UP Board Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Write a note on the protective tissue in plants. (Give appropriate diagram also)
Answer:
Protective Tissue In Plants
The protective tissue or the outermost covering of cells in plants is known as the epidermis, which performs a protective function (protecting plants from adverse conditions). It is usually made up of a single layer of cells. In dry habitats, the epidermis gets thicker to protect the plant from undue loss of water.

- On aerial parts of plants, epidermal cells often secrete a waxy, water-resistant layer on their outer surface. This waxy covering aids in protecting the plant against loss of water, mechanical injury, and invasion by parasitic fungi. The cells of epidermal tissue are present in a continuous layer without intercellular spaces.
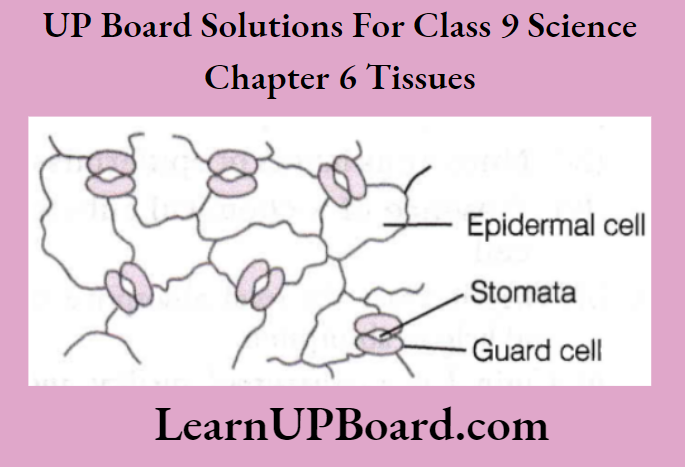
- Small pores are present on the epidermis of the leaf. These pores are called stomata. They are enclosed by two kidney-shaped cells called guard cells. They help in gaseous exchange and transpiration.
Read and Learn More Class 9 Science Solutions
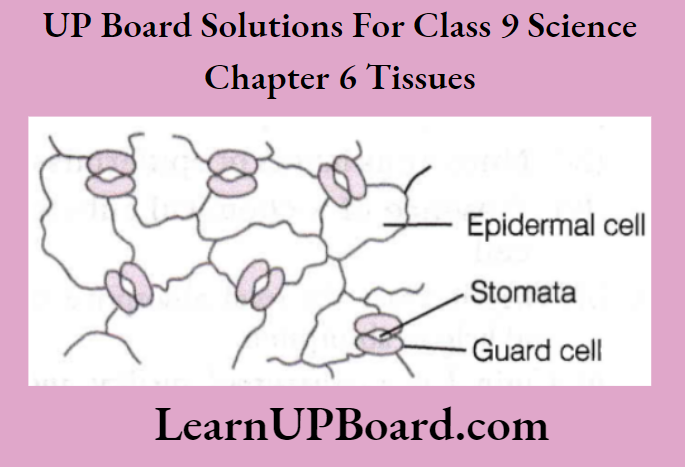
As the plant grows older, a strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of the stem. This forms a several-layer thick cork or bark of the tree in which cells are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces.
Question 2. List the characteristics of cork. How is it formed? Mention its role. NCERT Exemplar
Answer:
The common characteristics of a cork are as follows
- It is the outer protective tissue of older stems and roots.
- It is formed by a secondary lateral meristem called cork cambium.
- The mature cork becomes dead and filled with tannin, resin, and air.
- The cells are arranged compactly without intercellular spaces and several layers become thick, which are impermeable due to the deposition of suberin in their wall.
Formation of cork
As the plant grows older, the outer protective tissue undergoes certain changes. A strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of the stem. Cells on the outside are cut off from this epidermal layer. This forms several layers of thick cork or bark with no intercellular spaces.
Role of cork
- It prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
- It protects plants from the invasion of parasites and other harmful microorganisms.
Question 3. The transportation system of plants is composed of complex permanent tissue. They have their transportation system within themselves. Justify in detail with appropriate diagrams.
Answer:
- The transportation system of plants is composed of complex permanent tissue. These tissues are made up of more than one type of cells, and all these cells coordinate to perform a common specific function.
- These cells may appear structurally different, but they perform the same function. The permanent tissues are of two types
Xylem It helps in the transportation of water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
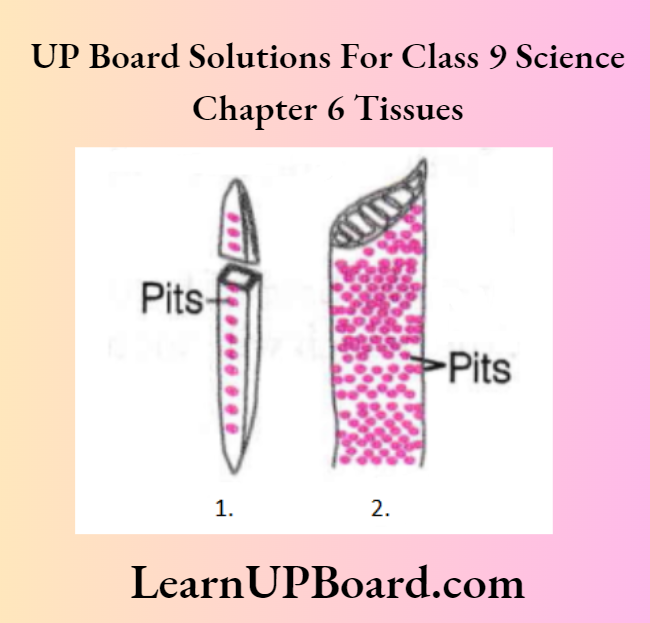
Elements Of Xylem
- Tracheids and Vessels Tubular structure, transport water and minerals vertically.
- Parenchyma Stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
- Fibers are Supportive in function.
The phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant. Food is prepared in leaves by the process of photosynthesis.
Elements of phloem
- Sieve tubes Tubular cells with perforated walls. These consist of living cells.
- Companion cells Small elongated cells with dense cytoplasm.
- Phloem parenchyma Thin-walled cells. Mainly function in storage and transportation of food.
- Phloem fibers Thick-walled cells. These are dead cells. Provide mechanical strength to tissue.
