UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe an activity to demonstrate endosmosis and exosmosis. Draw the diagram also.
Answer:
Activity to show endosmosis and exosmosis Put dried raisins in plain water and leave them for some time. Then place them into a concentrated solution of salt.
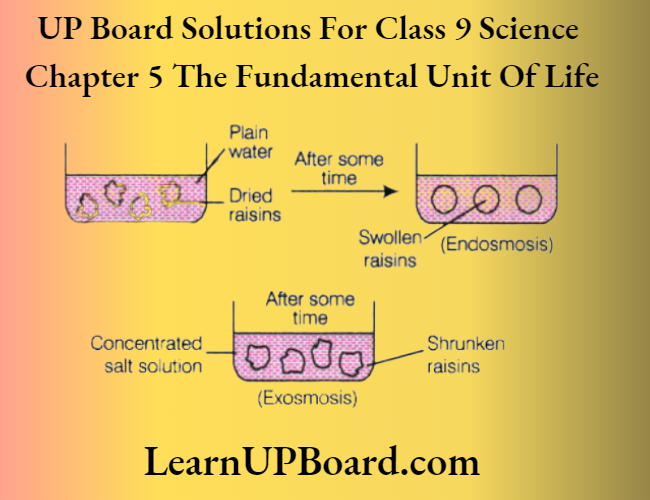
Observation
- When dried raisins are placed in plain water, raisins swell up due to the osmotic entry of water into raisins. Plain water is a hypotonic medium for raisins. Thus, endosmosis occurs.
- When swollen raisins are transferred to a concentrated solution, raisins shrink. Concentrated solution is a hypertonic medium for swollen raisins.
Thus, exosmosis occurs.
Read and Learn More Class 9 Science Solutions
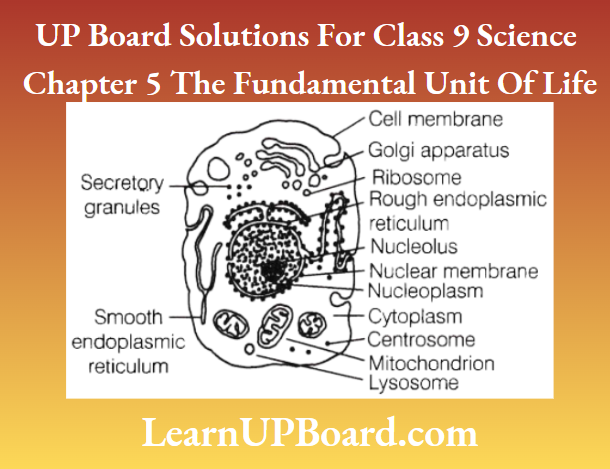
Question 2. Explain the main functional regions of a cell with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
The main functional regions of a cell
The plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus are the three main functional regions of a cell.
- Plasma membrane It is a thin, selectively permeable membrane, covering the cell and is made up of lipids and proteins.
- Cytoplasm It is an aqueous material containing a variety of cell organelles along with non-living inclusions.
- Nucleus It is the control centre of a cell. It contains the cell’s hereditary information (DNA).
Question 3. Given below statements have underlined words which may be incorrect. Rewrite these words and state one function for each of them other than those (if) given.
- The fundamental organisational unit of life is an organ.
- The cell wall is an active part of the cell and is selectively permeable.
- The presence of plasma membrane enables the cells of plants and fungi to exist in hypotonic media without bursting.
- The Golgi body functions both as a passageway for intracellular transport and as a manufacturing surface.
- Leucoplasts contain carotenoids and their primary function is storage.
Answer:
- Cells perform many important physiological functions in living organisms essential for life.
- Plasma membrane It acts as a mechanical barrier, preventing the leakage of cellular contents to the outside.
- Cell wall It helps in interaction among plant cells through cytoplasmic channels called plasmodesmata.
- Endoplasmic reticulum It functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing a surface for some biochemical activities of the cell.
- Chromoplasts impart colour to the parts of plants like flowers and fruits.
Question 4.
- Draw a neat labelled diagram of an animal cell.
- Name the structure, which helps in
- Energy production
- Exchange of materials between cytoplasm and nucleoplasm.
- Lipid synthesis
Answer:
- For the diagram of an animal cell.
- Mitochondria
- Nuclear pore
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Question 5. Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell? Give three similarities and one difference between mitochondria and plastids.
Answer:
Mitochondria are often associated with cellular respiration and energy generation of the cell. The energy required for various chemical activities is released by the mitochondria in the form of ATP molecules. For this reason, mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell.
Three similarities between mitochondria and plastids are as follows
- Both have their own DNA and ribosomes.
- External structures of mitochondria and plastids are similar.
