin-A and vitamin-K.
Question 21. Name the major nutrient, which we get from fish.
Answer:
Protein.
Question 22. How does Catla differ from Madrigal?
Answer:
Catla is a surface feeder, while mrigal is a bottom-feeding fish.
Question 23. What is mariculture?
Answer:
Mariculture
The cultivation of marine fishes like mullets, pearl spots, etc., in coastal waters of India on commercial scale is known as mariculture.
Question 24. Why fish culture is done with a combination of rice?
Answer:
Fish culture is done with a combination of rice, so that fishes get ample food in the paddy field and the latter can get water.
Question 25. Choose the odd one Mullets, bhetki, prawns, pearl spots.
Answer:
Prawn is the odd one. Except prawns all the others are finned fishes, while prawns are shellfish.
Question 26. Give two advantages of apiculture.
Answer:
Two advantages of apiculture are as follows
(1) It produces honey and wax.
(2) It is a low-investment additional income-generating activity for farmers.
Question 27. Give one example of each, local variety and foreign variety of bee.
Answer:
Local variety Apis cerana indica Foreign variety Apis mellifera.
UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Cultivation practices and crop yield are related to environmental conditions. Explain.
Answer:
Different crops and their cultivation practices require different climatic conditions such as temperature, photoperiod, etc., for their growth and completion of life cycle. Some crops are grown in hot and rainy season (Kharif crops), while some are grown in dry and winter season (Rabi crops), For Example. apple cannot grow in plains as it requires several days of low temperature exposure.
Question 2. Define the term hybridisation and photoperiod.
Answer:
Hybridisation: The cross between two genetically dissimilar plants to give rise to a new variety with desired trait is called hybridisation.
Photoperiod: The effect of light hours or daily duration of light exposure on the flowering of plant is called photoperiodism and this duration of time is called photoperiod.
Question 3. What is a GM crop? Name any one such crop, which is grown in India.
Answer:
Genetically Modified (GM) crop
- Crop which has been developed by introducing a new gene from any other source of organism to obtain desired characters is called Genetically Modified (GM) crop.
- Bt cotton is an example of GM crop in India. It is made insect resistant by introducing a new gene front a bacteria {Bacillus).
Question 4. Give any two differences between macronutrients and micronutrients.
Answer:
Differences between macronutrients and micronutrients are as follows
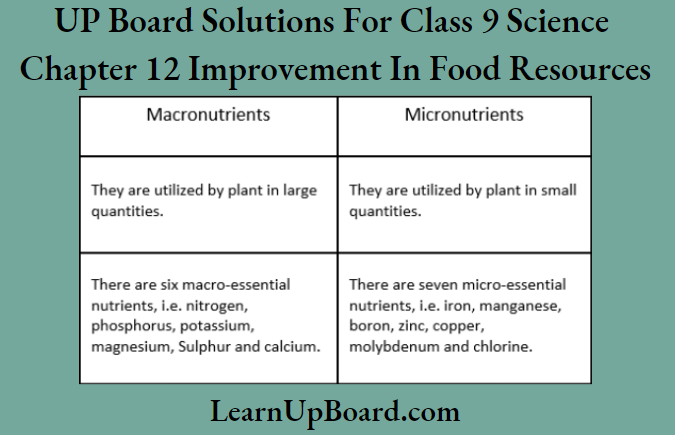
Question 5. What do you mean by vermicompost?
Answer:
Vermicompost Definition
Vermicompost is a kind of manure prepared by using earthworms to hasten the process of decomposition of plants and animals refuse.
Question 6. State two advantages of fertilisers over manures.
Answer:
The two advantages of fertilisers over manures are as follows
- A fertiliser is nutrient specific. It can specifically provide nutrients such as N, P, K to soil according to need.
- It is easy to transport and use.
Question 7. Why is excess use of fertilisers detrimental for environment?
Answer:
The excess use of fertilisers leads to water pollution. Excess fertilisers generally get washed away through irrigation, rainfall or drainage and pollute rivers, lakes, streams, etc. This disturbs the ecosystem, as the polluted water kills the aquatic animals and is also harmful for humans.