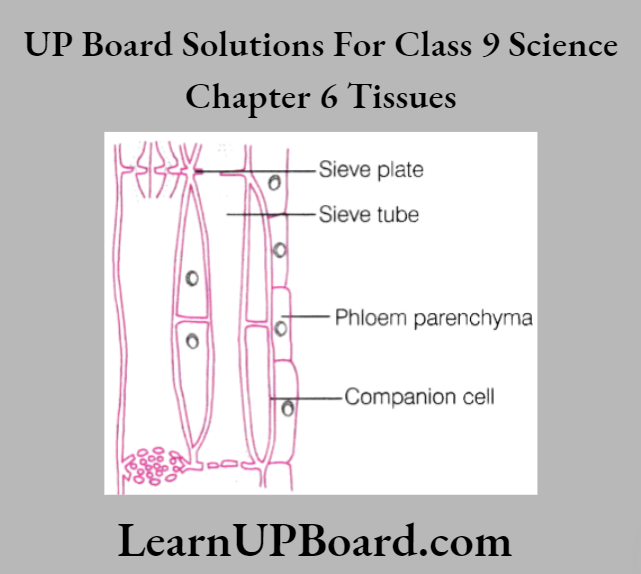
Both the xylem and phloem maintain a transportation system within the plants. There is continuous transportation of food, water, and minerals within the plant.
This transportation is necessary for the proper growth and maintenance of the plant.
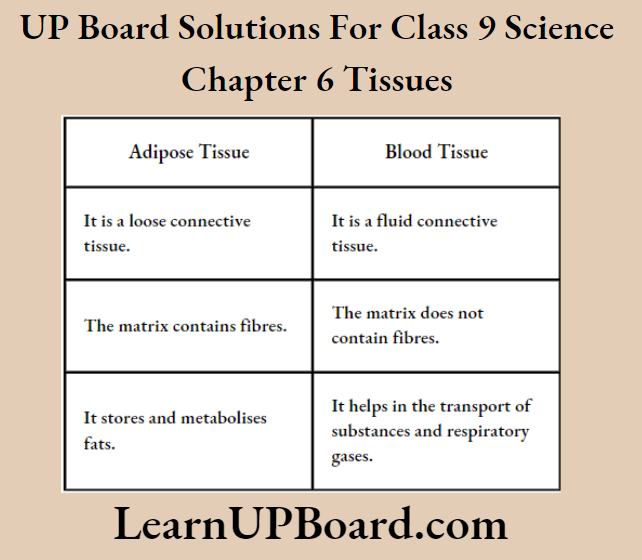
Question 4. How is adipose tissue different from blood tissue?
Answer:
Differences between adipose and blood tissue are as follows:
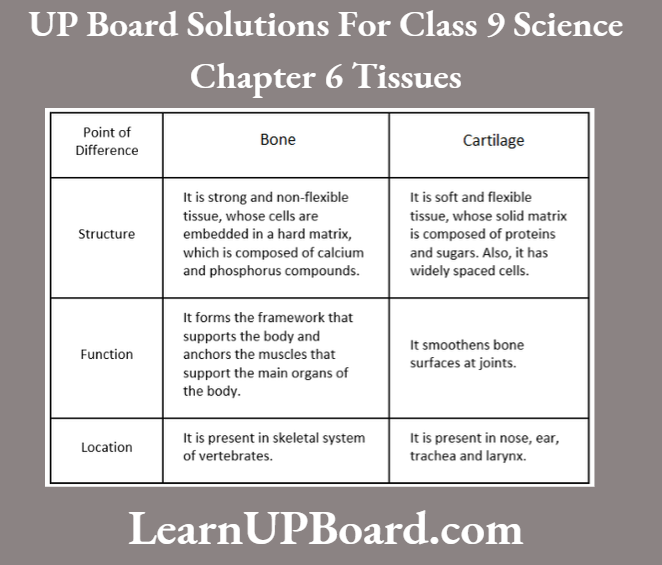
Question 5. Differentiate between bone and cartilage concerning structure, function, and location.
Answer:
Differences Between Bone And Cartilage Are As Follows
Question 6. Explain the significance of the following
- Hair-like structures on epidermal cells.
- The epidermis has a thick waxy coating of cutin in desert plants.
- Small pores in the epidermis of the leaf.
- Numerous layers of epidermis in cactus.
- Presence of a chemical suberin in cork cells.
Answer:
- They increase the total absorptive surface area and help in absorption.
- Cutin has a waterproof quality and helps in preventing water loss due to transpiration. It also protects plants from entry of pathogens, etc.
- They help in the gaseous exchange and transpiration process.
- To prevent water loss.
- Suberin makes cork cells impervious to gases and water.
Question 7. ‘We can control some of the actions of our body, but some are not in our control’. Comment on this statement,
Answer:
Some of the actions like moving our limbs, fingers, neck, etc., can be controlled by our will. We can move these parts of our body whenever we want to, but some actions of our body like contraction and relaxation of the heart, blinking of an eye, etc., are not under our will, i.e. we cannot stop the functioning of the heart if we want to do so. The actions, which can be manipulated by our wishes are known as voluntary actions.
The muscles, which can perform voluntary actions are voluntary.
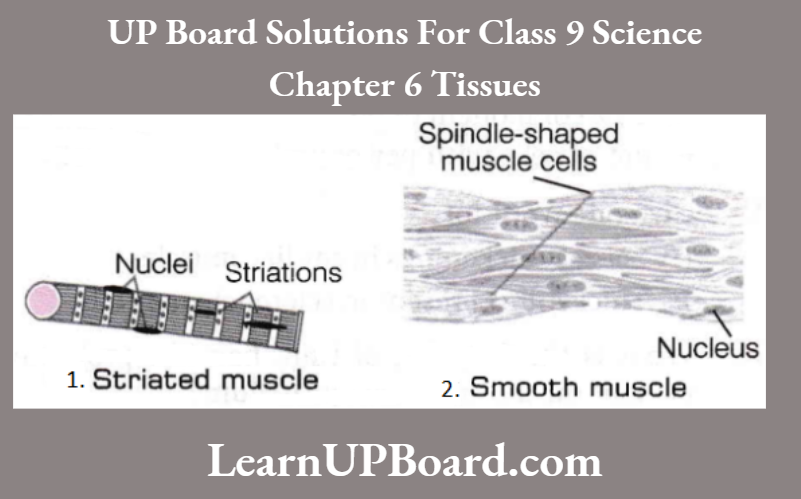
- These muscles are also called skeletal muscles or striated muscles. Spindle-shaped muscle cells (al Striated muscle Cb) Smooth muscle These muscles are mostly attached to bones and help in body movement.
- Their cells are long, cylindrical, unbranched, and multinucleate (having many nuclei).