- Both have more than one membrane layer.
One major difference between mitochondria and plastids is that mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cells, whereas plastids are present only in plant cells.
Question 6. Write the main functions of at least ten cell components.
Answer:
The main functions of at least ten cell components
- Plasma membrane It acts as a semipermeable membrane and allows only selective substances to pass through it.
- Chromosomes carry the hereditary characteristics of an organism from one generation to another.
- Lysosomes Breakdown of unwanted macromolecules is the main function of these organelles.
- Ribosomes These help in protein synthesis.
- Nucleus Control centre of the cell. Contains cellular DNA (genetic information) in the form of genes.
- Mitochondria The main function of mitochondria in aerobic cells is the production of energy by the synthesis of ATP.
- Nucleolus Biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and acts as a platform for protein synthesis.
- Cell wall It provides protection and rigidity to the plant cell.
- Chloroplasts These are the sites of photosynthesis within plant cells.
- The endoplasmic reticulum Serves as a channel for the transport of materials.
Question 7. Grass looks green, papaya appears yellow. Which Cell organelle is responsible for this?
Answer:
- Plastids These are found in plant cells only. Plastids are the major cell organelles in plants. On the basis of pigments present in plastids, they are divided into two types; the colourless leucoplasts and the pigmented chromoplasts.
- The colourless leucoplasts store starch, oil and protein granules whereas the pigmented chroloplasts have different colours and can be of several types.
- The most important ones are those containing the pigment chlorophyll, known as chloroplasts, which is responsible for the preparation of food by photosynthesis.
- Other chromoplasts contain non-green pigments, which are responsible for the characteristic colours of fruits and flowers.
Question 8. How are the following related to each other?
- Chromatin network and chromosomes
- Chloroplast and chromosomes
- Genes and DNA
Answer:
- The cell contains nuclear material which can be seen as an entangled mass of thread-like structure when it is not dividing. The chromatin material gets organised into rod-like structures called chromosomes when the cell is about to divide.
- Chloroplasts are green-coloured plastids which contain a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll.
- Genes are the functional segments of DNA (present on DNA) which control a specific trait by making specific proteins.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. A cell is a building block of an organism. Explain why.
Answer:
A cell is a building block of an organism.
The body of an organism is made up of various organ systems and these organ systems are made up of various tissues and tissues are the groups of cells performing the same function. Hence, a cell is a building block of an organism.
Question 2. Every multicellular organism has arisen from a single cell. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Every multicellular organism has arisen from a single cell.
Cells divide to produce cells similar to themselves. Thus, all cells are derived from pre-existing cells and every multicellular organism has arisen from a single cell, for example., the development of a human starts from a single diploid cell called a zygote formed by the fusion of an ovum and sperm.
Question 3. Illustrate the various functions performed by a cell.
Answer:
Cell performs various functions in our body such as
- Synthesis of substances like proteins and lipids.
- Secretion of enzymes.
- Removal of dead materials.
- Oxidation to generate energy.
Question 4. Describe the structural features of the cell membrane and cell wall. Why is a cell membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:
- The cell membrane is a flexible, semipermeable and living portion of a cell, which is made up of lipids and proteins. On the other hand, a cell wall is a tough, rigid and non-living portion of a plant cell, which is made up of cellulose.
- The plasma or cell membrane permits the entry and exit of selected materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents the movement of cell content outside the cell. Hence, it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Question 5. Explain in detail what you know about the structure of the nucleus.
Answer:
Robert Brown discovered the nucleus in the cell in 1831. The nucleus is the control centre of a cell.
The structure of the nucleus is composed of
- The nuclear membrane encloses the nucleus in eukaryotes. The nuclear membrane is penetrated by large nuclear pore complexes, which selectively transport molecules into or out of the nucleus.
- Nucleoplasm It is a kind of protoplasm found in the nucleus containing genetic material (DNA), chromosomes and nucleolus.
- Chromatin The chromatin material inside the nucleus is an organisation of DNA and protein. As a cell prepares itself to divide, the chromatin condenses and becomes thick enough to form specialised structures called chromosomes.
- Nucleolus It acts as the most important site of RNA synthesis. It was first recognised by Fontana in 1874.
Question 6.
- Where are chromosomes located? What is chromatin material and how does it change just before the cell divides?
- The functional segments of DNA are genes/ Give reason.
Answer:
- Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of the cells. Chromatin is a mass of thread-like structures. It condenses to form chromosomes just before the cell divides.
- Genes present in DNA segments carry the hereditary information in them, which is transferred from one generation to next. They determine the structural and functional aspects of the next generation.