Question 8. Organic matter has been given importance in production of crops. Is it true. If yes, why?
Answer:
Yes, organic matter is important for crops because of following reasons
- forms humus and makes the soil fertile.
- improves the soil structure and aeration of clayey soil.
- increases water holding capacity of sandy soil.
- helps in drainage.
- liberates minerals and improves growth of crop plants.
Question 9. Write about the fresh initiatives in the held of irrigation.
Answer:
Fresh initiatives in irrigation include
- Rainwater harvesting Conserving rainwater for multipurposes like washing, gardening or irrigation.
- Wastershed development It involves building check dams. It leads to an increase in groundwater levels.
Question 10. What is mixed cropping? How does it help a farmer?
Answer:
Mixed cropping
Mixed cropping is growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land, For Example. wheat + gram and groundnut + mustard. This reduces risk of total crop failure due to uncertain monsoon. It also helps the farmer to raise his livelihood.
Question 11. What is intercropping? Give one example and advantages of intercropping.
Answer:
Intercropping
Intercropping is a method of growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a specific pattern, For Example. soybean + maize.
Advantages of Intercropping
- Intercropping ensures maximum utilisation of the nutrients present in soil or supplied from outside.
- It also prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop in a field.
Question 12. Weeds are unwanted plants in the cultivated field. Give some methods to eradicate them.
Answer:
Some methods to remove weeds are as follows
- Mechanical removal Uprooting, weeding with hand or harrow, ploughing, etc.
- Preventive methods Proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crops, etc.
Question 13. Write the modes by which insects affect the crop yield.
Answer:
Insects affect the crop yield in three ways
- They cut the root, stem and leaf.
- They suck the cell sap from different parts.
- They bore into stem and fruits.
Question 14. Why using pesticides is not considered a good practice?
Answer:
Using pesticides in excessive amount creates problems because
- they are poisonous for some plants and animals.
- they cause environmental pollution.
Question 15. State the food requirements of dairy animals.
Answer:
Food requirements ot dairy animals are of two types
- Maintenance requirement, this is die food required to support the animal to live healthy lite.
- Milk producing requirement, this type of food is required during lactation period.
Question 16. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Answer:
Cross-breeding between exotic and indigenous breeds is done for improving catde breeds. This is done to get animals with desired qualities of both, For Example. long lactation period of exotic breed and resistance to diseases of local breeds.
Question 17. Name two internal parasites that affect cattle animals.
Answer:
- Worms They affect the stomach and intestine.
- Flukes They damage the liver.
Question 18. What is poultry farming? How does it help in solving food and nutrition problems?
Answer:
Poultry farming
Poultry farming is the method to rear domestic fowl for the production of eggs and meat. It helps in solving food and nutrition problem by providing a balanced diet for the human population. It also converts agricultural byproducts into high quality meat.
Question 19. Name two desirable traits for variety improvement in poultry farming.
Answer:
- Quality and quantity of chicks.
- Dwarf broiler parents for commercial chick production.
Question 20. Good management practices give good production of poultry birds. Enlist some management practices in poultry farming.
Answer:
- Management practices in poultry farming include
- Maintenance of temperature and hygienic conditions in housing and poultry feed.
- Prevention and control of diseases.
Question 21. Suggest some preventive measures for the diseases of poultry birds.
Answer:
Poultry fowl suffers from various diseases. These are caused by different agents found in nature and can affect the growth, quality and quantity of chicks. Fowls also suffer from nutritional deficiency. These diseases can be prevented by
- Providing nutritional diet to poultry birds.
- Cleaning and sanitation of shelter.
- Appropriate vaccination of poultry birds.
- Spraying disinfectant at regular intervals in the shelter.
Question 22. Give two examples of shellfishes.
Answer:
Two examples of shellfishes
- Crustaceans like prawns and lobsters.
- Molluscs like oysters and Octopus.
Question 23. Where can you do inland fisheries?
Answer:
Inland fisheries
- Inland fisheries are done in the following water resources
- Freshwater resources Canals, ponds, reservoirs, and rivers.