- The actions, which are not under our control are known as involuntary actions. These actions are performed by smooth muscles or involuntary muscles. Their cells are long with pointed ends (spindle-shaped) and uninucleate (single nucleus).
Question 8.
- What will happen if cells are not properly organized in tissue?
- Under certain circumstances, the squamous epithelium is known as stratified squamous epithelium. Justify.
Answer:
- Different organisms whether unicellular or multicellular need to perform many functions in the body such as respiration, digestion, and locomotion.
- In multicellular organisms, cells present in a group and specialized in one particular function form a tissue.
- Some tissues help in growth, while others in locomotion and some in body movement.
- So, if cells are not organized in these tissues, then highly organized and specialized processes will become disorganized.
- There will be no coordination in the functioning of the cells and body.
- When the simple squamous epithelium is arranged in a pattern of multilayers to prevent wear and tear, the epithelium is called the stratified squamous epithelium, for example., skin.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain the basic criteria for the classification of permanent tissue in plants.
Answer:
The following points form the basis of criteria for classification of permanent tissue in plants
- Whether the tissue is made up of one type of cell (simple) or more than one type of cell (complex).
- Function Supportive (parenchyma), protective (epidermis) or conducting (xylem and phloem).
- Whether the cell wall is thick or thin.
- Whether the cells are living or dead.
Question 2. List any six characteristics of parenchyma.
Answer:
The major characteristics of parenchyma are as follows
- The cells of the parenchyma are living and possess the power of division.
- Each parenchyma cell is isodiametric in shape with a thin cell wall and encloses dense cytoplasm and a small nucleus.
- The cells are loosely packed with large intercellular spaces between them.
- It is found in soft parts of plants such as the cortex of roots, ground tissue in the stem, and mesophyll cells of leaves.
- It serves as a packing tissue to fill the spaces between other tissues and maintains the shape of a plant.
- It stores waste products of plants such as tannin, gum, crystals, etc.
Question 3. Name the tissue responsible for the flexibility in plants. How would you differentiate it from other permanent tissues?
Answer:
Collenchyma tissue is responsible for providing flexibility in plants. Differences between collenchyma tissue and other permanent tissues (parenchyma and sclerenchyma) are as follows

Question 4.
- Identify the given figures.
- Give any two major differences between the structures identified.
- Describe the role performed by these two in the plant body.
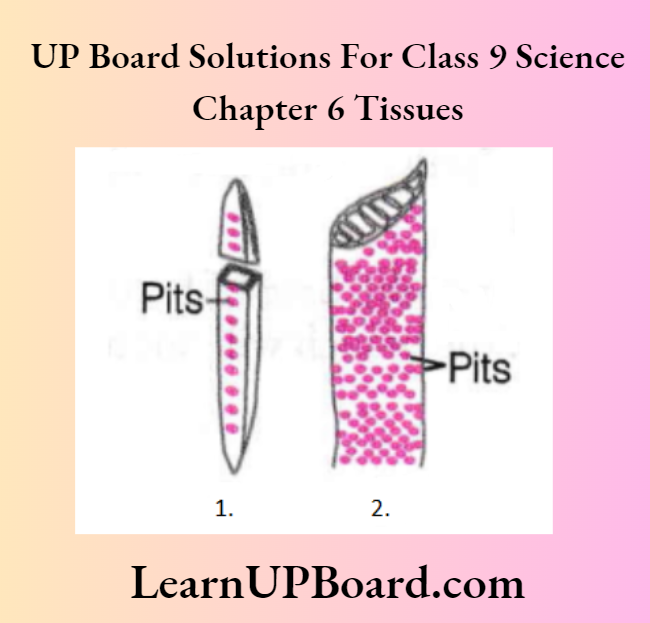
Answer:
- The given figures are of tracheids
- And Vessels
- Of xylem tissue.
- The differences between tracheids
- And Vessels
- Are as follows
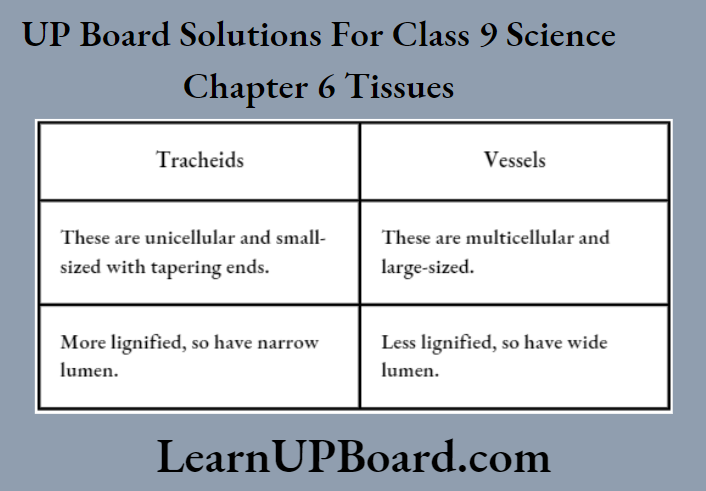
Tracheids and vessels are lignified tissues that provide mechanical strength to the plant body. They also function in carrying water and mineral salts from roots to different parts of the plant body vertically.
Question 5. Describe three functions of protective tissue in plants.
Answer:
Three functions of protective tissue in plants
Two types of protective tissues present in plants are epidermis and cork. The three common functions of these protective tissues are as follows
- Cork protects plants from invasion of parasitic microorganisms and excessive heat and cold.
- The cuticle of the epidermis checks the excessive evaporation of water.
- The epidermis allows transpiration and gaseous exchange through stomata.
Question 6. Give the name of the following
- Tissue is concerned with the conduction of food materials.
- Tissue capable of cell division.
- Multiple pores are present in the epidermis of the leaf.
Answer:
- Complex tissue (phloem)
- Meristematic tissue
- Stomata
Question 7. List the constituents of phloem. What will happen if the phloem at the base of a branch is removed?
Answer:
- Major constituents of phloem include sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
- If the phloem at the base of the branch is removed, then a lower area of the branch will not receive food from the leaves. But the plant will not die, as it will continue to receive food from other branches as food can move through phloem in both directions.
Question 8. Which is the simplest protective tissue present in the animal body? State its two functions.
Answer:
The most simple protective tissue present in the animal body is epithelial tissue. Its major functions are as follows
- It protects underlying cells from drying, injury, and infections.
- It helps in the elimination of waste products from the body.
Question 9. Name the type of epithelium present in the respiratory tract. What is its specialization?