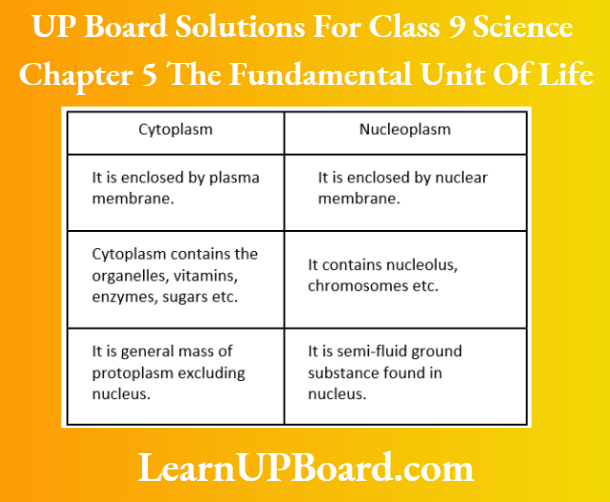
Question 7. State some differences between cytoplasm and nucleoplasm.
Answer:
Differences between cytoplasm and nucleoplasm are as follows:
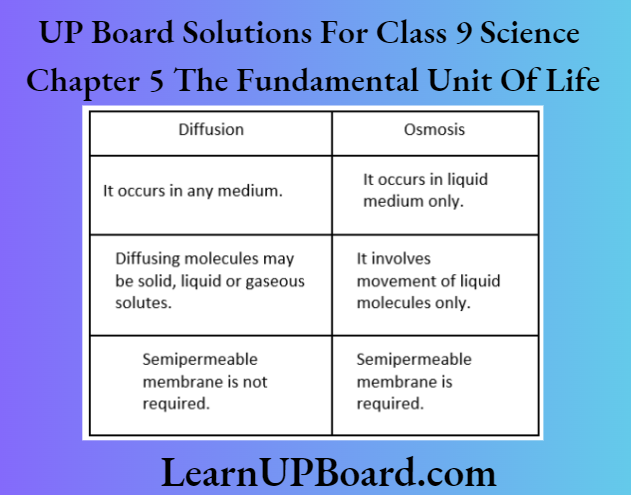
Question 8. Differentiate between diffusion and osmosis.
Answer:
Differences between diffusion and osmosis are as follows
Question 9. What do you mean by plasmolysis?
Answer:
Plasmolysis Definition:
When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis, shrinkage or contraction of the cell contents away from the cell wall occurs. This phenomenon is known as plasmolysis.
Question 10. What would happen, if a cell wall is not present in plant cells?
Answer:
- The shape of a cell will not remain definite because the cell wall provides structural strength to plant cells.
- The cell will not be able to withstand pressure and burst if placed in very dilute media.
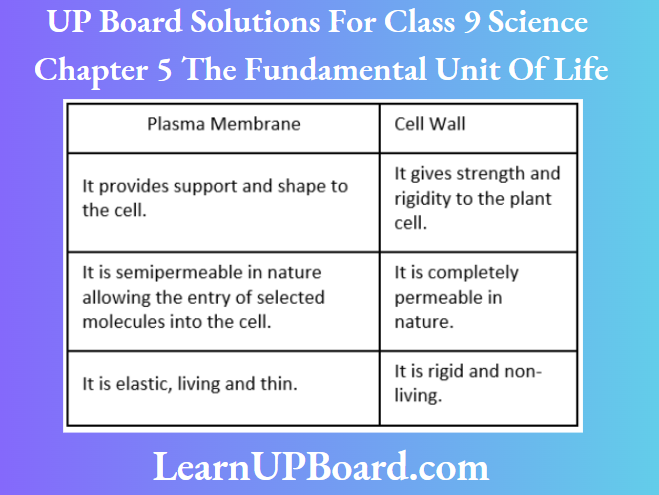
Question 11. Differentiate between Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). How endoplasmic reticulum is important for membrane biosynthesis?
Answer:
Differences between RER and SER are as follows:
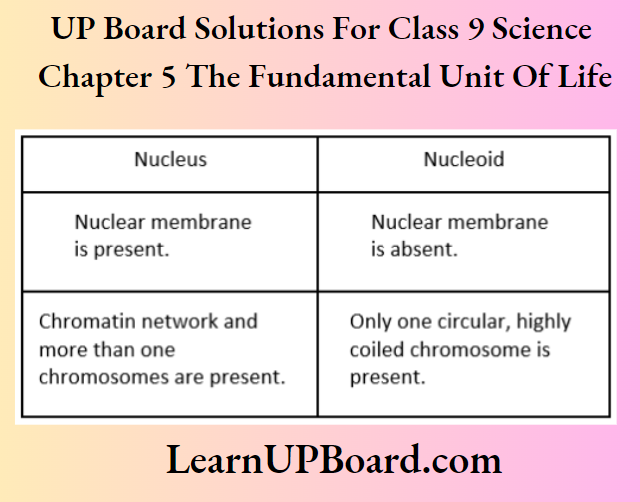
Question 12. Differentiate between nucleus and nucleoid.