- Brackish water resources These are the resources, where freshwater and seawater mix together, For Example. estuaries and lagoons.
Question 24. Which factors should be taken into consideration for fish culture?
Answer:
The three important factors required for fish culture include
- Topography, i.e. location of pond.
- Water resources and their quality.
- Soil quality.
Question 25. Explain, why does legume crop not require nitrogenous fertilisers.
Answer:
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, e.g. Rhizobium is present in the roots of leguminous plant. Therefore, they do not require nitrogenous fertilisers to fulfil their nitrogen requirements.
Question 26.
- Suppose you are incharge of a grain store. How will you find out the presence of pests? Mention any two indicators.
- Which method is most effective for destroying insects in stored food grains, spraying or fumigation?
Answer:
- Damaged stored grains, pests reduce them to perforated shells.
- Degraded quality, loss in weight and discolouration of grains.
- The fumigation method is more beneficial over spraying for destroying insects in stored food grains. In fumigation, the insect pests are exposed to the fumes of chemicals.
Question 27. Large population of cattles is present in our country, but milk production is meagre. Why?
Answer:
- Large population of cattle is present in our country, but milk production is meagre because of the following reasons
- The poor quality of feed is given to cattle. Most of the cattles are of indigenous breeds and give limited amount of milk.
- Proper hygienic housing of cattle is not done due to which they suffer from a number of diseases.
Question 28.
- Name the month during which kharif crop is grown.
- List any two factors for which crop variety improvement is done.
Answer:
- Kharif crop is grown during the months from June to October.
- Two factors for which crop variety improvement is done are as follows
- Higher yield To increase producrivity of crop per acre.
- Improved quality The definition of quality is different for different crops, e.g. baking quality is important in wheat, protein quality in pulses, etc.
Question 29. Group the following and tabulate them as energy yielding, protein yielding, oil yielding and fodder crops. Wheat, rice, berseem, maize, gram, oat, pigeon gram, Sudan grass, lentil, soybean, groundnut, castor and mustard.
Answer:
- Energy yielding crops Wheat, rice, maize and oats.
- Protein yielding crops Gram, lentil and pigeon gram.
- Oil yielding crops Groundnut, castor, soybean and mustard.
- Fodder crops Berseem and sudan grass.
Question 30. Why has improving crop yields become more important these days? List the major group of activities for improving crop yields. Which one of these activities is the most important and why?
Answer:
Due to continuously growing population, requirement of food is also increasing every year to feed this population. Extra farming land is not available in country to increase production. Therefore, it is necessary to increase crop yield to meet growing demands for food. The major activities for improving crop yields include
- crop variety improvement
- crop production management
- crop protection management Out of these three activities, crop variety improvement is very important. It helps to attain the crops of good yield, improved quality and resistant to various stresses.
Question 31. Discuss the role of hybridisation in crop improvement.
Answer:
The role of hybridisation in crop improvement
Hybridisation is a method of crossing between genetically dissimilar plants. It is of three types
- Intervarietal cross between two different varieties.
- Interspecific cross between two different species of same genus.
- Intcrgcncric cross between two different genera. In plant breeding, intervarictal hybridisation is mostly used to improve the crop variety.
- Improved varieties arc high yielding and resistant to diseases and pests. They have better quality and various other desirable traits. Thus, they play an important role in crop improvement.
Question 32. In agriculture practices, higher input gives higher yield. Discuss how?
Answer:
- In agriculture, higher yield can be obtained by using higher yielding varieties, modern technologies, improved farm practices with latest agricultural machines. All these require high cost and knowledge of new techniques.
- Finance thus, plays a very important role as the cost of input decides the outcome of cropping. Therefore, higher input gives higher yield in agricultural practices.
Question 33. What is manure? State two advantages of using manure. How does green manure differ from ordinary manure?
Answer:
Manure is an organic substance obtained through the decomposition of plant wastes like straw and animal wastes such as cow dung. The decomposition is brought about by microbes.
Advantages of using manure are as follows
- It enriches soil with nutrients without any pollution.
- It improves soil texture.
- It increases water holding capacity of soil by adding organic matter to it.