Answer:
The ciliated columnar epithelium is present in the respiratory tract of humans. It has specialized hair-like projections called cilia which help in the movement of substances and mucus forward. Thus, the name ciliated columnar epithelium.
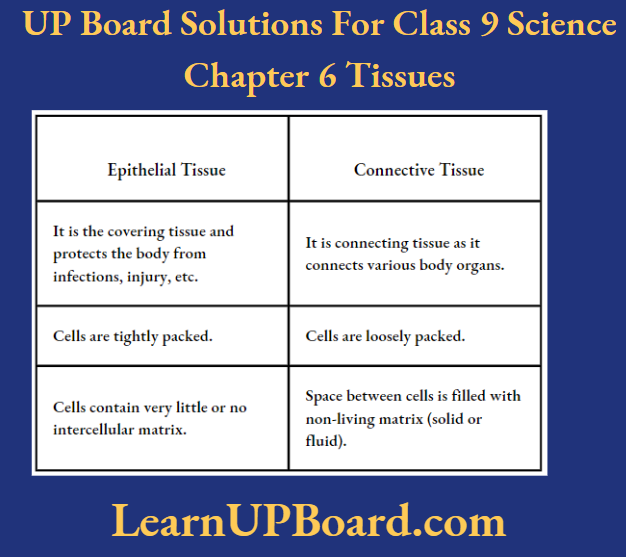
Question 10. Give three differences between epithelial tissue and connective tissue.
Answer:
Differences Between Epithelial And Connective Tissues Are As Follows:
Question 11. Mention three different types of blood cells with their functions. Draw diagrams also.
Answer:
Three different types of blood cells are as follows
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Contains hemoglobin, help in the transportation of gases, digested food, hormones, etc.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs) Integral part of the immune system, that help in fighting diseases by producing antibodies and engulfing germs and pathogens.
- Platelets Help in the clotting of blood.
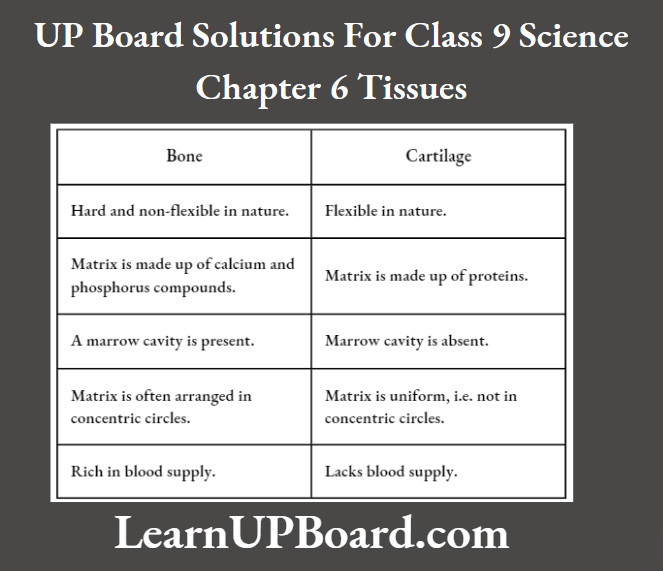
Question 12. Differentiate between bone and cartilage.
Answer:
Differences Between Bone And Cartilage Are As Follows:
Question 13. Name the tissue that smoothens bone’s surfaces at joints. Describe its structure with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Cartilage is the tissue that smoothens bone surfaces at joints. Structure It is a specialized connective tissue, which is compact and less vascular.
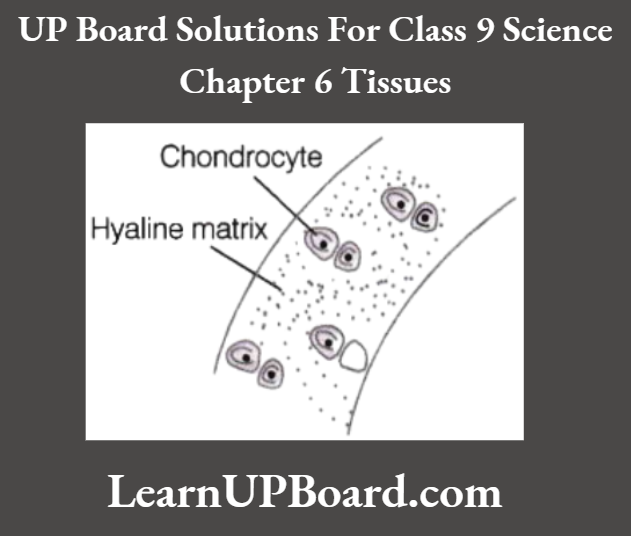
Its extensive matrix is composed of proteins and slightly hardened by calcium salts and also has a delicate network of collagen fibers, living cells, and chondrocytes. The chondrocytes are present in lacunae. Cartilage provides support and flexibility to body parts. It is present in the nose, trachea, ear, and larynx.
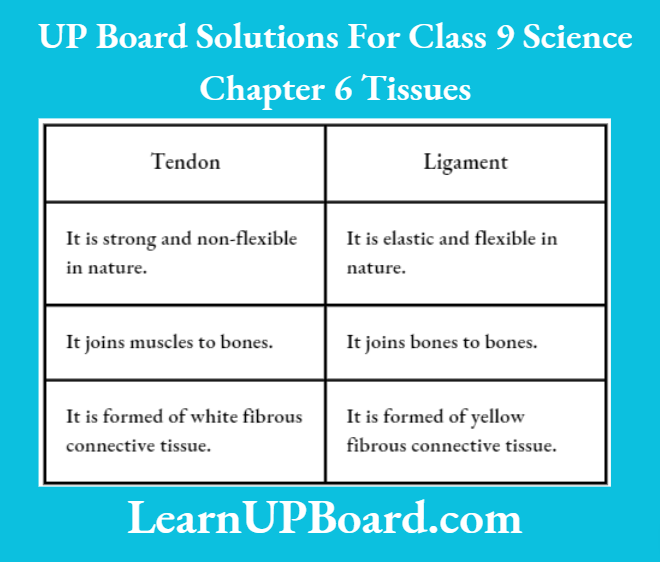
Question 14. Give the differences between tendon and ligament.
Answer:
The Differences Between Tendon And Ligament Are As Follows:
Question 15. State the functions of skeletal connective tissue.
Answer:
- The functions of skeletal connective tissue are as follows
- It gives a definite shape to the body.
- It protects the vital organs of the body, for example., the brain.
- It provides a surface for the attachment of muscles to increase their efficiency.