Answer:
Differences between nucleus and nucleoid are as follows:
Question 13. What does a chromosome contain?
Answer:
Chromosomes contain genetic information to be transferred from one generation to the next generation in the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid).
Question 14. Differentiate between Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). How endoplasmic reticulum is important for membrane biosynthesis?
Answer:
Differences between RER and SER are as follows
Question 15. Describe the phenomenon of membrane biogenesis. Give one function of ER.
Answer:
The phenomenon of membrane biogenesis
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps in the manufacture of lipid or fat molecules, important for cell function. Some of these lipids and proteins manufactured in RER help in building the cell membrane.
- This process is known as membrane biogenesis. ER functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing a surface for some of the biochemical activities of the cells.
Question 16. Name the organelle of the cell, which is involved in the formation of lysosomes. Write its functions in the cell.
Answer:
Golgi apparatus is the organelle involved in the formation of lysosomes.
The functions of the Golgi apparatus are
- Storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles.
- Helps to make complex sugars from simple sugars.
- Material synthesised near the ER is packaged and dispatched to various targets inside and outside the cell through the Golgi apparatus.
Question 17. Name two nucleic acids found in the cell. Write their functions.
Answer:
Two nucleic acids found in the cell are
- DNA and RNA are two nucleic acids present in the nucleus of a cell.
- Functions DNA is responsible for the storage and transmission of hereditary information, while RNA helps in the synthesis of protein. RNA is the genetic material of some viruses.
Question 18. Categorise the cells on the basis of the presence or absence of a nuclear membrane.
Answer:
Cells, which have nuclear membranes are called eukaryotic cells. On the contrary, the cells without nuclear membrane are called prokaryotic cells.
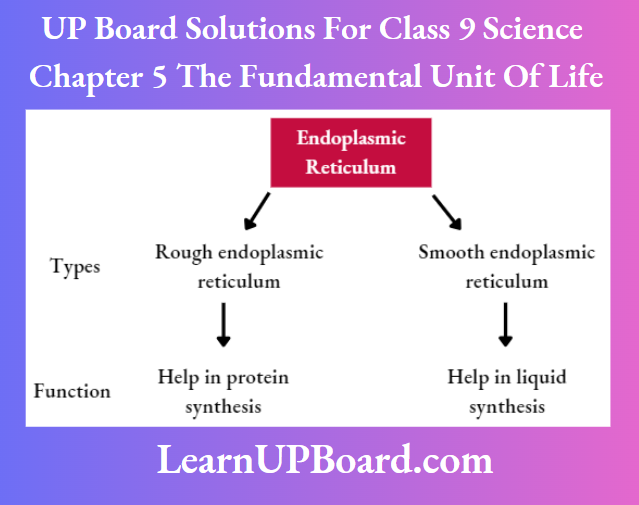
Question 19. What are the different types of endoplasmic reticulum found in an eukaryotic organism? Also, write one major function of each.
Answer:
The different types of endoplasmic reticulum found in an eukaryotic organism
Question 20. Write two functions indicating that lysosomes are the suicidal bags of the cell.
Answer:
The following two functions show that lysosomes are the suicidal bags of the cell
- Lysosomes are the waste disposal system of the cells. They help keep the cells clean by digesting cellular wastes generated in cell.
- Lysosomes also aid in phagocytosis. They digest foreign material entering the cell and kill them.
Question 21. Give scientific reasons for the following
- The inner membrane of mitochondria is deeply folded.
- Mitochondria are able to make some of their proteins.
Answer:
- The inner membrane of mitochondria is deeply folded as these folds create a large surface area for ATP-generating chemical reactions.
- Mitochondria contain their own DNA and ribosomes and hence, can make their own proteins.
Question 22. Bacteria do not have chloroplast, but some bacteria are photoautotrophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of the bacterial cell performs this?
Answer:
Bacterial cell do not have chloroplast yet some photoautotrophic bacteria perform photosynthesis due to the presence of light-absorbing pigments and reaction centres embedded in the cell membrane. The reaction centres exist in forms of sacs, tubes or sheets depending on the amount of surface area needed.
Question 23. Name the two cell organelles, which are bound by a double-layered membrane. Give one function of each.
Answer: Mitochondria- site of ATP-generating reactions. Chloroplasts- site of photosynthesis.