Green manure is different as it is obtained by growing green plants, which are then mulched by ploughing them into the soil. Later on, it forms green manure.
Question 34. Differentiate between compost and vermicompost.
Answer:
Differences between compost and vermicompost are as follows

Question 35. Define the following:
- Vermicompost
- Green manure
Answer:
- Vermieompost is a manure rich in pulverised organic matter and nutrients. The compost is prepared by using earthworms to hasten die process of decomposition of plants and animals refuse.
- Green manure is prepared by growing green plants in the field itself. It helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus content. For Example. sunhemp is grown in fields, mulched by ploughing and allowed to decompose in field for die preparation of green manure.
Question 36. Give some advantages of mixed cropping.
Answer:
Advantages of mixed cropping are as follows
- Chances of pest infestation is greatly reduced.
- By growing two or more crops simultaneously, soil fertility is improved.
- The risk of total crop failure due to uncertain monsoon is reduced.
Question 37. If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year, what measures will you suggest to the farmers for better cropping?
Answer:
Suggestions to farmers for better cropping in low rainfall area are as follows
- Enrich soil with humus, as it increases water holding capacity of soil.
- Reduce tilling.
- Use of drought resistant and early maturing varieties of crops.
- Better irrigation facilities and methods to conserve water.
Question 38. The food available is decreasing, day by day, both in quantity and in quality. What steps can be employed to improve this condition, when the population is increasing drastically?
Answer:
The following steps can be taken to improve the condition of food for present as well as for future generations
- By selecting good variety of crops having desirable agronomic traits. Such varieties can be developed using hybridisation technique and by genetic modification of crops.
- The field should be kept fertile and nutrient rich by using manure, etc.
- By using high yielding variety of seeds for high yield per acre.
- By using a beneficial cropping pattern such as mixed cropping, crop rotation, etc.
- By improving irrigation facilities and bringing more agricultural land under irrigation.
- By protecting crops from weeds, diseases, etc.
Question 39. Discuss various methods of weed control.
Answer:
The various methods of weed control are as follows
- Mechanical method Uprooting, weeding, ploughing, burying and flooding.
- Cultural method Proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation.
- Chemical method Spraying of chemicals like herbicides or weedicides.
- Biological control Use of insects or some organisms, which consume and destroy the weed plants, For Example. prickly-pear cactus (Opuntia) is controlled by insects and aquatic weeds are controlled by fish grass carp.
Question 40. Give one word for the following
- Farming without use of chemicals as fertilisers, herbicides and pesticides is known as
- Growing of wheat and groundnut on the same field is called
- Planting soybean and maize in alternate rows in the same field is called
- Growing different crops on a piece of land in pre-planned succession is known as
Answer:
- sustainable farming
- mixed cropping
- intercropping
- crop rotation
Question 41. Discuss, why pesticides should be used in very accurate concentration and in very appropriate manner?
Answer:
- Pesticides should be used in accurate concentration as they are very harmful to environment. Pesticides are non-biodegradable and can accumulate in organisms.
- The environmental impact of pesticides consists of the effects of pesticides on non-target species. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, because they are sprayed or spread across entire agricultural fields.
- Runoff can carry pesticides into aquatic environments. Wind can carry them to other fields, grazing areas, human settlements and undeveloped areas, potentially affecting other species. Other problems emerge from poor production, transport and storage practices.
Question 42. Explain the factors that are to be considered before deciding the nature of feed for cattle.
Answer:
Following factors should be considered before deciding the nature of feed for cattle
- Food requirements of dairy animals are of two types
- Maintenance requirement Food is required to support the animal to live a healthy life.
- Milk producing requirement Food type required during lactation period.
- Animal feed includes
- Roughage Largely fibrous.
- Concentrates High levels of proteins and other nutrients.
- The food requirements of catdes are different for every age and type of work they do.
Along with the ration, some feed additives can also be given to add micronutrients. It helps to promote the health and milk output of dairy animals.
Question 43. Cross-breeding programme is successfully done in poultry farming for variety improvement. Enlist some desirable traits for which cross-breeding is done in poultry birds.