Question 16. Write a note about the structure and significance of striated muscles with a diagram.
Answer:
Striated muscles are voluntary muscles, i.e. we can move these muscles according to our will.
- These are mostly attached to bones and help in body movement. They show alternate light and dark bands or striations (when stained appropriately).
- Cells of striated muscles are long, cylindrical, unbranched, and multinucleate, for example., muscles of limbs.
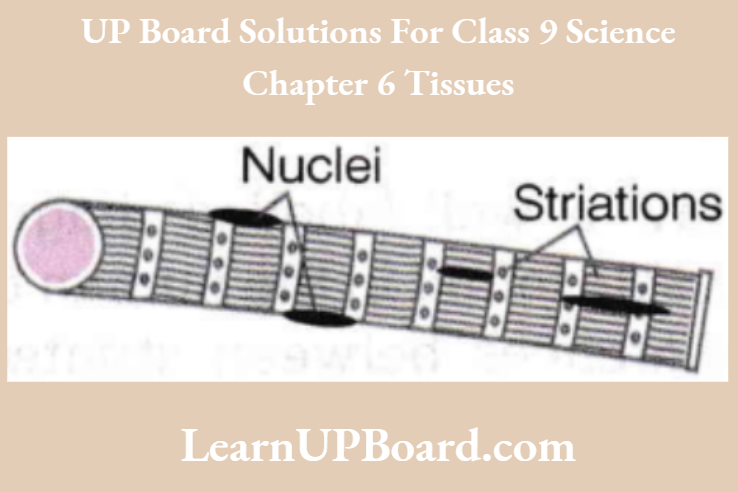
Question 17. Name the kinds of muscles found in your limbs and lungs. How do they differ from each other structurally and functionally?
Answer:
- Limbs Striated muscle.
- Structure Cells are long and cylindrical in shape, presence of dark and light bands, multinucleate and unbranched.
- Function Voluntary movement.
- Lungs Smooth/non-striated muscle.
- Structure Cells are spindle-shaped, absent of striation, uninucleate, and unbranched. Function Involuntary movement.
Question 18. Which type of muscle, smooth or striated is found in the iris of eye? Why are smooth muscles called involuntary muscles? In what way are they different from striated muscles concerning several nuclei?
Answer:
Smooth muscles are found in the iris of the eye. Smooth muscles are the muscles that cannot be moved or stopped according to our will. So, they are known as involuntary muscles. Smooth muscles are uninucleate, whereas striated muscles are multinucleate.
Question 19. Draw a labeled diagram of unstriated muscle tissue and mention its occurrence, features, and functions.
Answer:
The diagram of unstriated muscle tissue is given
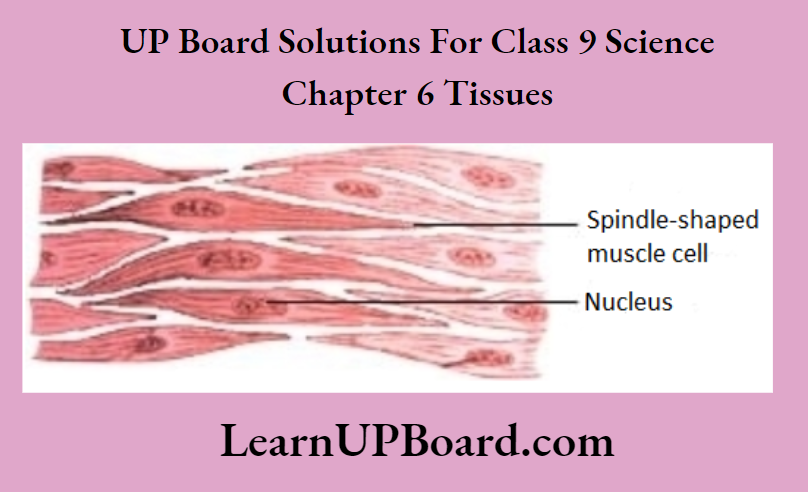
Occurrence These tissues are found in the walls of the alimentary canal, urinary bladder, esophagus, iris, bronchi, etc.
Features
- They are unbranched and non-striated.
- Cells are long, thin, and spindle-shaped.
- Each cell has a single central nucleus.
Functions
- These muscles do not work as per our will.
- These carry out the movement in the urinary bladder and gall bladder.
Question 20. What are neurons? Where are they found in the body? What function do they perform in the body of an organism?
Answer:
Neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. These are found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Functions
- These coordinate various body parts during any body function.
- These control all the activities of the body.
- These transmit messages in the form of nerve impulses to the brain and spinal cord.
Question 21. Differentiate between axon and dendrite.
Answer:
Differences Between axons and dendrites are As Follows:

Question 22. Give one function of each of the following.
- Stomata
- Cardiac muscle fibres
Answer:
- Stomata They help in the gaseous exchange between the plant and the atmosphere. Transpiration takes place through the stomata.
- Cardiac muscle fibers They help in rhythmic contraction and relaxation of heart throughout the life.
Question 23. Write functions of the following
- Areolar connective tissues
- Neurons
- Adipose connective tissues
- Cardiac muscles
Answer:
- Areolar connective tissues These fill the space inside the organs and support internal organs of the body. These also help in the repair of tissues.
- Neurons These are the fundamental cells of nervous tissue. These are highly specialized for being stimulated and then transmitting the stimulus very rapidly from one place to another within the body.
- Adipose connective tissues These are fat-storing tissue found below the skin between internal organs. The cells of this tissue are filled with fat globules. Due to the storage of fats, these act as an insulator.
Question 24. What happens, when
- Formation of cork in older stems does not occur.
- Blood platelets are removed from the blood.
Answer:
- If the formation of cork does not occur in older stems then the outer tissue will rupture due to the increase in girth and the plant will get infected by the parasites.
- Blood clotting will not occur at the site of injury. Bleeding will continue which may lead to death.
Question 25. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
The main points of difference between simple tissues and complex tissues are:
Question 26. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma based on their cell wall.
Answer:
Differences Between Parenchyma, Collenchyma, And Sclerenchyma Are As Follows:

Question 27. Give reasons for the following
- Meristematic cells have prominent nuclei and dense cytoplasm, but they lack vacuole.
- Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissue.
- We get a crunchy and granular feeling when we chew pear fruit.
- Branches of trees move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
- It is difficult to pull out a husk of coconut.
Answer:
- Meristematic cells undergo division and do not store food, thus lacking vacuole.
- Because their walls are lignified and form bundles for mechanical functions.