Question 24. Give a one-word answer to the following:
- Organelle containing chlorophyll.
- An organelle with cristae.
- An organelle with ribosomes attached to its surface.
- Living matter of the cell.
Answer:
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Protoplasm
Question 25. Why do some regions appear darker than other regions on staining the cell with methylene blue? Name the other solutions that can be used for staining.
Answer:
Different regions of cells get coloured differentially due to their chemical composition.
Other solutions that can be used for staining are iodine solution or safranin solution.
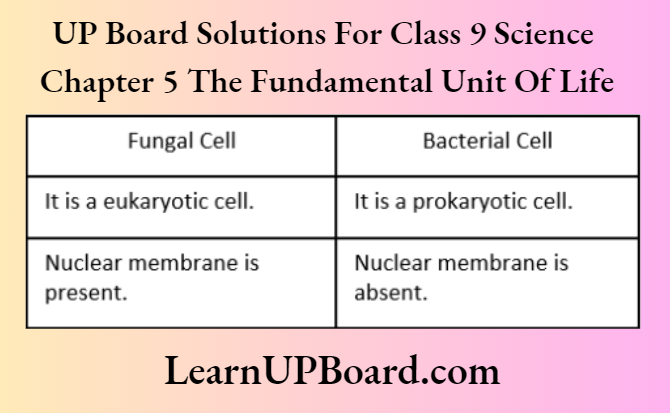
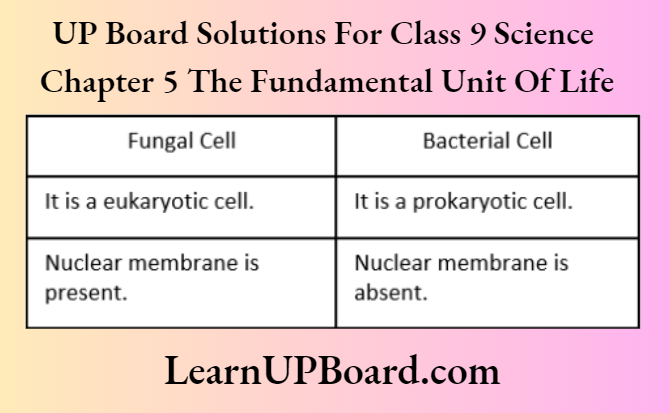
Question 26. How does a fungal cell differ from a bacterial cell?
Answer:
Differences between fungal cells and bacterial cells are as follows:
Question 27. Explain how do cell walls permit the cells of fungi to withstand very dilute external media without bursting.
Answer:
- Fungi withstand very dilute/hypotonic external media without bursting because of their cell walls.
- In such media, the cells swell up by taking up water through osmosis and hence, building up pressure against the cell wall. The wall exerts an equal pressure against the swollen cell, thus preventing it from bursting.
Question 28. Why does the skin of your fingers shrink when you wash clothes for a long time?
Answer:
- The solution of soaps and detergents is hypertonic as compared to the osmotic concentration of our skin.
- Therefore, washing clothes results in exosmosis in skin cells that come in contact with the soap solution. Due to this reason, the skin of the fingers shrinks while washing clothes for a long time.
Question 29. A person takes a concentrated solution of salt. After some time, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such a situation? Explain.
Answer:
The solution of salt is hypertonic, so causes irritation and excessive dehydration due to exosmosis in the intestine. This makes the person uncomfortable causing reverse movements such as vomiting.
Question 30. If you are provided with some vegetables to cook, during the cooking process you generally add salt to vegetables. After adding salt, vegetables release water. Which mechanism is responsible for this?
Answer:
On adding salt to vegetables, they release water due to exosmosis. When the external medium is hypertonic as compared to the osmotic concentration inside living cells, exosmosis occurs.
Question 31. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a very dilute external medium? Explain. Can diffusion lead to the same consequences?
Answer:
- In such conditions, the animal cell will gain water and would swell up or may even burst.
Due to endosmosis, water moves from the dilute external medium through the semipermeable cell membrane into the cell with low water concentration. - No, diffusion can not lead to the same consequences. It causes equal distribution. So, there will be no swelling or shrinkage of the cell.
Question 32. Why is endocytosis found in animals only?
Answer:
- Endocytosis is the process of swallowing food and other substances from an external medium by a plasma membrane. This is possible only when the plasma membrane is in direct contact with the external medium.
- It occurs only in animal cells because they lack cell walls. Plant cells contain cell walls, due to which their plasma membrane fails to perform endocytosis.
Question 33. The Golgi apparatus is also called the secretory organelle of the cell’. Why?
Answer:
The Golgi apparatus is also called a secretory organelle because secretion is the main function of the Golgi apparatus. The secretory proteins and lipids are packed and released on the surface by Golgi via exocytosis.