Answer:
The cross-breeding programmes between Indian breeds like Aseel and foreign breeds like Leghorn are carried out for variety improvement. It focusses on developing new varieties for the following desirable traits
- Number and quality of chicks The cross-bred variety should produce good quality chicks in large quantity.
- Dwarf broiler parent They help in commercial chick production.
- Summer adaptation capacity The variety should be adaptable to survive in high temperature and different climatic conditions.
- Low maintenance requirement
- It should decrease the investment charges.
- Reduction in the size of the egg-laying bird with the ability to utilise more fibrous and cheaper diets that is formulated using agricultural byproducts.
Question 44. Differentiate between layers and broilers. What type of food should be given to broilers?
Answer:

Question 45. Write a short note on marine fisheries.
Answer:
Marine fisheries
India’s marine fishery resources area include 7500 km long coastline and deep seas beyond it. Marine fishes are caught using many kinds of fishing nets from fishing boats. The yields are increased by locating large schools of fish in open sea by using satellites, etc.
- Popular marine fish varieties are pomfret, mackerel, tuna, sardines and Bombay duck.
- High economic value marine fishes are:
- Firmed fishes Mullets, bhetki and pearl spots.
- Shellfishes Prawns, mussels and oysters.
Question 46. Differentiate between
- inland fishery and marine fishery
- apiculture and aquaculture.
Answer:
Differences between inland and marine fisheries are as follows
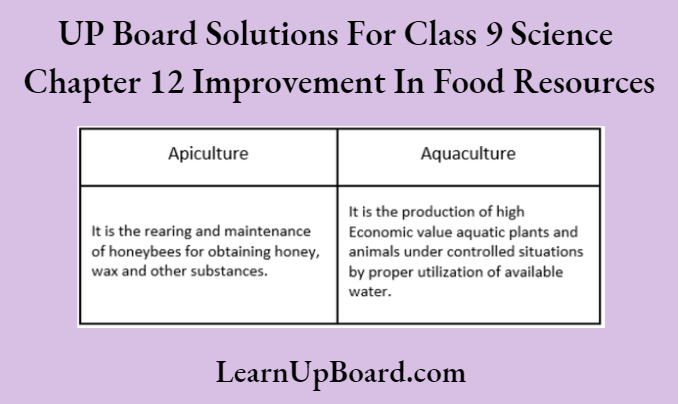
Question 47. What is honey? What does the quality of honey depend upon?
Answer:
Honey
Honey is a dense sweet liquid. It contains 20-40% sugar, small amount of minerals and vitamins. Apart from that, it also contains certain enzymes and pollen. It has medicinal value specially in problems related to digestion and liver.
The quality of honey depends upon the pasturage or flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. In addition to adequate quantity of pasturage, the kind of flowers available also determine the taste of honey.
Question 48. What are the advantages of bee-keeping?
Answer:
Following are the main advantages of bee-keeping
- Along with getting honey on a commercial scale, other products like wax, royal jelly and bee venom are also obtained from bee-keeping.
- Bee-keeping requires low investments due to which farmers, along with agriculture also prefer bee-keeping to generate additional income.
- It helps in cross-pollination. Pollens are transferred from one flower to another by bees, while collecting nectar.
Question 49. An Italian bee variety Apis mellifera has been introduced in India for honey production. Write about its merit over the other varieties.
Answer:
Merits of Italian bee variety Apis mellifera are as follows
- It is stingless.
- It stays in beehives for long period of time and breeds very well.
- It has high honey collection capacity.
Question 50. Differentiate between the following
- Capture fishery and culture fishery.
- Bee-keeping and poultry farming.