- Due to the presence of sclerenchymatous tissue (stone cell) or sclereids, we get a crunchy feeling when we chew pear fruit.
- The presence of collenchyma tissue provides flexibility to the branches of a tree.
- The husk of coconut is made up of sclerenchymatous fibers, which are closely packed.
Question 28. What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
The main functions of stomata are:
- They help in the exchange of gases with the atmosphere.
- They help in the transpiration of water.
Question 29. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibers.
Answer:
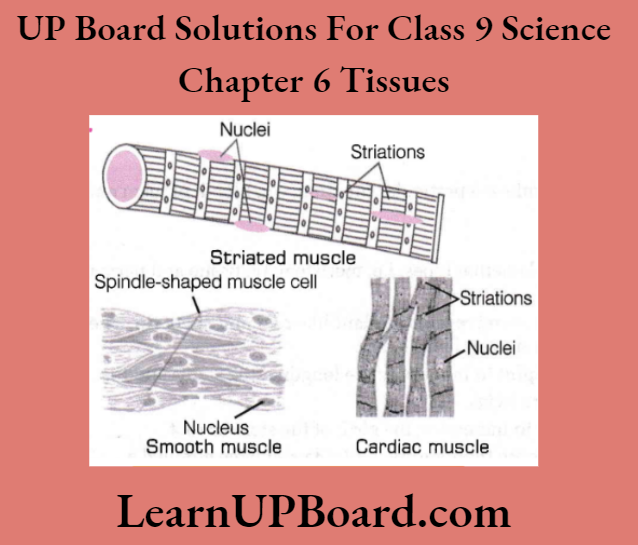
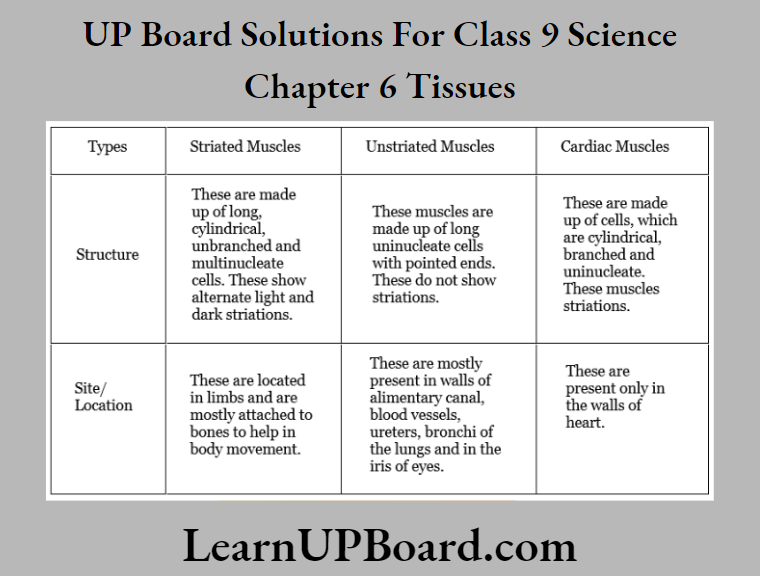
Question 30. Differentiate between striated, unstriated, and cardiac muscles based on their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
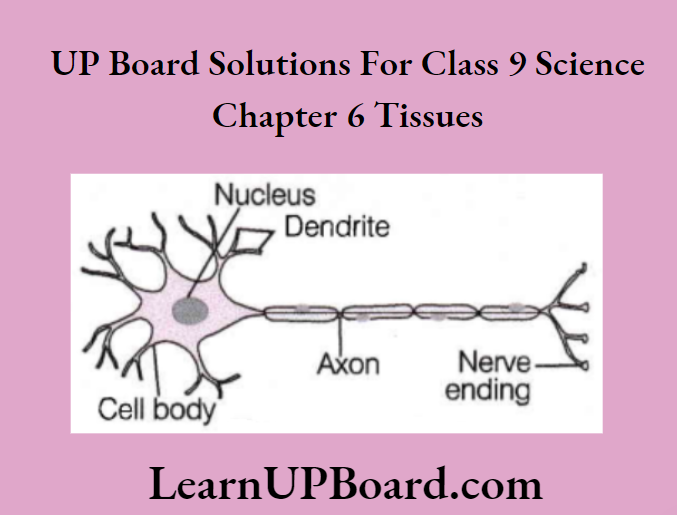
Question 31. Draw a labeled diagram of a neuron
Question 32. Name the following.
- Tissue that forms the inner lining of the mouth.
- Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
- Tissue that transports food in plants.
- Tissue that stores fat in our body.
- Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
- Tissue present in the brain.
Answer:
- Squamous epithelium
- Tendons
- Phloem
- Adipose tissue
- Blood
- Nervous tissue.
Question 33. Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, the bark of a tree, bone, the lining of the kidney tubule, and vascular bundle.
Answer:
- Skin Squamous epithelium
- The bark of tree Epidermal tissue
- Bone Connective tissue
- The lining of kidney tubule Cuboidal epithelium
- Vascular bundle Conductive tissue (xylem and phloem).
Question 34. What is the role of the epidermis in plants?
Answer:
Role of epidermis in plants:
- It helps in the protection of the internal organs of plants.
- It becomes thick and prevents water loss in plants living in very dry habitats.
- Its cell secretes a waxy, water-resistant layer on the outer surface, which protects against loss of water, mechanical injury, and infections.
- Leaf epidermis have stomata to help in gas exchange and transpiration.
- In old plants, the epidermal layer becomes thick and forms cork. Cork cells contain a chemical called suberin in their walls, which makes them impervious to gases and water.
Question 35. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
Cork is made up of several layers of epidermal cells. These cells of cork are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They also have a chemical called suberin in their walls, which makes cork impervious to gases and water.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
Parenchyma tissue is mainly found in soft parts of the plant such as roots, stems, and leaves and is also present in ground tissue of petioles.
Question 2.
- Which type of tissue is found at the shoot apex? Name another part of the plant body, where this type of tissue is found,
- If a plant is to show longitudinal growth, which kind of meristematic tissue will be promoted in the plants?
Answer:
- Apical meristem is found at the shoot apex. It is also present in the growing tips of roots.
- Intercalary meristem helps in the longitudinal growth of plants.
Question 3. What is the specific function of cardiac muscle?
Answer:
Specific function of cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscles contract and relax rhythmically throughout life.
Question 4.
- Identify the region of the stem marked A in the given diagram and the type of simple permanent tissue found in this region.
- Mention any two characteristic features of this tissue.