Question 35.
- Why lysosomes are known as ‘scavengers of the cell’?
- Lysosomes are self-destructive. True/ false. Give reason.
Answer:
- Lysosomes are called scavengers of the cell because they remove dead and worn-out cells by digesting them and act as a kind of waste disposal system of a cell.
- Lysosomes are self-destructive. This is true as during the breakdown of cell structure, lysosomes may burst and the enzymes contained in it may eat up their own cells.
Question 36. How many membranes are present in mitochondria? Give the characteristic features of these membranes. What is the advantage of such features?
Answer:
Mitochondria have two membranes. The outer membrane is very porous, while the inner membrane is deeply folded. A porous membrane helps in getting oxygen and food, while the folds create a large surface area for ATP-generating chemical reactions.
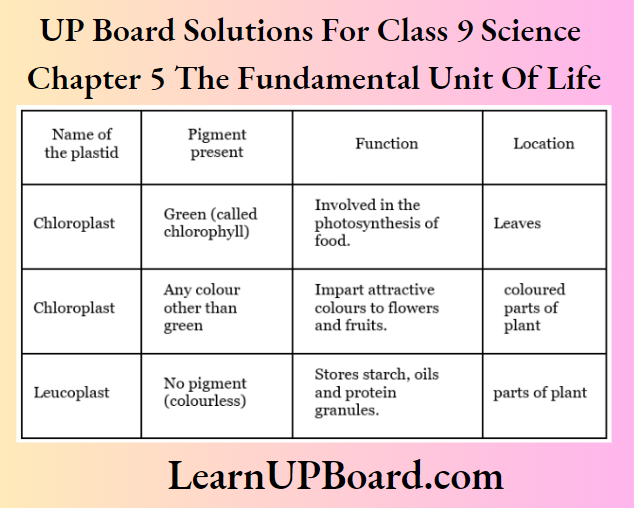
Question 37. Name a cell organelle found only in a plant cell and mention its various types along with their functions and location.
Answer:
Plastids are found only in plant cells.
Types of plastids are as follows
Question 38. Which type of plastid stores starch, oil and proteins?
Answer:
Leucoplasts are the plastids that function to store starch, oil and proteins hence, it is three types
- Amyloplasts – Store starch
- Elaioplasts – Store oil
- Aleuroplasts – Store proteins
Question 39. Why do plant cells possess large-sized vacuoles?
Answer:
Plant cell possesses large-sized vacuoles because
- It stores salt, sugar, amino acid, organic acid and some proteins.
- The vacuole contains cell sap and helps maintain the turgidity of a cell.
- They store some metabolic byproducts or end products of plant metabolism.
- lysosomal enzymes occur in the vacuole of plant cells.
Question 40. State the reason for the following
- Mitochondria is known as the powerhouse of the cell.
- Plant cell shrinks when kept in a hypertonic solution.
Answer:
- Oxidation of food takes place in mitochondria, which results in the release of energy in the form of ATP. This energy helps in various chemical activities needed for life. Hence, mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell.
- A hypertonic solution has a lower concentration of water than the cell. When a plant cell is kept in it, water present in the cell leaves the cell due to exosmosis. Therefore, the cell shrinks.
Question 41. Name the organelles, which show analogy written as under.
- Transporting channels of the cell.
- Powerhouse of the cell.
- Packaging and dispatching unit of the cell.
- Digestive bag of cells.
- Storage sac of the cell.
- Control room of the cell.
Answer:
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome
- Vacuole
- Nucleus
Question 42. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
Keep cup A empty
- Put one teaspoon of sugar in cup B.
- Put one teaspoon salt in cup C.
- Put one teaspoon of sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
- Keep them for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
- Explain, why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
- Why is potato A necessary for the experiment?
- Explain, why water does not gather in the hollowed-out portion of A and D.
Answer:
- The water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C due to the process of osmosis. The concentration of solute (sugar in cup B and salt in cup C) is higher inside the cup than in water.
- Hence, water flows from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
- Potato A acts as a reference of control for the experiment, which helps in comparing results.
- Water does not gather in the hollow portion of A and D for the following reasons:
- The hollow portion of potato A is empty and there is no concentration difference so, no osmosis occurs.
- The hollowed portion of potato D contains sugar, but the potato cup is boiled. Osmosis cannot occur as the semipermeable membrane is destroyed by boiling.