Answer:
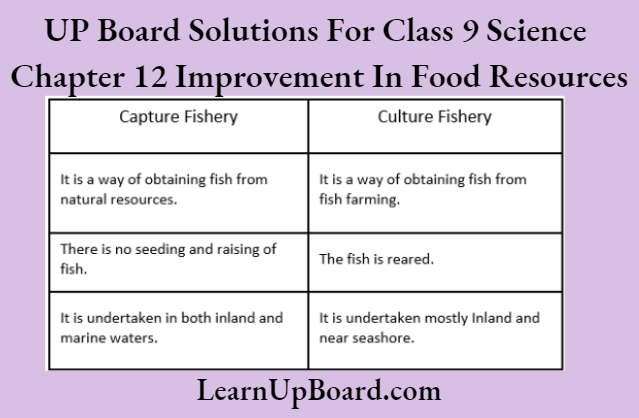
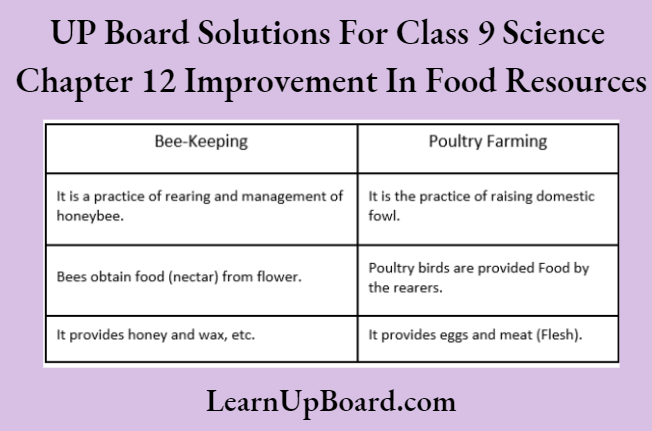
UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Improvement In Food Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How can crop variety improvement methods help farmers facing repeated crop failure? Describe three factors for which they could do crop improvement. Which is the most common method of obtaining improved varieties of crops? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Crop variety improvement basically focuses on developing a crop variety that can provide a good yield, resistant to diseases and pests, not responsive to fertilisers and is adaptable. Thus, it can lead to better crop produce.
Factors for which crop improvement can be done are as follows
- Higher yield Every farmer involved in agriculture needs to get a good yield to be economically stable. Crops need to be improved, so that they provide good productivity per acre.
- Improved quality Both quantity and quality are important for crop improvement, For Example. baking quality in wheat, protein quality in pulses and oil quality in oilseeds should be given consideration, while selecting an improved variety.
- Wider adaptability Varieties having wider adaptability can stabilise their growth in different environmental conditions.
There are two ways of getting a variety with desirable characteristics
- Genetic manipulation A gene is introduced in plant that provides the desirable characters.
- Hybridisation The most common method of obtaining improved variety of crops is hybridisation. Hybridisation is the cross between genetically dissimilar plants.
11 can be of three types
- Intervarieal Cross between two different varieties.
- Interspecific Cross between two different species of the same genus.
- Intergeneric Cross between two different genera.
Question 2. Mention the modern initiatives undertaken in India to supply water to the fields.
Answer:
The modern initiatives undertaken in India to supply water to the fields
Poor monsoons cause crop failure. The crops should be given water at appropriate stages of life to increase die expected yield of crops. Under such circumstances different kinds of irrigation systems are developed. It ensures the supply of water to agricultural lands.
Depending on the type of water resources, the irrigation systems are as follows
(1) Wells They are of two types
- Dug wells In this type of well, water is collected from water bearing strata.
- Tube wells In this type of well, water is lifted by pumps from deeper strata for irrigation.
(2) Canals In this system, canal receives water from one or more reservoirs or from rivers. The main branch is divided into branch canals with many distributaries to irrigate fields.
(3) River lift system It is most common in those areas, where canal flow is irregular or insufficient due to less number of reservoirs release. In lift system, water is directly drawn from rivers for irrigation in areas near to rivers.
(4) Tanks These are small storage reservoirs intercepting and storing the run-off of smaller catchment areas.
Question 3. Figure shows the two crop fields [plots A and B] that have been treated by manures and chemical fertilisers respectively, keeping other environmental factors same.