Answer:
- The region marked as A is the pith and the tissue is parenchyma.
- The cells of parenchyma are living, thin-walled and loosely packed.
- This tissue provides support to plants and also stores food.
Question 5.
- Plant tissue is observed under a microscope, as shown in the given figure. Identify the tissue.
- State the characteristic features of these cells.
- Name any two parts of the plant, where such cells are present.
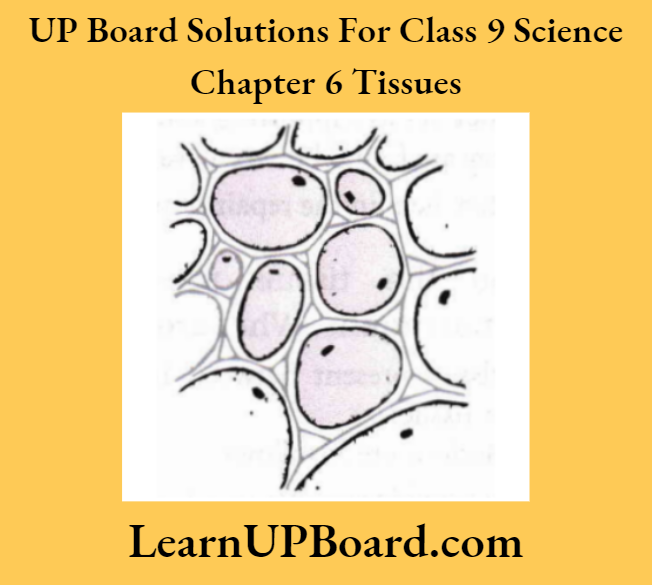
Answer:
- It is parenchyma.
- It consists of thin-walled unspecialized cells, which are loosely packed, i.e. having intercellular spaces. Each cell has a prominent nucleus.
- Pith
- Cortex
Question 6.
- Identify the tissue given in the following figure.
- Mention the characteristic features of the cells.
- Specify the function of this tissue.
- Name any one part of the plant, where these cells are present.
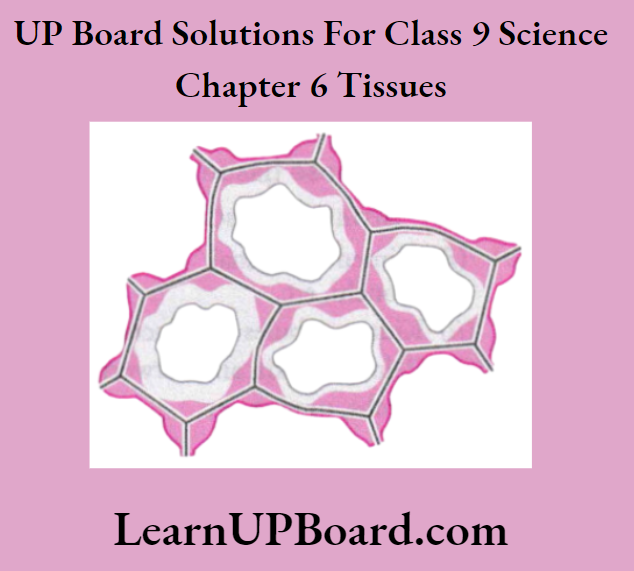
Answer:
- The tissue given in the figure is collenchyma.
- The cells of collenchyma are living, elongated, thickened at the corners, and have very little intercellular space.
- It provides mechanical support and flexibility to the plant.
- It is present in leafstalks, below the epidermis.
Question 7. What are the functions of collenchyma in plants?
Answer:
The functions of collenchyma are as follows
- It allows easy bending in various parts of a plant (leaf and stem) without breaking them.
- It also provides mechanical support to plants.
Question 8. Write the difference between aerenchyma and chlorenchyma.
Answer:
Differences between aerenchyma and chlorenchyma are as follows

Question 9.
- Identify the tissue shown in the figure.
- Specify any part of the plant, where such cells are present.
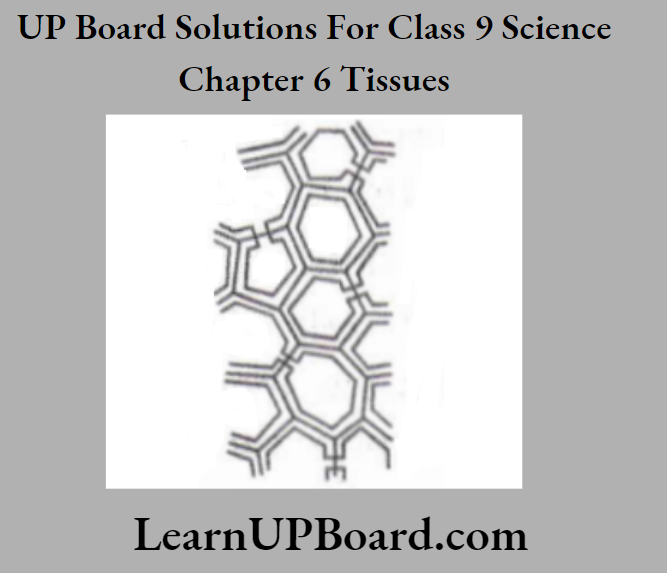
Answer:
- Sclerenchyma
- Sclerenchymatous cells are found
- Around vascular bundles
- In veins of leaves
Question 10. Write the functions of the following chemical substances found in plant tissues.
- Lignin
- Cutin
Answer:
- The functions of lignin are as follows
- It is a chemical substance, which acts as cement and provides strength to the plant.
- The presence of lignin in plants makes the walls of sclerenchyma thick.
- The functions of cutin are as follows
- It is a chemical substance having a waterproof quality, present in the epidermis of desert plants.
- It prevents excessive loss of water through transpiration.
Question 11. What is the difference between sclerenchyma and collenchyma?
Answer:
Differences Between Sclerenchyma And Collenchyma Are As Follows:

Question 12. Answer the following
- How is the epidermis of the plants living in very dry habitats adapted?
- Write functions of guard cells of stomata in the leaf.
Answer:
- The epidermis of the plants living in very dry habitats has a thick waxy coating of waterproof cutin over it. This prevents the loss of water.
- Guard cells help in exchange of gases with the atmosphere, due to the opening and closing of the stomatal pore.
Question 13.
- Epidermal cells help in the absorption of water and nutrients from soil. How?
- Write a note on a vascular bundle.
Answer:
- Epidermal cells in roots bear long hair-like outgrowth, i.e. root hairs that greatly increase the total absorptive surface area and help in increased absorption of water and nutrients from soil.