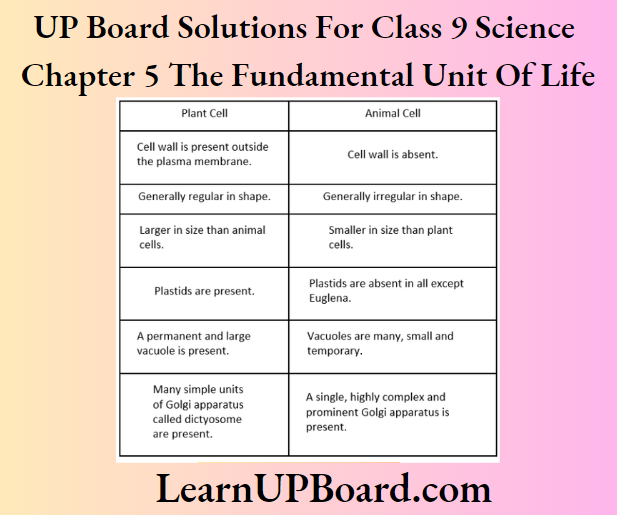
Question 43. Make a comparison and write down ways, in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer:
Comparison of Plant Cells and Animal Cells:
Question 44. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer:
In case the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down,
- All the useful substances will move out of the cell because the membrane is selectively permeable.
- The transportation of materials will be disturbed.
- The cell will lose its normal shape.
- This may lead ultimately to the death of the cell.
Question 45. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
Effects of the absence of Golgi apparatus on the life of a cell are as follows:
- The packaging and dispatching of different types of proteins to various targets inside and outside the cell will be influenced.
- The products of cells cannot be stored and modified later.
- This will affect the lysosome’s formation. This will cause an accumulation of worn-out and dead cell organelles within the cell, which may cause cell death.
Question 46. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer:
- Mitochondria are called the powerhouse of the cell. It contains oxidative enzymes, which oxidise the food and convert it into the energy currency of the cell in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
- This energy is used by body for making new chemical compounds and for doing other work. This is the reason, mitochondria are called the powerhouse of the cell.
Question 47. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer:
All living organisms are made up of cells, which perform various functions essential for the survival of the organisms, for example., respiration, digestion, excretion etc. Thus, a cell is the functional unit of life.
In unicellular organisms, a single cell carries out all the functions, while in multicellular organisms, a group of cells carry out different functions. Thus, a cell is the structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
Question 48. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:
- CO2 and other gases move in and out of the cell by the process of diffusion. When the concentration of carbon dioxide is higher inside the cell than outside, CO2 diffuses out of the cell.
- If the CO2 concentration inside the cell is less, CO2 moves inside the cell from outside. The water moves in and out of the cell by the process of osmosis.
- Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a region of its high concentration to a low concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Who coined the term ‘protoplasm’ for the fluid substance of the cell?
Answer: Purkinje in 1839 coined the term protoplasm’ for the fluid substance of the cell.
Question 2. Name two unicellular organisms.
Answer: Paramecium and Chlamydomonas are the two unicellular organisms.
Question 3. Name the smallest known cell.
Answer: Mycoplasma is the smallest known cell.
Question 4. Plant cells have large vacuoles each surrounded by a membrane. What is the name of this membrane?
Answer: The membrane that surrounds the vacuole is called tonoplast.
Question 5. Write an example of diffusion in a plant.
Answer: Excess of CO2 is present in the air as compared to leaf so, due to the process of diffusion, plants take CO2 from the atmosphere to carry out photosynthesis.
Question 6. Name the process in which diffusion takes place through a semipermeable membrane.
Answer: Osmosis takes place through a semipermeable membrane.
Question 7. During cooking, on adding salt to the vegetables, water is released. Name the mechanism involved.
Answer: Osmosis.
Question 8. What will happen if the already swollen raisin is kept in a salt solution?
Answer: The water flows out from the raisin and goes into the solution medium. Consequently, the raisin shrinks in size.
Question 9. Name the process by which unicellular freshwater organisms and most plant cells tend to gain water.
Answer: Endosmosis, i.e. inward movement of water into the cell from the surrounding medium.
Question 10. What is the function of cellulose in plant cells?
Answer: The plant cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose. Cellulose is a complex substance, which provides structural strength to plants.
Question 11. What does the nucleus contain?
Answer: The nucleus contains nucleolus and chromatin material.
Question 12. Why is the nucleus called the controller or brain of the cell?
Answer:
The nucleus coordinates and directs all the metabolic functions of the cell, which is why it is called the controller or brain of the cell.
Question 13. State two important functions of the nucleus of the cell.
Answer:
- The nucleus is the control centre of a cell.
- It consists of cells’ DNA (genetic information) in the form of genes to carry hereditary characteristics from one generation to another.
Question 14. What are chromosomes made up of?
Answer: Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins.
Question 15. What is DNA? Where is it present?