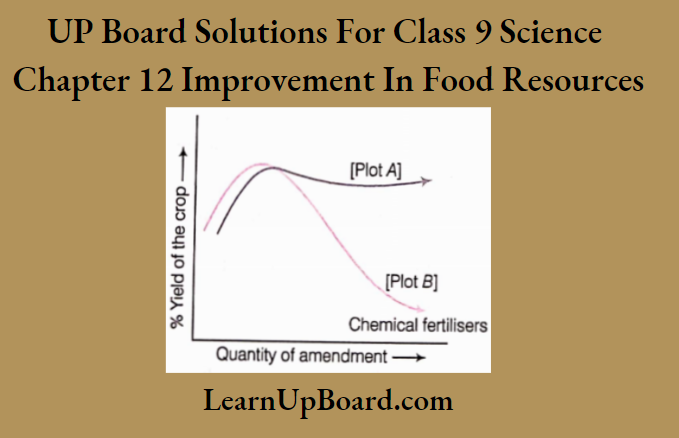
Observe the graph and answer the following questions.
- Why does plot B show sudden increase and then gradual decrease in yield?
- Why is the highest peak in plot A graph slightly delayed?
- What is the reason for the different patterns of the two graphs?
Answer:
- With the addition of chemical fertilisers, there is a sudden increase in yield due to the release of nutrients like N, P, K, etc., in high quantity.
- The gradual decline in the graph may be due to continuous use of high quantity of chemicals. It has killed microbes useful for replenishing the organic matter in the soil. This results in reduced the soil fertility.
- Manures supply small quantities of nutrients to the soil slowly. It takes time to mix with the soil. It increases water holding capacity and aeration of soil, thereby increasing soil fertility continuously.
- The difference in the two graphs is because of the fact that use of manure is beneficial for longer duration in cropping. The yield gets high when the quantity of manure increases.
- In case of plot B, the chemical fertilisers may cause various problems, when used continuously for long time. Loss of microbial activity reduces decomposition of organic matter. As a result soil fertility is lost that affects the yield.
Question 4. (1) Which factors are responsible for causing loss of storage grains? State some preventive measures for storage of foodgrains.
(2) What do you mean by animal husbandry? State two advantages of it.
Answer:
(1) Factors responsible for the loss during storage of grains are as follows
- Biotic factors as insects, rodents, birds, mites and bacteria.
- Abiotic factors as moisture content, temperature etc.
Preventive measures for storage of foodgrains include:
- Drying
- Maintenance of hygiene
- Fumigation
- Improved storage structure.
(2) Animal husbandry It is a science of rearing, feeding, caring, breeding and utilisation of animals.
Advantages of animal husbandry are as follows
- It is beneficial for farmers as increased yield brings more income and raises their living standard.
- It helps us to undertake proper management of domestic animals.
Question 5. Name two typos of animal food and writo thoir functions.
Answer:
The dairy cattle is given it balanced ration. It contains all nutrients in proportionate amounts. A ration is the amount of food, which is given to the animal during a twenty-four hour period.
The animal foal includes two types of substances
- Roughage It largely contains fibres such as green fodder, silage, hay (straw of cereals) and legumes, (For Example. berseem, cowpca and agathi).
- Concentrates The concentrates used in feed of cattle and buffaloes arc a mixture of substances. These arc rich in one or more nutrients, For Example. cotton seeds, oil seeds, grains of maize, oats, barley, jowar, bajra and gram. Their byproducts such as wheat bran, rice bran (polish), gram husk, oilseeds, cakes and molasses are also used.
1. Green fodder and dry grasses (roughage) = 15-20 kg
2. Grain mixture (concentrates) = 4-5 kg
3. Water = 30-35 litres.
Besides above mentioned nutritious food material, dairy animals require certain additive feeds. They promote the growth of the animals. They contain antibiotics, minerals and hormones. They facilitate good yield of milk and protect them from diseases.
Question 6. What do you understand by composite fish culture? Describe in detail with its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
Composite fish culture
- Composite fish culture system is adopted for intensive fishing.
- Characteristics of composite fish culture These are as follows
- Both local as well as imported fish species can be used in such systems.
- Combination of five or six fish species is used in a single fish pond.
- These species have different feeding habits.
- The species are selected so that they do not compete for food among them because of their different food habits. Some examples are as follows
- Catla Surface feeders.
- Rohu Feeds in the middle zone of the pond. Mrigal Bottom feeders.