- The vascular bundle is formed of two main components known as xylem and phloem. Both of them are the conducting tissues that help in the conduction of water, minerals (xylem), and food (phloem) throughout the plant body.
Question 14. The diagram shows the part of a xylem vessel.
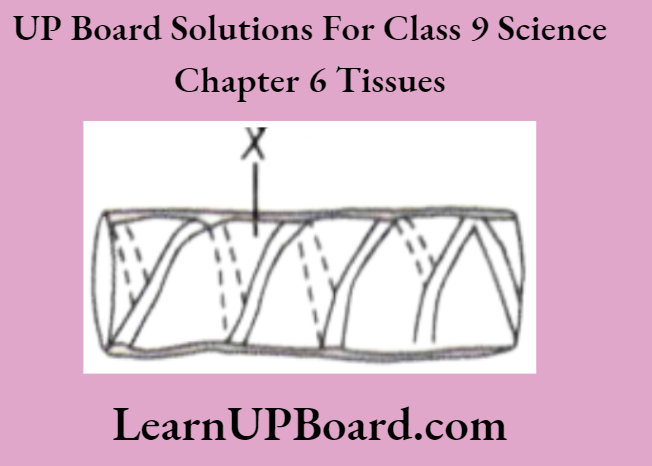
What is the function of the spiral structure X? What is it made up of?
Answer:
The spiral structure X is made up of lignified cellulose, which provides mechanical support to the xylem vessel.
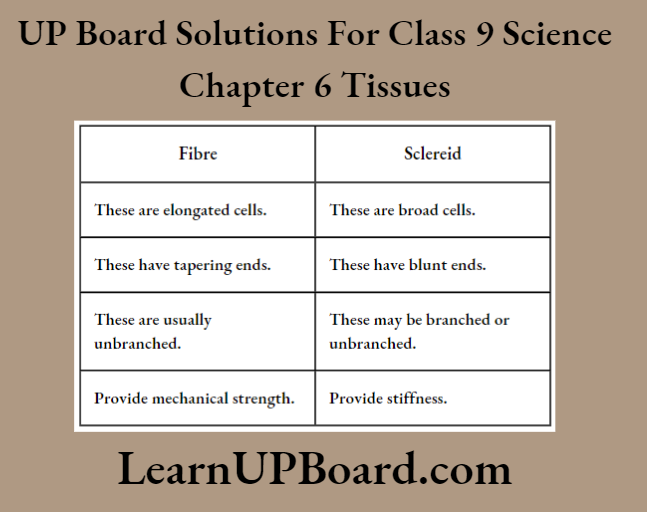
Question 15. Give differences between sclerenchyma fibers and sclereids.
Answer:
The Differences Between Fibres And Sclereids Are As Follows:
Question 16. What is epithelial tissue? State the type of epithelial tissue present in the lining of blood vessels.
Answer:
Epithelial tissue
The outermost covering or protective tissue in the animal body is called epithelial tissue. Simple squamous epithelium covers the lining of blood vessels.
Question 17. What is the function of areolar tissues?
Answer:
The function of areolar tissues
- They act as supporting and packing tissue as they are found between visceral organs.
- They help in the repair of tissue.
Question 18. Name the tissue present between internal organs. What are its functions?
Answer:
The tissue present between internal organs is areolar tissue.
Its functions are as follows
- To provide support to internal organs.
- To repair body tissue.
Question 19.
- What will happen if the ligament gets overstretched?
- Why are skeletal muscles known as striated muscles?
Answer:
- Overstretching of ligament leads to sprain.
- Skeletal muscles are known as striated muscles because they show dark and light bands or stripes or striation.
Question 20. Determine the location of the following tissues:
- Unstriated muscle fibers
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Adipose tissue
- Striated muscle fibers
Answer:
- Alimentary canal, iris of the eye, ureter, bronchi, etc.
- Kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands.
- Below the skin and between internal organs.
- Limbs, tongue, etc.
Question 21. Cutting of rose plants is done timely in gardens, but still, it regains its length. Give reason.
Answer:
The rose plant regains its length because of the presence of intercalary meristem at the base of leaves or internodes on twigs. The cells of these tissues divide and increase the length of the plant.
Question 22. Do the roots of a plant continue growing after their tips are removed? Explain giving reasons.
Answer:
- No, roots do not grow after the removal of their tips. Normally, the apical meristem is present at the tip of the root, which divides repeatedly to increase its length.
- When tips are removed, the apical meristem is also removed and no further growth in the length of roots occurs.
Question 23. Water hyacinth floats on the water’s surface. Explain.
Answer:
Water hyacinth floats on the water’s surface.
Aerenchyma (a type of parenchyma) is present in water hyacinth, which encloses a lot of air and makes the plant lighter than water so that it can float on the surface of the water.
Question 24. A mango tree has several branches. Which tissue helps in the sideways conduction of water in the branches?
Answer:
Xylem vessels are very long tube-like structures formed by a row of cells placed end to end. The transverse walls between these cells are partially or completely dissolved to form continuous water channels. Thus, xylem vessels help in the sideways conduction of water.
Question 25. It is known that the function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body. Can you explain the cause of this peculiar ability of the heart?
Answer:
The heart is made up of cardiac muscles. These cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles (not under the control of our will). These muscles show continuous rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life thereby, helping the heart to pump blood in our body.
Question 26. What is a tissue?
Answer:
Tissue
The group of cells combined together to perform a common function is called a tissue, for example., blood, and muscle.
Question 27. What is the utility of tissue in multicellular organisms?
Answer: The human body works with the principle of division of labor. The cells specializing in one function are grouped to perform a common function.
Question 28. Name the types of simple tissue.
Answer:
The three main types of simple tissues are:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma.
Question 29. Where is apical meristem found?
Answer: Apical meristem is present in the growing tips of stems and roots of plants.
Question 30. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer: Sclerenchymatous tissue.
Question 31. What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
The main constituents of phloem are:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibers.
Question 32. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer: Muscular tissue.
Question 33. What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
A neuron possesses a cell body and various processes emerging from it. These processes include a long axon and short dendrites.
Question 34. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
Features of cardiac muscles are listed below:
- These are involuntary muscles.
- Cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleated.
- These muscles show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
Question 35. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Functions of areolar tissue are as follows:
- Areolar tissue fills the space inside the organs and supports them.
- It helps in the repair of the tissue.
Question 36. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Four elements make up xylem tissue which include:
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem fibers.