Answer: DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It is the genetic map of an organism, present in the nucleus.
Question 16. How DNA is present in a cell which is
- Dividing?
- Not dividing?
Answer:
- Chromosomes
- Part of chromatin material.
Question 17. Which organelle is called the factory of ribosomes?
Answer: Nucleolus is called the factory of ribosomes.
Question 18. Name two structures, which are found in plant cell, but not in animal cell.
Answer: Chloroplast and cell walls are found in plant cell, but not in animal cells.
Question 19. Give the name of a structure and its function, which is found only in animal cells, but not in plant cells.
Answer: Centrioles are present only in animal cells and help in cell division.
Question 20. Which of the following are present in animal cells? Chloroplast, nucleus, vacuoles, cell wall and mitochondria Nucleus, vacuoles and mitochondria are present in animal cells. What are dictyosomes?
Answer: In plants, Golgi bodies are called dictyosomes.
Question 21. Is there any animal cell that lacks lysosomes?
Answer: Mammalian RBCs (Red Blood Corpuscles) lack lysosomes.
Question 22. In which cell organelle, the complete breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen takes place?
Answer:
The complete breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen in a cell is called aerobic respiration. It takes place in mitochondria.
Question 23. Name the energy currency of the cell.
Answer: Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is considered by biologists to be the energy currency of cells.
Question 24. Where- does the ATP synthesis occur in mitochondria?
Answer: ATP synthesis occurs in folds of the inner membrane of mitochondria called cristae.
Question 25. Which is the most widely occurring plastid and where is it present?
Answer: The most widely occurring plastid is chloroplast. It is present in all green plants.
Question 26. Name the type of plastid that helps in the process of photosynthesis.
Answer: Chloroplast helps in the process of photosynthesis.
Question 27. Where stroma is present in a cell?
Answer: Stroma is present in the chloroplast of the cell.
Question 28. Which organelles are present only in plant cells and possess their own genome and ribosomes?
Answer: Plastids are found in plant cells only and contain DNA, RNA and ribosomes.
Question 29. Why plastids are called the ‘kitchens of the cell’?
Answer:
Because they contain pigments which can trap sun energy and convert it into chemical energy, i.e. food called glucose.
Question 30. Who discovered cells and how?
Answer:
Cells were discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He observed cells in a cork slice with the help of a primitive microscope. The cork slice resembled the structure of a honeycomb consisting of many small compartments or box-like structures. Hooke called these boxes as cells.
Question 31. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:
The plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane because it allows the entry and exit of some selected molecules only through the cells. It also prevents the movement of some other materials.
Question 32. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell? Or Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
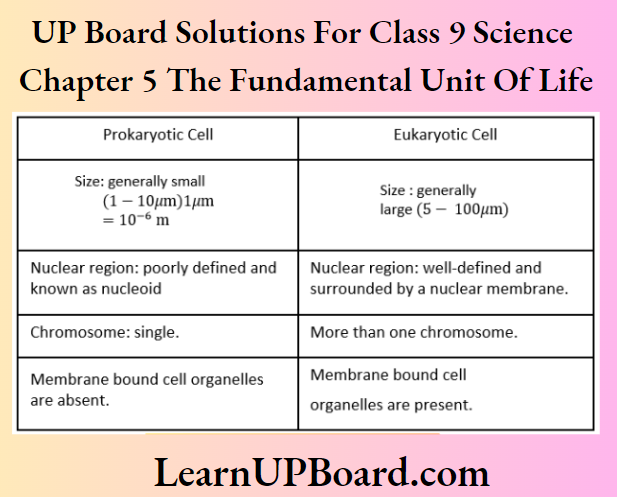
Question 33. Can you name two organelles we have studied that contain their genetic material?
Answer: Mitochondria and plastids are the two cell organelles that contain their genetic material.
Question 34. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer:
Living cells are capable of performing certain basic functions due to the presence of cell organelles present in it. If these are destroyed then cells will not be able to work properly and will die after some time.
Question 35. Why are lysosomes known as suicidal bags?
Answer:
Lysosomes contain powerful digestive enzymes. During the disturbance in cellular metabolism, lysosomes may burst and digest their cell. Therefore, they are called suicidal bags of the cell.
Question 36. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer: Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis inside the cell.
Question 37. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:
The synthesis of lipids occurs in the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). The proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes, which are attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER).
Question 38. How does Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:
Amoeba obtains its food through endocytosis. It is the process of ingestion of food through the plasma membrane. This occurs due to the flexibility of the plasma membrane, which enables the Amoeba to engulf food and other materials from its surroundings.
Question 39. What is osmosis?
Answer:
Osmosis
Osmosis is a process of diffusion of water from a region of its higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