- Common carps Bottom feeders.
- Grass carps Weed feeders.
Advantages of composite fish culture These are as follows
- All the food available in the pond is utilised.
- There is no competition for food.
- There is an increase in the fish yield from the pond. Disadvantages of composite fish culture These are as follows
Lack of availability of good quality fish seeds.
Question 7. (1) What is the term used for the scientific management of livestock ?
(2) What do you moan by tho term apiary and pasturage?
(3) Mention any two desirable traits, for which cross-breeding programmes between Indian and foreign breeds are undertaking in poultry farming.
Answer:
- Animal husbandry is the term used for scientific management of livestock.
- Apiary Bee farm, which is established for the commercial production of honey, etc., is known as apiary.
- Pasturage It is the flora (flowers) present in the surroundings of apiary that provide nectar to bees. Quantity and quality of honey direedy depends upon pasturage.
- Two desirable traits for which cross-breeding between Indian and foreign breeds are undertaken in poultry farming are:
- Number and quality of chicks.
- Tolerance to high temperature.
Question 8. You are living in an area with abundant greenery and pasturage. A farmer living near your home is not satisfied with the income he gets from his agricultural land.
Which additional income-generating activity will you suggest him in such a scenario?
Or What are other suggestions you would give him for setting the activity?
Answer:
Apiculture is the best-suited activity in such a scenario that I would suggest to him. It is a low investment, additional income-generating activity. It is the method of rearing, care, and management of honeybees to obtain honey, wax, and other substances.
Utilities of apiculture are as follows
- Honey is used for the consumption and manufacturing of other useful products.
- Bees wax is used in various medicinal preparations.
- Bees help in cross-pollination of crops as bee transfers pollen grain from one flower to another, while collecting nectar.
It will also suggest him to use following varieties of bees in apiculture
- Apis cerana indica Commonly known as Indian bee.
- Apis dorsata Commonly known as rock bee.
- Apisflorea Commonly known as little bee.
- Apis mellifera This is the Italian bee that has been brought in to increase the yield of honey.
- I will also explain him the importance of Italian bee in apiary.
- The advantages of Italian bees are as follows
- They have good honey collection capacity.
- They are stingless.
- They stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed very well.
- They are very good for commercial production.
- He should also take care of the pasturage around the apiary as the value or quality of honey depends on it.
Question 9. (1) The black and the white dots in the given picture are an indication of two different types of cropping patterns. Identify the cropping patterns.

(2) Mention one advantage of each cropping pattern.
(3) How are the two cropping patterns different from each other?
Answer:
(1) 1 – Mixed cropping
2 – Intercropping
(2) 1 – Such cropping pattern gives insurance against failure of one of the crops.
2 – It ensures maximum utilisation of nutrients supplied.
(3) Intercropping differs from mixed cropping in several ways, which are as follows

Question 10. One of your family friend is thinking to open a dairy farm for economic purpose. He wants to earn profit by selling milk. He discussed this matter with your father. What additional information can you give based on your knowledge for maintenance of cattles?
Answer:
The following information can be given in accordance with dairy farm
- Exotic breeds can be selected for long lactation period (For Example. Jersey and Brown Swiss).
- Necessary maintenance
Proper cleaning of the sheds should be done regularly.
They should be sheltered under well-ventilated roofed sheds that will protect them against rain, heat and cold.
The floor should be kept sloping, so as to keep it dry and to facilitate cleaning.
Animals should be brushed regularly to clean dirt and loose hair.
(3) Food requirements Cattles need a balanced ration having all the nutrients in proportional amount.
Along with feeds, feed additives should also be given containing micronutrients. They would promote good health and milk production of cattles.
Animal feed should include
- Roughage Largely fibrous.
- Concentrates Low in fibre, but contain higher levels of proteins and other nutrients.
(4) Protection against diseases should also be taken care of.
The parasites of cats are of two types
- External parasites Living on the skin.
- Internal parasites Affect the stomach, intestine, and liver.
Bacteria and viruses also cause infectious diseases.
Vaccination and proper medical treatment should be done at regular intervals against diseases.
